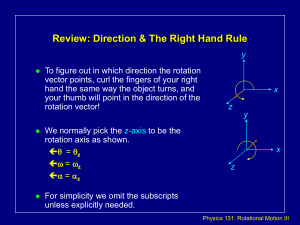
What is angular momentum?
... is no net torque (the forces are internal)so L is a constant but the moment of inertia changes and since L = Iω as I decreases ω increases. So if I decreases by a factor of 2 then ω increases by a factor of 2. The kinetic energy is = Iω2 so if I decreases the kinetic energy increases by the amount o ...
... is no net torque (the forces are internal)so L is a constant but the moment of inertia changes and since L = Iω as I decreases ω increases. So if I decreases by a factor of 2 then ω increases by a factor of 2. The kinetic energy is = Iω2 so if I decreases the kinetic energy increases by the amount o ...
3.6MB Word - Clydeview Academy
... Force is a vector quantity. If several forces act on an object they can be added together. This allows us to calculate whether they are balanced or unbalanced. Balanced forces 4N 4N Forces are balanced so object will remain at rest (or move with constant velocity if it is moving) ...
... Force is a vector quantity. If several forces act on an object they can be added together. This allows us to calculate whether they are balanced or unbalanced. Balanced forces 4N 4N Forces are balanced so object will remain at rest (or move with constant velocity if it is moving) ...
Uniform Circular Motion 2
... In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizo ...
... In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizo ...
Document
... c) The force exerted on the astronaut is larger than the force exerted on the spacecraft. d) The spacecraft does not move, but the astronaut moves to the right with a constant speed. e) The force exerted on the spacecraft is larger than the force exerted on the astronaut. ...
... c) The force exerted on the astronaut is larger than the force exerted on the spacecraft. d) The spacecraft does not move, but the astronaut moves to the right with a constant speed. e) The force exerted on the spacecraft is larger than the force exerted on the astronaut. ...
Period 5 Activity Sheet Solutions: Forces and Newton’s Laws
... 1) Your instructor will demonstrate two toy cars moving up an incline. Explain the differences in the motion of the cars as they go up the incline. As the cars go up the incline, the car with metal wheels slips sooner than the car with rubber band wheels because there is more friction between the ru ...
... 1) Your instructor will demonstrate two toy cars moving up an incline. Explain the differences in the motion of the cars as they go up the incline. As the cars go up the incline, the car with metal wheels slips sooner than the car with rubber band wheels because there is more friction between the ru ...
College Physics, 2e (Knight)
... 20) Your younger brother is supposed to mow the lawn using a push mower. He reasons from Newton's Third Law that the mower will push back with the same force he exerts on the mower; therefore nothing will move and attempting to mow the lawn is pointless. What is wrong with his reasoning? Answer: The ...
... 20) Your younger brother is supposed to mow the lawn using a push mower. He reasons from Newton's Third Law that the mower will push back with the same force he exerts on the mower; therefore nothing will move and attempting to mow the lawn is pointless. What is wrong with his reasoning? Answer: The ...
Mechanics and Properties of Matter Revision Questions Multiple
... rest by a force of 5 N for 2s. An identical block Y is accelerated from rest by a force of 5 N for 4s. The ratio of the kinetic energy of X to the kinetic energy of Y after acceleration is ...
... rest by a force of 5 N for 2s. An identical block Y is accelerated from rest by a force of 5 N for 4s. The ratio of the kinetic energy of X to the kinetic energy of Y after acceleration is ...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach
... 14 . 1111 A crate pu shed along the fl oor with ve loci ty Vi slides a distance d afte r the pushi ng force is removed. a. If the mass of the crate is doubled but the ini tial veloc ity is not changed, what distance does the crate slide before stoppi ng? Ex plain. b. If the initi al ve loc ity of th ...
... 14 . 1111 A crate pu shed along the fl oor with ve loci ty Vi slides a distance d afte r the pushi ng force is removed. a. If the mass of the crate is doubled but the ini tial veloc ity is not changed, what distance does the crate slide before stoppi ng? Ex plain. b. If the initi al ve loc ity of th ...
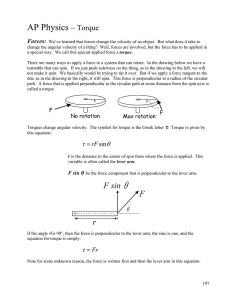
AP Physics – Applying Forces
... We’ve learned that forces change the velocity of an object. But what does it take to change the angular velocity of a thing? Well, forces are involved, but the force has to be applied in a special way. We call this special applied force a torque. There are many ways to apply a force to a system that ...
... We’ve learned that forces change the velocity of an object. But what does it take to change the angular velocity of a thing? Well, forces are involved, but the force has to be applied in a special way. We call this special applied force a torque. There are many ways to apply a force to a system that ...
Ch33
... The Science of Statics • system feels no net force: Fext,net = 0 system momentum is constant CM does not accelerate, and we assume that it is not translating either • system feel no net force moment : text,net = 0 system angular momentum is constant, and we assume no rotational motion either ...
... The Science of Statics • system feels no net force: Fext,net = 0 system momentum is constant CM does not accelerate, and we assume that it is not translating either • system feel no net force moment : text,net = 0 system angular momentum is constant, and we assume no rotational motion either ...
tc mani̇sa celal bayar university physics i laboratory manuals 2016
... PROJECTILE MOTION Projectile motion of an object is simple to analyze if we make two assumptions: (1) the free-fall acceleration is constant over the range of motion and is directed downward, and (2) the effect of air resistance is negligible. With these assumptions, we find that the path of a proje ...
... PROJECTILE MOTION Projectile motion of an object is simple to analyze if we make two assumptions: (1) the free-fall acceleration is constant over the range of motion and is directed downward, and (2) the effect of air resistance is negligible. With these assumptions, we find that the path of a proje ...
Work Problems
... Justification: For the particle speed to increase, the net work done to the particle must be positive. With a positive net work, there will be a positive net force that is applied to the particle (W = Fd). With a net positive force, there will be a net positive acceleration (F = ma), which will caus ...
... Justification: For the particle speed to increase, the net work done to the particle must be positive. With a positive net work, there will be a positive net force that is applied to the particle (W = Fd). With a net positive force, there will be a net positive acceleration (F = ma), which will caus ...
ISNS3371_012307_bw
... Newton’s laws: 1. An object’s momentum will not change if left alone 2. A force can change an object’s momentum, but… 3. Another equal and opposite force simultaneously changes some other object’s momentum by same amount ...
... Newton’s laws: 1. An object’s momentum will not change if left alone 2. A force can change an object’s momentum, but… 3. Another equal and opposite force simultaneously changes some other object’s momentum by same amount ...