Chapter 7 Rotational Motion - Doane College Physics Web Server
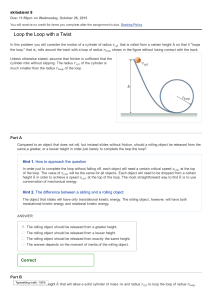
... Notice how just the simple statement that the child jumps on the merry-go-round, with its implication of a completely inelastic collision means that 39% of the initial kinetic energy is lost. What happens to it? You are invited to postulate a different final situation. Assume the child makes a compl ...
... Notice how just the simple statement that the child jumps on the merry-go-round, with its implication of a completely inelastic collision means that 39% of the initial kinetic energy is lost. What happens to it? You are invited to postulate a different final situation. Assume the child makes a compl ...
File - Mr. Graham`s AP Physics 1 & AP Physics C
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...
File - Phy 2048-0002
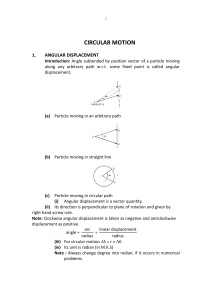
... equilibrium then it does not accelerate. We can say that SF = 0 • An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
... equilibrium then it does not accelerate. We can say that SF = 0 • An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
Chapter 12 - FIA Science
... Balanced forces are forces that combine to produce a net force of zero. When forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero and there is no change in the object’s motion. An unlimited number of individual forces can act on an object and still produce a net force of zero. ...
... Balanced forces are forces that combine to produce a net force of zero. When forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero and there is no change in the object’s motion. An unlimited number of individual forces can act on an object and still produce a net force of zero. ...
fan cart physics
... below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ 2. Press Play ( ) and observe the cart. In which direction does the cart move? __________________ By blowing to the left, the fans exert a force on the cart that pushes it to the right. T ...
... below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ 2. Press Play ( ) and observe the cart. In which direction does the cart move? __________________ By blowing to the left, the fans exert a force on the cart that pushes it to the right. T ...
Unit 2 - aqaphysics.co.uk
... The diagram shows two balls that are released at the same time, one is released and the other has a horizontal velocity. We see that the ball shot from the cannon falls at the same rate at the ball that was released. This is because the horizontal and vertical components of motion are independent of ...
... The diagram shows two balls that are released at the same time, one is released and the other has a horizontal velocity. We see that the ball shot from the cannon falls at the same rate at the ball that was released. This is because the horizontal and vertical components of motion are independent of ...
ch. 5-2 forces powerpoint
... • Describe forces, and explain how forces act on objects. • Determine the net force when more than one force is acting on an object. ...
... • Describe forces, and explain how forces act on objects. • Determine the net force when more than one force is acting on an object. ...
Meter Stick Balance
... 1. Hang the meter stick with no weight from a knife-edge near the 50 cm mark. This is the fulcrum. 2. Adjust the fulcrum location until the meter stick balances horizontally. This will likely not be 50.0 cm since the wooden meter stick is non-uniform. Record the location of the fulcrum to 3 signific ...
... 1. Hang the meter stick with no weight from a knife-edge near the 50 cm mark. This is the fulcrum. 2. Adjust the fulcrum location until the meter stick balances horizontally. This will likely not be 50.0 cm since the wooden meter stick is non-uniform. Record the location of the fulcrum to 3 signific ...
Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration
... of motion involve similar changes. In fact, rarely does any object’s motion stay the same for very long. ...
... of motion involve similar changes. In fact, rarely does any object’s motion stay the same for very long. ...
Forces - Cloudfront.net
... change in its motion. It is easier to push a 10 kg object into motion than it is a 3000 kg car. dynamics All of this begins the topic of _______________, or why objects move. ...
... change in its motion. It is easier to push a 10 kg object into motion than it is a 3000 kg car. dynamics All of this begins the topic of _______________, or why objects move. ...
Chapter Objectives
... 1. From position and time, calculate displacement, average velocity, and average acceleration 2. Find distance given velocity and time 3. Distinguish between velocity and speed 4. Distinguish between average speed and instantaneous speed 5. Distinguish between velocity and acceleration 6. Find the v ...
... 1. From position and time, calculate displacement, average velocity, and average acceleration 2. Find distance given velocity and time 3. Distinguish between velocity and speed 4. Distinguish between average speed and instantaneous speed 5. Distinguish between velocity and acceleration 6. Find the v ...
Our Dynamic Universe notes
... An observer on Earth is looking at a space craft in space orbiting a planet. The observer and the space craft are in different frames of reference and the space craft is travelling close to the speed of light. To the observer, the time it takes for the space craft to make one orbit will appear much ...
... An observer on Earth is looking at a space craft in space orbiting a planet. The observer and the space craft are in different frames of reference and the space craft is travelling close to the speed of light. To the observer, the time it takes for the space craft to make one orbit will appear much ...

![Physics for SciEngrs [3rd]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015834502_1-903d7f9c800dd53147166e2caa63cce8-300x300.png)