Force and Motion
... you!! It is actually this upward force by the rope that makes you move up! This is the “reaction” force (by the rope on you) to the force that you exerted on the rope. And voilá, this is Newton’s Third Law. ...
... you!! It is actually this upward force by the rope that makes you move up! This is the “reaction” force (by the rope on you) to the force that you exerted on the rope. And voilá, this is Newton’s Third Law. ...
document
... force is greater than this maximum static friction, the couch begins moving and kinetic friction begins to act on it instead of static friction ...
... force is greater than this maximum static friction, the couch begins moving and kinetic friction begins to act on it instead of static friction ...
ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS FROM PHYS 1401 (for PHYS 1402)
... 1) A car decelerates uniformly and comes to a stop after 10 s. The car's average velocity during deceleration was 50 km/h. What was the car's deceleration while slowing down? A) 10 km/h-s B) 5 km/h-s C) 8 km/h-s D) 4 km/h-s E) 9.8 m/s2 Answer: A 2) Eric watches a jet powered truck during an "air-sho ...
... 1) A car decelerates uniformly and comes to a stop after 10 s. The car's average velocity during deceleration was 50 km/h. What was the car's deceleration while slowing down? A) 10 km/h-s B) 5 km/h-s C) 8 km/h-s D) 4 km/h-s E) 9.8 m/s2 Answer: A 2) Eric watches a jet powered truck during an "air-sho ...
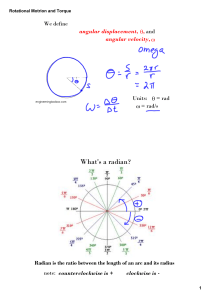
ME 242 Chapter 13
... A car is traveling at 20 m/s on a level road, when the brakes are suddenly applied and all four wheels lock. mk = 0.5. The total distance traveled to a full stop is (use Energy Method, g = 10 m/s2) (A) 40 m (B) 20 m (C) 80 m (D) 10 m (E) none of the above ...
... A car is traveling at 20 m/s on a level road, when the brakes are suddenly applied and all four wheels lock. mk = 0.5. The total distance traveled to a full stop is (use Energy Method, g = 10 m/s2) (A) 40 m (B) 20 m (C) 80 m (D) 10 m (E) none of the above ...
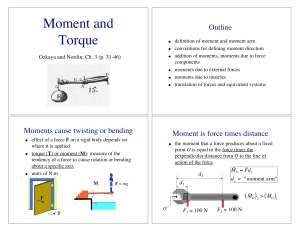
Moment and Torque
... that muscles can undergo, their close proximity to joints allows for large ranges of joint rotation Disadvantage: high muscle forces (and therefore joint forces) are required to balance external loads ...
... that muscles can undergo, their close proximity to joints allows for large ranges of joint rotation Disadvantage: high muscle forces (and therefore joint forces) are required to balance external loads ...
Work and Energy
... where h is the distance the mass was raised. Record your values in the data table. Does the work done on the mass correspond to the change in gravitational potential energy? Should it? 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring ...
... where h is the distance the mass was raised. Record your values in the data table. Does the work done on the mass correspond to the change in gravitational potential energy? Should it? 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring ...