Chapter 2: Kinematics in One Dimension
... objects is, it would be noticeable if it were the only force around. However, on Earth the gravity of Earth overpowers these other gravities, not to mention the fact that the gravity between you & other objects are pulling in all sorts of directions, so they cancel out. Far away from planets, the gr ...
... objects is, it would be noticeable if it were the only force around. However, on Earth the gravity of Earth overpowers these other gravities, not to mention the fact that the gravity between you & other objects are pulling in all sorts of directions, so they cancel out. Far away from planets, the gr ...
2.2 Some Common Speeds
... A frame of reference is best described as “your point of _________________.” An inertial frame of reference is one that is either _____________ or moving with constant _________________. A non inertial frame of reference is _____________________. CONSEQUENCES As far as Newton’s 1st law is concerned ...
... A frame of reference is best described as “your point of _________________.” An inertial frame of reference is one that is either _____________ or moving with constant _________________. A non inertial frame of reference is _____________________. CONSEQUENCES As far as Newton’s 1st law is concerned ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 2. Suppose several more horses were hitched up to the same cart. How would this affect the speed of the cart? __________________________________________________________ Although these questions may seem simple, they form the basis of Newton’s second law of motion. The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ can be ...
... 2. Suppose several more horses were hitched up to the same cart. How would this affect the speed of the cart? __________________________________________________________ Although these questions may seem simple, they form the basis of Newton’s second law of motion. The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ can be ...
Mechanical advantage: Levers
... move the load if you are further away from the fulcrum than the load. In fact the further you are the less effort is needed. A famous philosopher once said "Give me a lever long enough and I will move the world". You may have played on the see-saw and tried to lift, using your hands, a person on the ...
... move the load if you are further away from the fulcrum than the load. In fact the further you are the less effort is needed. A famous philosopher once said "Give me a lever long enough and I will move the world". You may have played on the see-saw and tried to lift, using your hands, a person on the ...
Lecture14a
... • Archimedes Principle says that if an object of volume Vobj is totally submerged in a fluid of density ρfluid • The upward buoyant force is B = ρfluidgVobj • Of course, the downward gravitational force is Fg = Mg = ρobjgVobj • If the object is floating submerged & not moving, by Newton’s 2nd Law i ...
... • Archimedes Principle says that if an object of volume Vobj is totally submerged in a fluid of density ρfluid • The upward buoyant force is B = ρfluidgVobj • Of course, the downward gravitational force is Fg = Mg = ρobjgVobj • If the object is floating submerged & not moving, by Newton’s 2nd Law i ...
Slide 1
... Ladybug Revolution - PhET - Join the ladybug in an exploration of rotational motion. Rotate the merry-go-round to change its angle, or choose a constant angular velocity or angular acceleration. Explore how circular motion relates to the bug's x,y position, velocity, and acceleration using vectors o ...
... Ladybug Revolution - PhET - Join the ladybug in an exploration of rotational motion. Rotate the merry-go-round to change its angle, or choose a constant angular velocity or angular acceleration. Explore how circular motion relates to the bug's x,y position, velocity, and acceleration using vectors o ...
Rotational Motion - My Teacher Pages
... • Example- Spinning Ferris wheel or an orbiting satellite • Object moves in a circular path and at a constant speed • The object is accelerating, however, because the direction of the object’s velocity is constantly changing • Centripetal acceleration Directed toward the center of the circle • Net ...
... • Example- Spinning Ferris wheel or an orbiting satellite • Object moves in a circular path and at a constant speed • The object is accelerating, however, because the direction of the object’s velocity is constantly changing • Centripetal acceleration Directed toward the center of the circle • Net ...
LAWS OF MOTION interview
... "Of course, but only if you refrain from using such awkward tenses of English like gnarly or dude. Anyway, my third law is perhaps the most recognized, but the most misunderstood. This law states that: When an object exerts a force on a second object, the second object will exert a force of equal ma ...
... "Of course, but only if you refrain from using such awkward tenses of English like gnarly or dude. Anyway, my third law is perhaps the most recognized, but the most misunderstood. This law states that: When an object exerts a force on a second object, the second object will exert a force of equal ma ...
Lecture6
... • The driving force of motion of ordinary vehicles such as cars and locomotives is friction. A car moves because a reaction to the force exerted by the tire produces a force by the road on the wheel. • What is then driving force of a rocket? When an explosion occurs in a spherical chamber with fue ...
... • The driving force of motion of ordinary vehicles such as cars and locomotives is friction. A car moves because a reaction to the force exerted by the tire produces a force by the road on the wheel. • What is then driving force of a rocket? When an explosion occurs in a spherical chamber with fue ...
Kinematics - Conroe High School
... Some dragsters are built so that the front wheels are far ahead of the rear wheels. The main reason for this is a. to streamline the dragster b. to provide better traction. c. to keep the front of the car down. ...
... Some dragsters are built so that the front wheels are far ahead of the rear wheels. The main reason for this is a. to streamline the dragster b. to provide better traction. c. to keep the front of the car down. ...
Name(s) Hr. ____ Investigating Newton`s Second Law by Pulling a
... wagon, we have two horizontal forces: your pull force (creating a tension in the string) and friction. Friction works against your pull force. We can subtract these two forces to get the net force. However, Newton’s second law is expressed: Fnet = ma So, if we know our net force, we can then divide ...
... wagon, we have two horizontal forces: your pull force (creating a tension in the string) and friction. Friction works against your pull force. We can subtract these two forces to get the net force. However, Newton’s second law is expressed: Fnet = ma So, if we know our net force, we can then divide ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Motion, Forces, and Energy in More Than One Dimension
... In Chapter 3 we discussed the motion of an object in free-fall near the Earth where the motion was purely vertical. Such motion results when the initial velocity of the object has no horizontal component. Gravity is a purely vertical force resulting in a constant vertical acceleration; as we just ar ...
... In Chapter 3 we discussed the motion of an object in free-fall near the Earth where the motion was purely vertical. Such motion results when the initial velocity of the object has no horizontal component. Gravity is a purely vertical force resulting in a constant vertical acceleration; as we just ar ...
Chapter 7 Rotational Motion - Doane College Physics Web Server
... Notice how just the simple statement that the child jumps on the merry-go-round, with its implication of a completely inelastic collision means that 39% of the initial kinetic energy is lost. What happens to it? You are invited to postulate a different final situation. Assume the child makes a compl ...
... Notice how just the simple statement that the child jumps on the merry-go-round, with its implication of a completely inelastic collision means that 39% of the initial kinetic energy is lost. What happens to it? You are invited to postulate a different final situation. Assume the child makes a compl ...
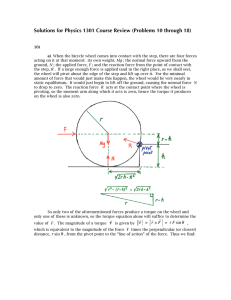
ch02 equilibrium and forces 2012
... Any push or pull on an object Resistance of two objects in contact moving past each other Resistance of an object moving through the atmosphere Force that pushes back on one object resting on another ...
... Any push or pull on an object Resistance of two objects in contact moving past each other Resistance of an object moving through the atmosphere Force that pushes back on one object resting on another ...
File - Mr. Graham`s AP Physics 1 & AP Physics C
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...