QUIZ
... Force = Mass x Acceleration Body Weight = Mass x Accelerationgravity Example: Mass: 80 kg Accelgrav: 9.81 m/s/s Answer: 785 Kg m/s2 ...
... Force = Mass x Acceleration Body Weight = Mass x Accelerationgravity Example: Mass: 80 kg Accelgrav: 9.81 m/s/s Answer: 785 Kg m/s2 ...
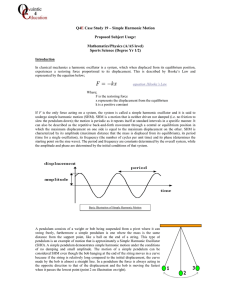
1.9 Simple Harmonic Motion
... Not only the mass oscillates when it is released, but also the spring itself. The period of oscillation is affected by the mass of the spring. ...
... Not only the mass oscillates when it is released, but also the spring itself. The period of oscillation is affected by the mass of the spring. ...
Newton`s Laws - Ipod Physics
... The horse moves, dragging the wagon with it, by pushing the earth away from it. The earth pushes back on the horse, so the horse and wagon move. The earth moves away as well, but, because its mass is so huge (as previously discussed), we can’t measure its acceleration. ...
... The horse moves, dragging the wagon with it, by pushing the earth away from it. The earth pushes back on the horse, so the horse and wagon move. The earth moves away as well, but, because its mass is so huge (as previously discussed), we can’t measure its acceleration. ...
Fall 2008 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Problem 11. A toy car on a ramp is given a quick upward push. As a result of the push, the car travels up the ramp a bit, then rolls back down again. As the car is moving up the ramp, the net force on it is: a. Up the ramp, and increasing in magnitude b. Up the ramp, and decreasing in magnitude c. U ...
... Problem 11. A toy car on a ramp is given a quick upward push. As a result of the push, the car travels up the ramp a bit, then rolls back down again. As the car is moving up the ramp, the net force on it is: a. Up the ramp, and increasing in magnitude b. Up the ramp, and decreasing in magnitude c. U ...
BilaksPhysiks
... 2. Which of the following choices correctly describes the x-component of the proton’s motion? A: The proton is accelerating in the xdirection (ax>0) B: There is no motion in the x-direction. C: The x-component of the proton’s velocity vx is constant. ...
... 2. Which of the following choices correctly describes the x-component of the proton’s motion? A: The proton is accelerating in the xdirection (ax>0) B: There is no motion in the x-direction. C: The x-component of the proton’s velocity vx is constant. ...
Static Equilibrium. Supports, Loads, Driven Oscillations
... block, and then place a small wedge 6” away from the end (board is 6’, remember). How much can we exert ...
... block, and then place a small wedge 6” away from the end (board is 6’, remember). How much can we exert ...
Motion and Forces Powerpoint
... 4. You can tell how fast objects are moving if you look at a graph of speed and time. 5. To apply a force, one object must be touching another object. 6. If an object is at rest, there are no forces acting on it. ...
... 4. You can tell how fast objects are moving if you look at a graph of speed and time. 5. To apply a force, one object must be touching another object. 6. If an object is at rest, there are no forces acting on it. ...
L 5: F
... motion–position, velocity, and acceleration? In this lab you will pay attention to forces and how they affect motion. You will first develop an idea of a force as a push or a pull. You will learn how to measure forces. By applying forces to a cart and observing the nature of its resulting motion gra ...
... motion–position, velocity, and acceleration? In this lab you will pay attention to forces and how they affect motion. You will first develop an idea of a force as a push or a pull. You will learn how to measure forces. By applying forces to a cart and observing the nature of its resulting motion gra ...
Lesson 15 notes – Newton 1 and 3 - science
... (a) Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force. (1) If it is acted on by a resultant force it will either accelerate, decelerate or change direction (1) depending on the direction of the force.(1) … (3) (b)… ...
... (a) Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force. (1) If it is acted on by a resultant force it will either accelerate, decelerate or change direction (1) depending on the direction of the force.(1) … (3) (b)… ...