Kinematics and Dynamics Worksheets in MS Word
... In most situations there will be more than one force acting on an object. If we want to calculate the acceleration of the object we must first find the unbalanced force. The combination of forces is known as the resultant. Example: The engine of the car provides a driving force of 2 500 newtons. The ...
... In most situations there will be more than one force acting on an object. If we want to calculate the acceleration of the object we must first find the unbalanced force. The combination of forces is known as the resultant. Example: The engine of the car provides a driving force of 2 500 newtons. The ...
sy12_oct12_f11
... contact? This occurs when the normal force goes to zero or, equivalently, when all the weight is used to achieve circular motion. Fc = mg = m v2 /r v = (gr)½ (just like an object in orbit) Note this approach can also be used to estimate the maximum walking speed. Physics 207: Lecture 12, Pg 12 ...
... contact? This occurs when the normal force goes to zero or, equivalently, when all the weight is used to achieve circular motion. Fc = mg = m v2 /r v = (gr)½ (just like an object in orbit) Note this approach can also be used to estimate the maximum walking speed. Physics 207: Lecture 12, Pg 12 ...
Vectors
... and 41 Newtons [S]. If the rope is not moving, find the force of the fourth boy. 25. Three forces act on an object, which is equilibrium. The first two forces are 60 lbs [NW] and 33 lbs [E]. Find the 3rd force. 26. A speaker in the auditorium is supported by two cables that are 120 apart. If the sp ...
... and 41 Newtons [S]. If the rope is not moving, find the force of the fourth boy. 25. Three forces act on an object, which is equilibrium. The first two forces are 60 lbs [NW] and 33 lbs [E]. Find the 3rd force. 26. A speaker in the auditorium is supported by two cables that are 120 apart. If the sp ...
Problem 5 - grandpasfsc105
... The initial velocity is horizontal; the magnitude is 10 m/s. Then the equation of motion along horizontal axis has the following form: After 0.2 seconds the dart hits the target. From this condition and from the above equation we can find the distance between the point where the dart is released and ...
... The initial velocity is horizontal; the magnitude is 10 m/s. Then the equation of motion along horizontal axis has the following form: After 0.2 seconds the dart hits the target. From this condition and from the above equation we can find the distance between the point where the dart is released and ...
Chapter 5
... (b) The direction is down. 15. (a) – (c) In all three cases the scale is not accelerating, which means that the two cords exert forces of equal magnitude on it. The scale reads the magnitude of either of these forces. In each case the tension force of the cord attached to the salami must be the same ...
... (b) The direction is down. 15. (a) – (c) In all three cases the scale is not accelerating, which means that the two cords exert forces of equal magnitude on it. The scale reads the magnitude of either of these forces. In each case the tension force of the cord attached to the salami must be the same ...
Inquiry 6.1 Gravity`s effect on objects in motion
... the questions on your paper. Remember to include part of the question in all of your answers. Purpose: How does gravity affect an object that is in motion? Background Info: Gravity: a force that pulls objects towards each other and/or pulls all objects to the center of that object. Law of Inertia: O ...
... the questions on your paper. Remember to include part of the question in all of your answers. Purpose: How does gravity affect an object that is in motion? Background Info: Gravity: a force that pulls objects towards each other and/or pulls all objects to the center of that object. Law of Inertia: O ...
Section 9.1 Impulse and Momentum
... Momentum - product of an object’s mass and velocity. It is a vector quantity that has the same direction as the velocity of the object. It is denoted by “p” (lower case). It is mass in motion. The unit for Momentum is kg m/s. To find Momentum you use p = m*v Δp = mΔv FΔt = mΔv = mvF – mvI = Δp = pF ...
... Momentum - product of an object’s mass and velocity. It is a vector quantity that has the same direction as the velocity of the object. It is denoted by “p” (lower case). It is mass in motion. The unit for Momentum is kg m/s. To find Momentum you use p = m*v Δp = mΔv FΔt = mΔv = mvF – mvI = Δp = pF ...
June 06
... Most candidates found something that they could do and quite a few could do most of the paper but there were several widespread difficulties. First there was a part question that very few could do: Q 7 (iii) proved inaccessible to most candidates, partly because the response we were looking for was ...
... Most candidates found something that they could do and quite a few could do most of the paper but there were several widespread difficulties. First there was a part question that very few could do: Q 7 (iii) proved inaccessible to most candidates, partly because the response we were looking for was ...
Time (s)
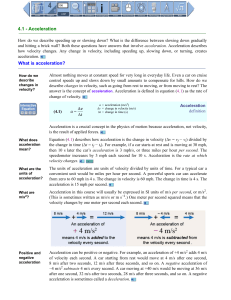
... the same time due to their ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY being the same!!! All objects will accelerate downwards at the same rate if air friction is ignored so they will hit the ground at the same time! The acceleration g = 10m/s2 ...
... the same time due to their ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY being the same!!! All objects will accelerate downwards at the same rate if air friction is ignored so they will hit the ground at the same time! The acceleration g = 10m/s2 ...
Circular Motion - Saptarshi Classes
... 44) The maximum speed with which a car can be driven safely along a curve road of radius 17.32 m and banked at 300 with the horizontal is a) 5 m/s b) 10 m/s c) 15 m/s d) 20 m/s 45) The tangent of the banking angle is a) Proportional to v b) Inversely proportional to v2 c) Proportional to the radius ...
... 44) The maximum speed with which a car can be driven safely along a curve road of radius 17.32 m and banked at 300 with the horizontal is a) 5 m/s b) 10 m/s c) 15 m/s d) 20 m/s 45) The tangent of the banking angle is a) Proportional to v b) Inversely proportional to v2 c) Proportional to the radius ...