PowerPoint File
... generates shear flow; flow profile calculated self-consistently, coupled to polymer deformation. hydrodynamic periodic boundary conditions ...
... generates shear flow; flow profile calculated self-consistently, coupled to polymer deformation. hydrodynamic periodic boundary conditions ...
Physics Pre-AP/AP Power Standards
... Calculate impulse from the area under the curve of a force versus time graph. Recognize examples of elastic and inelastic collisions and explain which conservation laws apply to each type of collisions. Demonstrate proficiency in solving problems involving conservation of momentum in collisions in o ...
... Calculate impulse from the area under the curve of a force versus time graph. Recognize examples of elastic and inelastic collisions and explain which conservation laws apply to each type of collisions. Demonstrate proficiency in solving problems involving conservation of momentum in collisions in o ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... on the floor, you feel the force the floor exerts on you. The larger your weight, the larger the force exerted by the floor will be on you. When sitting, you feel the force of the chair. If you do a pull-up, you feel the force of the bar on your hands. When you are at rest, or moving at constant vel ...
... on the floor, you feel the force the floor exerts on you. The larger your weight, the larger the force exerted by the floor will be on you. When sitting, you feel the force of the chair. If you do a pull-up, you feel the force of the bar on your hands. When you are at rest, or moving at constant vel ...
Physics Pre-AP/AP Power Standards
... Calculate impulse from the area under the curve of a force versus time graph. Recognize examples of elastic and inelastic collisions and explain which conservation laws apply to each type of collisions. Demonstrate proficiency in solving problems involving conservation of momentum in collisions in o ...
... Calculate impulse from the area under the curve of a force versus time graph. Recognize examples of elastic and inelastic collisions and explain which conservation laws apply to each type of collisions. Demonstrate proficiency in solving problems involving conservation of momentum in collisions in o ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... The simplest of all these will be the case of translation. A Rigid body where each point of this rigid body they have exactly same displacement, same velocity, same acceleration. So, effectively what we can do? Then this is more or less equivalent to a particle with the same velocity or displacement ...
... The simplest of all these will be the case of translation. A Rigid body where each point of this rigid body they have exactly same displacement, same velocity, same acceleration. So, effectively what we can do? Then this is more or less equivalent to a particle with the same velocity or displacement ...
MOTION ANALYSIS Prepared for the Televised Course "Physical Science: The Threshold
... plot to be 12.9 s – 8.2 s = 4.7 s, a 0.6% error when compared with the calculated value. ...
... plot to be 12.9 s – 8.2 s = 4.7 s, a 0.6% error when compared with the calculated value. ...
Since W = Fd, and v =d/t, we can also express power as
... Newton's Laws are fundamental in that they explain the causes of motion of (relatively) large, solid masses. These laws involve the relationship of forces and motion, particularly (a) rest, (b) constant velocity, (c) constant acceleration. For our purposes, forces in mechanics have only 4 sources: ...
... Newton's Laws are fundamental in that they explain the causes of motion of (relatively) large, solid masses. These laws involve the relationship of forces and motion, particularly (a) rest, (b) constant velocity, (c) constant acceleration. For our purposes, forces in mechanics have only 4 sources: ...
Kinetic Energy and Work
... Two springs with negligible masses, one with spring constant k1 and the other with spring constant k2, are attached to the endstops of a level air track as in Figure. A glider attached to both springs is located between them. When the glider is in equilibrium, spring 1 is stretched by extension xi1 ...
... Two springs with negligible masses, one with spring constant k1 and the other with spring constant k2, are attached to the endstops of a level air track as in Figure. A glider attached to both springs is located between them. When the glider is in equilibrium, spring 1 is stretched by extension xi1 ...
Force - Kuropas 7-4 science
... one force is stronger than others, the forces are unbalanced forces. Unbalanced forces cause a change in motion; speed and/or direction. • When two forces act in the same direction on an object, the net force is equal to the sum of the two forces. • When two unequal forces act in opposite directions ...
... one force is stronger than others, the forces are unbalanced forces. Unbalanced forces cause a change in motion; speed and/or direction. • When two forces act in the same direction on an object, the net force is equal to the sum of the two forces. • When two unequal forces act in opposite directions ...
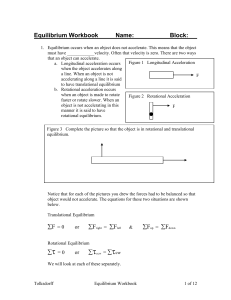
Equilibrium Workbook
... when the object accelerates along a line. When an object is not F accelerating along a line it is said to have translational equilibrium b. Rotational acceleration occurs when an object is made to rotate Figure 2 Rotational Acceleration faster or rotate slower. When an object is not accelerating in ...
... when the object accelerates along a line. When an object is not F accelerating along a line it is said to have translational equilibrium b. Rotational acceleration occurs when an object is made to rotate Figure 2 Rotational Acceleration faster or rotate slower. When an object is not accelerating in ...
AP Clicker Forces
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backward) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wha ...
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backward) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wha ...
Newton`s Third Law of Motion CHECK YOUR ANSWER
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
File - wentworth science
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...