Lesson 2 - Choteau Schools
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion (cont.) • In a force pair, one force is called the action force and the other force is called the reaction force. – When you push against an object, the force you apply is called the action force. – The force applied by the object back against you is called the reaction ...
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion (cont.) • In a force pair, one force is called the action force and the other force is called the reaction force. – When you push against an object, the force you apply is called the action force. – The force applied by the object back against you is called the reaction ...
Document
... 4-5 Newton’s Third Law of Motion Any time a force is exerted on an object, that force is caused by another object. Newton’s third law: Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts an equal force in the opposite direction on the first. ...
... 4-5 Newton’s Third Law of Motion Any time a force is exerted on an object, that force is caused by another object. Newton’s third law: Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts an equal force in the opposite direction on the first. ...
Chap04
... Fighting Over a Toy Anudja is holding a stuffed dog with a mass of 0.30 kg, when Sarah decides that she wants it and tries to pull it away from Anudja. If Sarah pulls horizontally on the dog with a force of 10.0 N and Anudja pulls with a horizontal force of 11.0 N, what is the horizontal acceleratio ...
... Fighting Over a Toy Anudja is holding a stuffed dog with a mass of 0.30 kg, when Sarah decides that she wants it and tries to pull it away from Anudja. If Sarah pulls horizontally on the dog with a force of 10.0 N and Anudja pulls with a horizontal force of 11.0 N, what is the horizontal acceleratio ...
Practice Final
... A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/s D) 18 m/s E) none of these 6) How long does it take for a sport car at rest to reach 27 m/s if its acceleration is ...
... A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/s D) 18 m/s E) none of these 6) How long does it take for a sport car at rest to reach 27 m/s if its acceleration is ...
Refraction
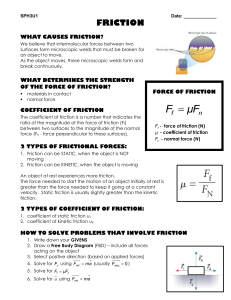
... 1. Friction can be STATIC, when the object is NOT moving 2. Friction can be KINETIC, when the object is moving An object at rest experiences more friction. The force needed to start the motion of an object initially at rest is greater than the force needed to keep it going at a constant velocity. St ...
... 1. Friction can be STATIC, when the object is NOT moving 2. Friction can be KINETIC, when the object is moving An object at rest experiences more friction. The force needed to start the motion of an object initially at rest is greater than the force needed to keep it going at a constant velocity. St ...
Biomechanics - study
... skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accelerates the javelin by pulling it from way behind his body and r ...
... skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accelerates the javelin by pulling it from way behind his body and r ...
Springs & Strings
... 27•• IP The equilibrium length of a certain spring with a force constant of k = 250 N/m is 0.18 m. (a) What force is required to stretch this spring to twice its equilibrium length? (b) Is the force required to compress the spring to half its length the same as in part (a)? Explain. (a) ...
... 27•• IP The equilibrium length of a certain spring with a force constant of k = 250 N/m is 0.18 m. (a) What force is required to stretch this spring to twice its equilibrium length? (b) Is the force required to compress the spring to half its length the same as in part (a)? Explain. (a) ...
Physics Phlashcards REVISED
... The unit of potential difference is the ________, represented by __________. Since this is often too large when dealing with charges, the _________, represented by ________, and equal to ___________________________J is used. ...
... The unit of potential difference is the ________, represented by __________. Since this is often too large when dealing with charges, the _________, represented by ________, and equal to ___________________________J is used. ...
UNIT 4 Lab
... (i) What is the Newton’s Third Law pair force for the normal force of the table on the box? In which diagram does this force appear? Explain. (ii) What is the Newton’s Third Law pair force for the gravitational force of the Earth on the box? In which diagram does this force appear? Explain. (iii) C ...
... (i) What is the Newton’s Third Law pair force for the normal force of the table on the box? In which diagram does this force appear? Explain. (ii) What is the Newton’s Third Law pair force for the gravitational force of the Earth on the box? In which diagram does this force appear? Explain. (iii) C ...
Unit 4 - Youngstown City Schools
... There are other things to think about in terms of moving objects. In fact, it is the most asked question of all two year olds: Why? The next several lessons answer the question: Why do things move the way they do? dynamics – the study of why objects move the way they do; Newton’s focus of study. New ...
... There are other things to think about in terms of moving objects. In fact, it is the most asked question of all two year olds: Why? The next several lessons answer the question: Why do things move the way they do? dynamics – the study of why objects move the way they do; Newton’s focus of study. New ...
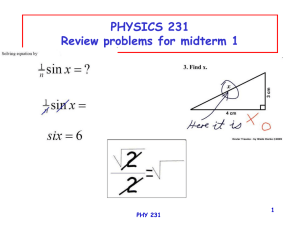
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1 1 PHY 231
... Initially, the velocity is pointing up, but is decreasing in magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the spee ...
... Initially, the velocity is pointing up, but is decreasing in magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the spee ...
2.0 Forces reading Forces reading
... move across it. For the purpose of our study of physics at The Physics Classroom, there are two types of friction force static friction and sliding friction. Sliding friction results when an object slides across a surface. As an example, consider pushing a box across a floor. The floor surface offer ...
... move across it. For the purpose of our study of physics at The Physics Classroom, there are two types of friction force static friction and sliding friction. Sliding friction results when an object slides across a surface. As an example, consider pushing a box across a floor. The floor surface offer ...