SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND RAOTATIONAL DYNAMICS Various
... The centre of mass of the system of three particles coincides with the centroid of the triangle formed by the particles. The results of equations (i) and (ii) can be generalized to a system of n particles distributed in space. The centre of mass of such a system is at (X, Y, Z), where ...
... The centre of mass of the system of three particles coincides with the centroid of the triangle formed by the particles. The results of equations (i) and (ii) can be generalized to a system of n particles distributed in space. The centre of mass of such a system is at (X, Y, Z), where ...
Slide 1
... A blue car moves along a street with two passengers. One sits in the front passenger seat of the car and the other passenger sits in the back seat. A red car moves in the same direction and is passing the blue car. A green car moving faster than the blue car, is directly behind the blue car. There ...
... A blue car moves along a street with two passengers. One sits in the front passenger seat of the car and the other passenger sits in the back seat. A red car moves in the same direction and is passing the blue car. A green car moving faster than the blue car, is directly behind the blue car. There ...
Mechanics - akamdiplomaphysics
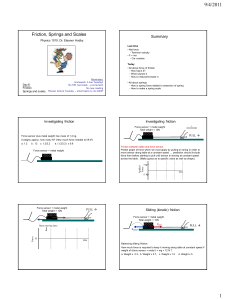
... and if it is stretched by an amount x, then if k is the tension required to produce unit extension (called the spring constant and measured in Nm-1) the stretching tension is also kx and so ...
... and if it is stretched by an amount x, then if k is the tension required to produce unit extension (called the spring constant and measured in Nm-1) the stretching tension is also kx and so ...
Lab 1500-5 - Otterbein University
... control the release of air bags in an automobile. It contains very thin “fingers” micromachined out of silicon arranged like the plates of a capacitor (a device to hold electric charge, to be studied next quarter). When the fingers flex, the capacitance (ability of the fingers to hold electric charg ...
... control the release of air bags in an automobile. It contains very thin “fingers” micromachined out of silicon arranged like the plates of a capacitor (a device to hold electric charge, to be studied next quarter). When the fingers flex, the capacitance (ability of the fingers to hold electric charg ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
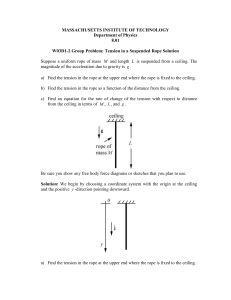
... W03D1-2 Group Problem: Tension in a Suspended Rope Solution Suppose a uniform rope of mass M and length L is suspended from a ceiling. The magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is g . a) Find the tension in the rope at the upper end where the rope is fixed to the ceiling. b) Find the tension ...
... W03D1-2 Group Problem: Tension in a Suspended Rope Solution Suppose a uniform rope of mass M and length L is suspended from a ceiling. The magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is g . a) Find the tension in the rope at the upper end where the rope is fixed to the ceiling. b) Find the tension ...
force of gravity
... acceleration of the moon to the acceleration of objects on earth. Believing that gravitational forces were responsible for each, Newton was able to draw an important conclusion about the dependence of gravity upon distance. This comparison led him to conclude that the force of gravitational attracti ...
... acceleration of the moon to the acceleration of objects on earth. Believing that gravitational forces were responsible for each, Newton was able to draw an important conclusion about the dependence of gravity upon distance. This comparison led him to conclude that the force of gravitational attracti ...
Topic 4: Dynamics – Force, Newton’s Three Laws, and Friction
... continue in a straight line, but it doesn’t. Why not? Newton 2nd Law: 1. If a net force gets larger on an accelerating mass, how will the mass respond? 2. If a truck loaded with bricks is accelerating, but many bricks fall off during acceleration, what will now happen to the motion of the truck? 3. ...
... continue in a straight line, but it doesn’t. Why not? Newton 2nd Law: 1. If a net force gets larger on an accelerating mass, how will the mass respond? 2. If a truck loaded with bricks is accelerating, but many bricks fall off during acceleration, what will now happen to the motion of the truck? 3. ...
Newton`s Laws PPT
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
Chapter 10 - galileo.harvard.edu
... wheel has a translational speed v. Draw a picture. The lowermost point on the wheel has a net forward velocity: 2v v zero not enough information to say back ...
... wheel has a translational speed v. Draw a picture. The lowermost point on the wheel has a net forward velocity: 2v v zero not enough information to say back ...
PhysicalScienceLawsofMotion(Ch.2)
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • According to Newton’s first law of motion, if the net force on an object is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest, and a moving object will continue moving in a straight line with constant speed. • As a result, balanced forces and unbalanced forces have different ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • According to Newton’s first law of motion, if the net force on an object is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest, and a moving object will continue moving in a straight line with constant speed. • As a result, balanced forces and unbalanced forces have different ...
CEENbot Pull - Mechatronics
... friction there would be no force to act in opposition to our desired motion. Thus friction is the force that fulfills Newton’s 3rd law - for every action there is an opposite and equal reaction. We cannot move in a desired direction unless friction works against us in the opposite direction. Frictio ...
... friction there would be no force to act in opposition to our desired motion. Thus friction is the force that fulfills Newton’s 3rd law - for every action there is an opposite and equal reaction. We cannot move in a desired direction unless friction works against us in the opposite direction. Frictio ...
Forces and Motion
... constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balanced with gravity. What will happen in the following scenarios? • A. a coin and a feather are dropped, they have the same mass. • B. two coins are dropped, one is heavier but bo ...
... constant speed. This speed is called terminal velocity. • This occurs because eventually air resistance will be evenly balanced with gravity. What will happen in the following scenarios? • A. a coin and a feather are dropped, they have the same mass. • B. two coins are dropped, one is heavier but bo ...