Newton's Second Law of Motion
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
PH212Chapter10_12
... wheel has a net forward velocity: 2v v zero not enough information to say back ...
... wheel has a net forward velocity: 2v v zero not enough information to say back ...
MECHANICS Lecture notes for Phys 111 Abstract
... A airplane that is flying level needs to accelerate from a speed of 200 m/s to a speed of 240 m/s while it flies a distance of 1.20 km. What must be the acceleration of the plane? same as above, a = . . . A ball rolls across a floor with an acceleration of a = −0.1m/s2 in a direction opposite to its ...
... A airplane that is flying level needs to accelerate from a speed of 200 m/s to a speed of 240 m/s while it flies a distance of 1.20 km. What must be the acceleration of the plane? same as above, a = . . . A ball rolls across a floor with an acceleration of a = −0.1m/s2 in a direction opposite to its ...
act04
... the string, and friction of the cart on the track. Check to see if any of these forces are related by Newton’s Third Law (Third Law pairs). Newton’s Third Law pairs are forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the pur ...
... the string, and friction of the cart on the track. Check to see if any of these forces are related by Newton’s Third Law (Third Law pairs). Newton’s Third Law pairs are forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the pur ...
Monday, April 1, 2013
... If particle#1 exerts force on particle #2, there must be a reaction force that the particle #2 exerts on #1. Both the forces are internal forces, and the net force in the entire SYSTEM is still 0. Now how would the momenta of these particles look like? ...
... If particle#1 exerts force on particle #2, there must be a reaction force that the particle #2 exerts on #1. Both the forces are internal forces, and the net force in the entire SYSTEM is still 0. Now how would the momenta of these particles look like? ...
Section 2 Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation
... • As the car enters the ramp and travels along a curved path, the passenger, because of inertia, tends to move along the original straight path. • If a sufficiently large centripetal force acts on the passenger, the person will move along the same curved path that the car does. The origin of the cen ...
... • As the car enters the ramp and travels along a curved path, the passenger, because of inertia, tends to move along the original straight path. • If a sufficiently large centripetal force acts on the passenger, the person will move along the same curved path that the car does. The origin of the cen ...
Momentum and Impulse
... 1. In which case (A or B) is the change in velocity the greatest? 2. In which case (A or B) is the change in momentum the greatest? 3. In which case (A or B) is the impulse the greatest? 4. In which case (A or B) is the force which acts upon the ball the greatest (assume contact times are the same i ...
... 1. In which case (A or B) is the change in velocity the greatest? 2. In which case (A or B) is the change in momentum the greatest? 3. In which case (A or B) is the impulse the greatest? 4. In which case (A or B) is the force which acts upon the ball the greatest (assume contact times are the same i ...
Friction
... between objects that are sliding with respect to one another. • Once enough force has been applied to the object to overcome static friction and get the object to move, the friction changes to sliding (or kinetic) friction. • Sliding (kinetic) friction is less than static friction. • If the componen ...
... between objects that are sliding with respect to one another. • Once enough force has been applied to the object to overcome static friction and get the object to move, the friction changes to sliding (or kinetic) friction. • Sliding (kinetic) friction is less than static friction. • If the componen ...
Lecture 1: Rotation of Rigid Body
... A small block with mass 0.250 kg is attached to a string passing through a hole in a frictionless, horizontal surface. The block is originally revolving in a circle with a radius of 0.800 m about the hole with a tangential speed of 4.00 m/s. The string is then pulled slowly from below, shortening th ...
... A small block with mass 0.250 kg is attached to a string passing through a hole in a frictionless, horizontal surface. The block is originally revolving in a circle with a radius of 0.800 m about the hole with a tangential speed of 4.00 m/s. The string is then pulled slowly from below, shortening th ...
Momentum and Impulse
... Newton’s Second Law can be used to relate the momentum of an object to the resultant force acting on it ...
... Newton’s Second Law can be used to relate the momentum of an object to the resultant force acting on it ...
46) A furniture crate of mass 60
... perpendicular components on a body placed on an inclined plane. Also, refer a book like the Physics volume 1 by Resnick and Halliday to understand how to draw free body diagram of any such body (you can see this in the attached file also). In all problems we assume that the value of g = 9.8 m/s2. In ...
... perpendicular components on a body placed on an inclined plane. Also, refer a book like the Physics volume 1 by Resnick and Halliday to understand how to draw free body diagram of any such body (you can see this in the attached file also). In all problems we assume that the value of g = 9.8 m/s2. In ...
Lecture 2c - Newton`s Laws & Applications
... 2. For one object, draw a free-body diagram, showing all the forces acting on the object. Make the magnitudes and directions as accurate as you can. Label each force. If there are multiple objects, draw a separate diagram for each one. ...
... 2. For one object, draw a free-body diagram, showing all the forces acting on the object. Make the magnitudes and directions as accurate as you can. Label each force. If there are multiple objects, draw a separate diagram for each one. ...
Resultant velocity of a horizontal projectile
... These formulae are only appropriate for rectilinear motion (i.e. velocity and acceleration in a straight line). This is inadequate for most real situations, so we introduce here the concept of curvilinear motion, where an object is moving in a plane along a specified curved path. We generally expres ...
... These formulae are only appropriate for rectilinear motion (i.e. velocity and acceleration in a straight line). This is inadequate for most real situations, so we introduce here the concept of curvilinear motion, where an object is moving in a plane along a specified curved path. We generally expres ...
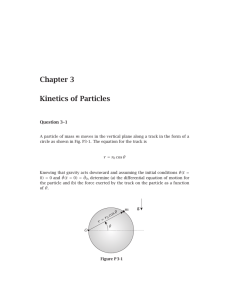
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles
... directions of en and eb . Therefore, the reaction force exerted by the track can be eliminated if the scalar product with et is taken with both sides of Eq. (3.27) as (Nn en +Nb eb −mg sin θ er −mg cos θ eθ )·et = (mr0 θ̈et +2mr0 θ̇ 2 en )·et (3.28) Then, observing that en · et = eb · et = 0, Eq. (3 ...
... directions of en and eb . Therefore, the reaction force exerted by the track can be eliminated if the scalar product with et is taken with both sides of Eq. (3.27) as (Nn en +Nb eb −mg sin θ er −mg cos θ eθ )·et = (mr0 θ̈et +2mr0 θ̇ 2 en )·et (3.28) Then, observing that en · et = eb · et = 0, Eq. (3 ...
Physics 380: Physics and Society Lecture 2: Newton`s Laws, Mass
... weaker than the others, but again only at the microscopic scale is more obscure. It is not something you will run across in your day to day activities, but the weak force is actually very, very important to life on earth because the weak force is responsible for the process called beta decay and it’ ...
... weaker than the others, but again only at the microscopic scale is more obscure. It is not something you will run across in your day to day activities, but the weak force is actually very, very important to life on earth because the weak force is responsible for the process called beta decay and it’ ...
ppt
... Galileo’s experiment A piece of wooden moulding or scantling, about 12 cubits [about 7 m] long, half a cubit [about 30 cm] wide and three finger-breadths [about 5 cm] thick, was taken; on its edge was cut a channel a little more than one finger in breadth; having made this groove very straight, smo ...
... Galileo’s experiment A piece of wooden moulding or scantling, about 12 cubits [about 7 m] long, half a cubit [about 30 cm] wide and three finger-breadths [about 5 cm] thick, was taken; on its edge was cut a channel a little more than one finger in breadth; having made this groove very straight, smo ...
Fall 2009 solutions - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... b. at the end points of the motion c. same value at every point 11. The spring force will be largest the farthest from equilibrium. Therefore the acceleration will be largest there, too. Choice B. Problem 12. A bat flying at 20 m/s emits a chirp at 35 kHz. If this sound pulse is reflected by a wall, ...
... b. at the end points of the motion c. same value at every point 11. The spring force will be largest the farthest from equilibrium. Therefore the acceleration will be largest there, too. Choice B. Problem 12. A bat flying at 20 m/s emits a chirp at 35 kHz. If this sound pulse is reflected by a wall, ...
Chapter 1
... resistance and water resistance are fluid) • Forces between solid objects studied primarily in sports biomechanics—An athlete and some other object (opponent, ground, implement) • To put a shot, an athlete must be holding the shot • To jump up, an athlete must be in contact with the ground and push ...
... resistance and water resistance are fluid) • Forces between solid objects studied primarily in sports biomechanics—An athlete and some other object (opponent, ground, implement) • To put a shot, an athlete must be holding the shot • To jump up, an athlete must be in contact with the ground and push ...