Newton`s Laws and Forces APS 2 longer with pix
... ONLY. (More mass means more inertia.) Inertia has nothing to do with size, speed, or anything else. ...
... ONLY. (More mass means more inertia.) Inertia has nothing to do with size, speed, or anything else. ...
Lecture04
... Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion: • Codified kinematics work by Galileo and other early experimenters • Introduced mathematics (calculus) as the language of Physics • Allowed detailed, quantitative prediction and control (engineering). • Ushered in the “Enlightenment” & “Clockwork Universe”. • Are accurate ...
... Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion: • Codified kinematics work by Galileo and other early experimenters • Introduced mathematics (calculus) as the language of Physics • Allowed detailed, quantitative prediction and control (engineering). • Ushered in the “Enlightenment” & “Clockwork Universe”. • Are accurate ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Notes
... c. When a swimmer pushes against the water (action), the water pushes against the swimmer (reaction). The reaction force pushes the swimmer forward. ...
... c. When a swimmer pushes against the water (action), the water pushes against the swimmer (reaction). The reaction force pushes the swimmer forward. ...
given a space curve r(t)
... Velocity and Acceleration: assuming r(t) is position of an object in space; • the velocity of the object is v(t) = r0(t); • the speed of the object is v(t) = |v(t)| = |r0(t)|; • the acceleration of the object is a(t) = v0(t) = r00(t); • Newton’s Second Law of Motion: F = ma = mr00(t), for a force F ...
... Velocity and Acceleration: assuming r(t) is position of an object in space; • the velocity of the object is v(t) = r0(t); • the speed of the object is v(t) = |v(t)| = |r0(t)|; • the acceleration of the object is a(t) = v0(t) = r00(t); • Newton’s Second Law of Motion: F = ma = mr00(t), for a force F ...
a force
... Momentum (p) – the mass of an object times its velocity (p=mv) Force (f) – anything that can cause a change in an object’s momentum As long as the object’s mass does not change, a force causes a change in velocity, or an acceleration (a) ...
... Momentum (p) – the mass of an object times its velocity (p=mv) Force (f) – anything that can cause a change in an object’s momentum As long as the object’s mass does not change, a force causes a change in velocity, or an acceleration (a) ...
what is physics
... When the velocity of an object changes, the object accelerates. Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity: a = v / t (Acceleration [m/s2] = Velocity [m/s] / Time [s]) Example 2. A car goes from rest to 20 m/s in 6 s. What is its acceleration? 2A. (1) a = v / t (2) a = 20 m/s / 6 s (3) a = 3 ...
... When the velocity of an object changes, the object accelerates. Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity: a = v / t (Acceleration [m/s2] = Velocity [m/s] / Time [s]) Example 2. A car goes from rest to 20 m/s in 6 s. What is its acceleration? 2A. (1) a = v / t (2) a = 20 m/s / 6 s (3) a = 3 ...
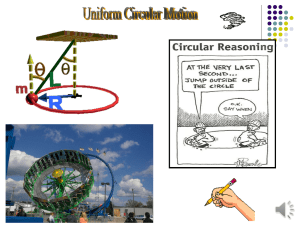
Circular Motion - the SASPhysics.com
... Simple Harmonic Motion Summary • What is SHM? • What sort of systems display SHM? • How can we describe SHM? ...
... Simple Harmonic Motion Summary • What is SHM? • What sort of systems display SHM? • How can we describe SHM? ...
Unit 3: FORCE
... constructed and the force with which they are pressed together. 1. Contact between irregularities on the surfaces of objects obstructs motion. 2. Kinetic (sliding) friction is less than static (at rest) friction. 3. Static friction is a force tangential to the surfaces, exerted by one surface on ano ...
... constructed and the force with which they are pressed together. 1. Contact between irregularities on the surfaces of objects obstructs motion. 2. Kinetic (sliding) friction is less than static (at rest) friction. 3. Static friction is a force tangential to the surfaces, exerted by one surface on ano ...
Conceptual Physics
... 41. A 2000-kg truck travels at 5 m/s. A 1000-kg car travels at 10 m/s. How do their kinetic energies compare? Bigger truck so 2x the energy But ½ the velocity so ¼ the energy So truck has ½ the KE of the car 42. What does this say about the braking force needed to stop a car as its speed increases? ...
... 41. A 2000-kg truck travels at 5 m/s. A 1000-kg car travels at 10 m/s. How do their kinetic energies compare? Bigger truck so 2x the energy But ½ the velocity so ¼ the energy So truck has ½ the KE of the car 42. What does this say about the braking force needed to stop a car as its speed increases? ...
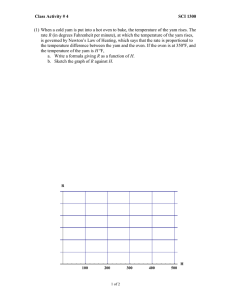
The following table converts degrees Fahrenheit to degrees
... (1) When a cold yam is put into a hot oven to bake, the temperature of the yam rises. The rate R (in degrees Fahrenheit per minute), at which the temperature of the yam rises, is governed by Newton’s Law of Heating, which says that the rate is proportional to the temperature difference between the y ...
... (1) When a cold yam is put into a hot oven to bake, the temperature of the yam rises. The rate R (in degrees Fahrenheit per minute), at which the temperature of the yam rises, is governed by Newton’s Law of Heating, which says that the rate is proportional to the temperature difference between the y ...
Lecture-05-09
... (a) Is the force experienced by the child more than, less than, or the same as the force experienced by the parent? (b) Is the acceleration of the child more than, less than, or the same as the acceleration of the parent? Explain. (c) If the acceleration of the child is 2.6 m/s2 in magnitude, what i ...
... (a) Is the force experienced by the child more than, less than, or the same as the force experienced by the parent? (b) Is the acceleration of the child more than, less than, or the same as the acceleration of the parent? Explain. (c) If the acceleration of the child is 2.6 m/s2 in magnitude, what i ...
force
... Newton’s universal law of gravitation: Every object in the universe exerts a gravitational attraction to all other objects in the universe The amount of gravitational force depends upon the mass of the objects and the distance between the objects ...
... Newton’s universal law of gravitation: Every object in the universe exerts a gravitational attraction to all other objects in the universe The amount of gravitational force depends upon the mass of the objects and the distance between the objects ...
Cross Products
... when viewed from the u direction. 3. Multiply that vector by | u |. Note that if u and v point in the same direction then uv is zero. Torque. One application of the cross product is to calculating the torque of a force acting on an object. Suppose we have an object that occupies more than a single ...
... when viewed from the u direction. 3. Multiply that vector by | u |. Note that if u and v point in the same direction then uv is zero. Torque. One application of the cross product is to calculating the torque of a force acting on an object. Suppose we have an object that occupies more than a single ...
notes on Intro to Force - Link 308
... between two objects, results in the change in velocity (that is – acceleration) – Example: pull on a spring, the string will move – Pull on a wagon, the wagon will move – Catching a football, the ball will stop – Kick a soccer ball, the ball will move – Your turn – let’s come up with 2 more examples ...
... between two objects, results in the change in velocity (that is – acceleration) – Example: pull on a spring, the string will move – Pull on a wagon, the wagon will move – Catching a football, the ball will stop – Kick a soccer ball, the ball will move – Your turn – let’s come up with 2 more examples ...
Generalized =
... a very short period of time. If we integrate F = ma = mx” we see that a large force over a short time creates a sudden change in the momentum, mx � . This is called an "impulse." If the gun is fired straight up, the graph of the elevation of the bullet, plotted against t, starts at zero, then rises i ...
... a very short period of time. If we integrate F = ma = mx” we see that a large force over a short time creates a sudden change in the momentum, mx � . This is called an "impulse." If the gun is fired straight up, the graph of the elevation of the bullet, plotted against t, starts at zero, then rises i ...