Physics Lab Exam - La Salle University
... the percent errors. Include your last name in the title of your graph, for example, “Smith: Cart on Incline.” Print them. C. Indicate on both graphs where the velocity and acceleration are in the same direction and where they are in the opposite direction. Ideal Acceleration ...
... the percent errors. Include your last name in the title of your graph, for example, “Smith: Cart on Incline.” Print them. C. Indicate on both graphs where the velocity and acceleration are in the same direction and where they are in the opposite direction. Ideal Acceleration ...
Physics Chapter 6 Name: Lab: Tug of War Date: Purpose: Observe
... 2. Pair up with another group. Attach a string between the two cars. Make the string snug between the two cars. Turn each car on and observe a tug of war between the cars. Explain the result of your tug of war in relation to the net force and the measured force that each car exerts. ...
... 2. Pair up with another group. Attach a string between the two cars. Make the string snug between the two cars. Turn each car on and observe a tug of war between the cars. Explain the result of your tug of war in relation to the net force and the measured force that each car exerts. ...
SAMPLE TEST 1: PHYSICS 103
... Elise and Keith run on a track at a constant speed of 10 mph. If Elise travels along the inner radius of the track and Keith travels along the outer radius and they both have the same mass, which of the following statements must be true: A. The centripetal force on both students is the same B. The c ...
... Elise and Keith run on a track at a constant speed of 10 mph. If Elise travels along the inner radius of the track and Keith travels along the outer radius and they both have the same mass, which of the following statements must be true: A. The centripetal force on both students is the same B. The c ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... a) the top b) the bottom c) halfway between top and bottom d) the force is the same over the whole motion 1b) Is the net force doing work on you? a) YES b) NO 2) If the mass of the moon were doubled, what would happen to its centripetal acceleration? a) it would increase b) it would decrease c) it w ...
... a) the top b) the bottom c) halfway between top and bottom d) the force is the same over the whole motion 1b) Is the net force doing work on you? a) YES b) NO 2) If the mass of the moon were doubled, what would happen to its centripetal acceleration? a) it would increase b) it would decrease c) it w ...
Document
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object is made up of. The units of mass are kilograms, and because body ‘weight’ is often given in kilograms the two terms are often used to mean the same thing. However, weight is a force that is exerted on the body by gravity. Weight is directly proport ...
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object is made up of. The units of mass are kilograms, and because body ‘weight’ is often given in kilograms the two terms are often used to mean the same thing. However, weight is a force that is exerted on the body by gravity. Weight is directly proport ...
and the three laws of motion
... “ Every body continues in its state of rest or uniform speed in a straight line unless it is compelled to change that state by a net force acting on it.” ...
... “ Every body continues in its state of rest or uniform speed in a straight line unless it is compelled to change that state by a net force acting on it.” ...
Physical Science Review - elyceum-beta
... • The object with the greater inertia requires more force to alter its rate of motion • Which object on your desk top has the most inertia? ...
... • The object with the greater inertia requires more force to alter its rate of motion • Which object on your desk top has the most inertia? ...
Circular Motion Web Quest
... 17. Does the sensation of being thrown outward from the center of a circle mean that there was definitely an outward force? ...
... 17. Does the sensation of being thrown outward from the center of a circle mean that there was definitely an outward force? ...
Chapter 3 - Cloudfront.net
... Acceleration: A Change in Motion • Acceleration can only occur if a force acts on it… • Without a force…there can be no acceleration!! ...
... Acceleration: A Change in Motion • Acceleration can only occur if a force acts on it… • Without a force…there can be no acceleration!! ...
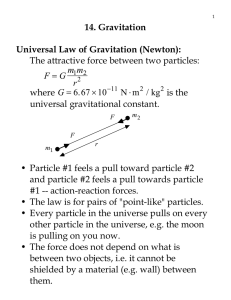
14. Gravitation Universal Law of Gravitation (Newton): G
... Calculate the gravitational force due to a hollowed sphere, assuming that the mass of the ...
... Calculate the gravitational force due to a hollowed sphere, assuming that the mass of the ...
Physics Midterm Study Guide
... Know how to enter powers of 10 in calculations reliably in your calculator Dependent and independent variables in an experiment are the only ones we want to allow to change Position, x , is the distance and direction from the origin. It is in bold font because its direction is important Displacement ...
... Know how to enter powers of 10 in calculations reliably in your calculator Dependent and independent variables in an experiment are the only ones we want to allow to change Position, x , is the distance and direction from the origin. It is in bold font because its direction is important Displacement ...
SCRIBBLE PAD
... • An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. • Objects at rest – Not moving – Won’t move unless a push or pull is exerted on them ...
... • An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. • Objects at rest – Not moving – Won’t move unless a push or pull is exerted on them ...
1 Physics 20 10 Summer 2016 Richard In "chretsen Exam 2
... For each of the following trajectories, draw in the specified vectors at the 5 points along the object's path. Keep in mind that a vector's length displays its magnitude. x-component of velocity ...
... For each of the following trajectories, draw in the specified vectors at the 5 points along the object's path. Keep in mind that a vector's length displays its magnitude. x-component of velocity ...
CPphysics review 1-10
... and catches it in the same spot as it returns to the mitt. At what point in the ball's path does it experience zero velocity and zero acceleration? a) midway on the way up b) at the top of its trajectory c) the instant before it arrives in the catcher's mitt d) at no point in the ball's path ...
... and catches it in the same spot as it returns to the mitt. At what point in the ball's path does it experience zero velocity and zero acceleration? a) midway on the way up b) at the top of its trajectory c) the instant before it arrives in the catcher's mitt d) at no point in the ball's path ...
Document
... central idea and some supporting information; can summarize the main ideas but struggles to use original language when paraphrasing or does not include essential details ...
... central idea and some supporting information; can summarize the main ideas but struggles to use original language when paraphrasing or does not include essential details ...
Day 3
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
OWL Ch02 Review Game
... The relationship among force, mass, and acceleration is stated in ____. a. the law of conservation of momentum b. Newton's first law of motion c. Newton's second law of motion d. Newton's third law of motion ...
... The relationship among force, mass, and acceleration is stated in ____. a. the law of conservation of momentum b. Newton's first law of motion c. Newton's second law of motion d. Newton's third law of motion ...
(True ) or (False)?
... Each of four particles moves along an x axis. Their coordinates (in meters) as functions of time (in seconds) are given by: particle 1: x(t) = 3.5 − 2.7t3 particle 2: x(t) = 3.5 +2.7t3 particle 3: x(t) = 3.5 +2.7t2 particle 4: x(t) = 3.5 − 3.4t − 2.7t2 Which of these particles have constant accelera ...
... Each of four particles moves along an x axis. Their coordinates (in meters) as functions of time (in seconds) are given by: particle 1: x(t) = 3.5 − 2.7t3 particle 2: x(t) = 3.5 +2.7t3 particle 3: x(t) = 3.5 +2.7t2 particle 4: x(t) = 3.5 − 3.4t − 2.7t2 Which of these particles have constant accelera ...