Newtons Laws and Its Application
... Question: An object falls from rest, under the action of gravity and the air friction F =- v, what is the speed at time t, and when t→∞? ...
... Question: An object falls from rest, under the action of gravity and the air friction F =- v, what is the speed at time t, and when t→∞? ...
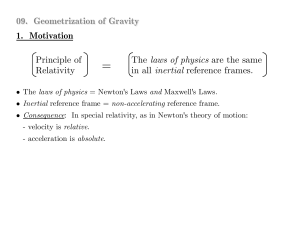
09. General Relativity: Geometrization of Gravity
... In any given gravitational field (described by some Φ), all objects fall with the same acceleration a = −∂Φ. • This is regardless of the object's internal properties (it's mass, charge, etc.). The gravitational force is universal: it affects all objects in the same way. • Constrast with the electrom ...
... In any given gravitational field (described by some Φ), all objects fall with the same acceleration a = −∂Φ. • This is regardless of the object's internal properties (it's mass, charge, etc.). The gravitational force is universal: it affects all objects in the same way. • Constrast with the electrom ...
Newton`s Laws - Dr. Robert MacKay
... • The acceleration of an object describes how fast its velocity changes. • If an object travels in a straight line with constant speed the acceleration is zero. • Whenever an object either changes speed of changes direction it is accelerating. ...
... • The acceleration of an object describes how fast its velocity changes. • If an object travels in a straight line with constant speed the acceleration is zero. • Whenever an object either changes speed of changes direction it is accelerating. ...
Unit II Forces
... If no net force acts on the system, the total momentum of the system does not change. ...
... If no net force acts on the system, the total momentum of the system does not change. ...
Circular Motion - Garnet Valley School District
... A 0.50 kg box is attached to string on a frictionless horizontal table. The box revolves in a circle of radius 2.8 m. If the box completes 1 revolution every 2.0 seconds, what is the tension in the string? FN r ...
... A 0.50 kg box is attached to string on a frictionless horizontal table. The box revolves in a circle of radius 2.8 m. If the box completes 1 revolution every 2.0 seconds, what is the tension in the string? FN r ...
Force and Motion
... Two balls are thrown from the top of a cliff. Ball S is thrown upwards at the same time Ball T is thrown out horizontally. A. Ball T will hit the ground first. B. Ball S will hit the ground first. C. Ball S and Ball T will hit the ground at the same time. D. We must know the masses of Ball S and Bal ...
... Two balls are thrown from the top of a cliff. Ball S is thrown upwards at the same time Ball T is thrown out horizontally. A. Ball T will hit the ground first. B. Ball S will hit the ground first. C. Ball S and Ball T will hit the ground at the same time. D. We must know the masses of Ball S and Bal ...
Applications of Newton`s Law
... 6-3 Translational Equilibrium When an object is in translational equilibrium, the net force on it is zero: ...
... 6-3 Translational Equilibrium When an object is in translational equilibrium, the net force on it is zero: ...
Our Place in the Cosmos Elective Course
... years earlier, believed that the natural state of objects was to be at rest - an object in motion would tend toward this natural state - a reasonable empirical rule due to friction ...
... years earlier, believed that the natural state of objects was to be at rest - an object in motion would tend toward this natural state - a reasonable empirical rule due to friction ...
HW#6: Fallin` Up
... Date___________________ Block__________________ HW#6 Reading: Gravity and Motion ...
... Date___________________ Block__________________ HW#6 Reading: Gravity and Motion ...
Newton`s 2nd and 3rd Laws
... object equals the object’s mass times the object’s acceleration • If the same force is applied to 2 objects of different mass, the less ...
... object equals the object’s mass times the object’s acceleration • If the same force is applied to 2 objects of different mass, the less ...
external forces. - Mahidol University
... Inertial frames are frames of reference that are not accelerating (i.e. not moving or moving at constant velocity) A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to the distant stars is the best approximation of an inertial frame, and for our purposes we can consider the Earth as bein ...
... Inertial frames are frames of reference that are not accelerating (i.e. not moving or moving at constant velocity) A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to the distant stars is the best approximation of an inertial frame, and for our purposes we can consider the Earth as bein ...
The NET Force
... (your velocity increases) • In an elevator when it starts to go up (you are at rest then start moving) • In a car going around a curve at constant speed (the direction of your velocity changes) • You are on a bus that is slowing down (your velocity decreases) • you are in an elevator and the cable b ...
... (your velocity increases) • In an elevator when it starts to go up (you are at rest then start moving) • In a car going around a curve at constant speed (the direction of your velocity changes) • You are on a bus that is slowing down (your velocity decreases) • you are in an elevator and the cable b ...
on forces
... is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely propo ...
... is zero the object continues in its original state of motion; if it was at rest, it remains at rest. If it was moving with a certain velocity, it will keep on moving with the same velocity. Second Law: The acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it, and inversely propo ...
Skydiving: falling with constant velocity
... (your velocity increases) • In an elevator when it starts to go up (you are at rest then start moving) • In a car going around a curve at constant speed (the direction of your velocity changes) • You are on a bus that is slowing down (your velocity decreases) • you are in an elevator and the cable b ...
... (your velocity increases) • In an elevator when it starts to go up (you are at rest then start moving) • In a car going around a curve at constant speed (the direction of your velocity changes) • You are on a bus that is slowing down (your velocity decreases) • you are in an elevator and the cable b ...
KIN340-Chapter12
... The push or pull acting on the body measured in Newtons (N) The relationship between the forces which affect a body, and the state of motion of that body, can be summarized by Newton’s three Laws of Motion: 1. Law of Inertia A body will continue in its state of rest or motion in a straight line, unl ...
... The push or pull acting on the body measured in Newtons (N) The relationship between the forces which affect a body, and the state of motion of that body, can be summarized by Newton’s three Laws of Motion: 1. Law of Inertia A body will continue in its state of rest or motion in a straight line, unl ...
File
... 7. A 3750kg loaded elevator is being pulled up to the third floor at a constant rate. Calculate the net force on the elevator. 8. A submarine accelerates up through the water on its ascent to the surface. The submarine has a mass of 142000 tons and experiences a buoyant force of 1.42x109N. Calculate ...
... 7. A 3750kg loaded elevator is being pulled up to the third floor at a constant rate. Calculate the net force on the elevator. 8. A submarine accelerates up through the water on its ascent to the surface. The submarine has a mass of 142000 tons and experiences a buoyant force of 1.42x109N. Calculate ...