Ball launcher
... The world record for running 100 m is about 10 seconds. What is the average speed? Red 5 m/sec Yellow 0 m/sec Green 10 m/sec Blue 0.1 m/sec When is the runner accelerating? Red Mostly at the very beginning of the race Yellow The acceleration is constant Green All the time, but more at the beginning ...
... The world record for running 100 m is about 10 seconds. What is the average speed? Red 5 m/sec Yellow 0 m/sec Green 10 m/sec Blue 0.1 m/sec When is the runner accelerating? Red Mostly at the very beginning of the race Yellow The acceleration is constant Green All the time, but more at the beginning ...
Work, Power, Energy Multiple Choice PSI Physics
... 28. A block with a mass of m crosses a rough horizontal surface at a constant speed of v. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is µ. How much power must be produced in order to overcome the friction force? A. mg B. µmg C. zero D. µg E. µmgv 29. A motorbike engine ca ...
... 28. A block with a mass of m crosses a rough horizontal surface at a constant speed of v. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is µ. How much power must be produced in order to overcome the friction force? A. mg B. µmg C. zero D. µg E. µmgv 29. A motorbike engine ca ...
21 circ motion gravitation mc File
... 17. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the Earth, then which of the following is true? (A) F1 is much greater than F2. (B) F1 is slightly greater than F2. (C) F1 is equal to ...
... 17. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the Earth, then which of the following is true? (A) F1 is much greater than F2. (B) F1 is slightly greater than F2. (C) F1 is equal to ...
Harmonic Motion
... A diving board oscillates with a frequency of 5.0 cycles per second with a person of mass 70. kg. What is the spring constant of the board? ...
... A diving board oscillates with a frequency of 5.0 cycles per second with a person of mass 70. kg. What is the spring constant of the board? ...
Force
... much it wants to stay at rest. If an object is moving with constant velocity, the object’s inertia is a measure of how much it wants to maintain its current speed and direction. (Refer to Newton’s Laws for a more complete explanation) ...
... much it wants to stay at rest. If an object is moving with constant velocity, the object’s inertia is a measure of how much it wants to maintain its current speed and direction. (Refer to Newton’s Laws for a more complete explanation) ...
Student Exam Review
... force A. would not be affected B. would decrease C. would increase, as well D. could do any of the three things mentioned above (unknown) 85. What is Archemides principle? a. The weight of a fluid is equal to the force of gravity times the fluid's mass. b. Pressure increases with depth. c. The bouya ...
... force A. would not be affected B. would decrease C. would increase, as well D. could do any of the three things mentioned above (unknown) 85. What is Archemides principle? a. The weight of a fluid is equal to the force of gravity times the fluid's mass. b. Pressure increases with depth. c. The bouya ...
lab - Seattle Central College
... Purpose: In this lab, we check a special case of Newton’s laws, namely that the sum of the forces acting on an object in equilibrium is zero. Since forces are vectors, we will practice doing vector additions. First, we measure the forces acting on an object in equilibrium (a ring). Then, we check th ...
... Purpose: In this lab, we check a special case of Newton’s laws, namely that the sum of the forces acting on an object in equilibrium is zero. Since forces are vectors, we will practice doing vector additions. First, we measure the forces acting on an object in equilibrium (a ring). Then, we check th ...
June 2006 - 6677 Mechanics M1 - Question paper
... Whenever a numerical value of g is required, take g = 9.8 m s2. When a calculator is used, the answer should be given to an appropriate degree of accuracy. ...
... Whenever a numerical value of g is required, take g = 9.8 m s2. When a calculator is used, the answer should be given to an appropriate degree of accuracy. ...
mechanical energy
... Question 9 • A 4,000 kg satellite is traveling in a circular orbit 200 km above the surface of the earth. A 3.0 gram marble is dropped inside the satellite. What is the force of gravity on the marble as viewed by the observers on the earth? (Me = 5.98 x 1024 kg, Re = 6.37 x 106 m, G = 6.67 x 10-11 ...
... Question 9 • A 4,000 kg satellite is traveling in a circular orbit 200 km above the surface of the earth. A 3.0 gram marble is dropped inside the satellite. What is the force of gravity on the marble as viewed by the observers on the earth? (Me = 5.98 x 1024 kg, Re = 6.37 x 106 m, G = 6.67 x 10-11 ...
Dynamics-cause of motion
... Why don’t things move on their own on a frictionless surface? Something keeps them from moving That “something” must be universal ...
... Why don’t things move on their own on a frictionless surface? Something keeps them from moving That “something” must be universal ...
Chapter 4 Motion
... Astronauts inside the space shuttle float as if no gravity were acting on them. However, Earth's gravity at the shuttle isn't zero or even near zero. The shuttle's orbit is close enough to Earth that gravity is almost as strong there as it is on Earth. Why do the astronauts seem to be weightless? Th ...
... Astronauts inside the space shuttle float as if no gravity were acting on them. However, Earth's gravity at the shuttle isn't zero or even near zero. The shuttle's orbit is close enough to Earth that gravity is almost as strong there as it is on Earth. Why do the astronauts seem to be weightless? Th ...
Name
... 63. After 5.00 seconds, approximately what is the vertical component of the projectile’s velocity? (1) 450 m/s (2) 500. m/s (3) 49 m/s (4) 0.0 m/s 64. The maximum height to which the projectile rises is approximately (1) 2.50 x 103 m (2) 1.25 x 104 m (3) 1.54 x 104 m (4) 4.42 x 104 m 65. A projectil ...
... 63. After 5.00 seconds, approximately what is the vertical component of the projectile’s velocity? (1) 450 m/s (2) 500. m/s (3) 49 m/s (4) 0.0 m/s 64. The maximum height to which the projectile rises is approximately (1) 2.50 x 103 m (2) 1.25 x 104 m (3) 1.54 x 104 m (4) 4.42 x 104 m 65. A projectil ...
1999 Solution Q11
... velocity changing v = u - gt Vvertical = v0sin - gt acceleration = -g velocity changing v = u + gt v = 0 + gt acceleration = g ...
... velocity changing v = u - gt Vvertical = v0sin - gt acceleration = -g velocity changing v = u + gt v = 0 + gt acceleration = g ...
Circular Motion Lab
... Write the formula for centripetal force as well as centripetal acceleration in the box below. Label each variable with the appropriate set of units. ...
... Write the formula for centripetal force as well as centripetal acceleration in the box below. Label each variable with the appropriate set of units. ...
Newton`s Second Law
... The goal of this experiment is to investigate the relationship between force, mass and acceleration. You will be verifying a powerful physical law well known as Newton's second law. F = ma You will also be comparing the gravitational mass of an object with its inertial mass. Where: m=W/g (gravitati ...
... The goal of this experiment is to investigate the relationship between force, mass and acceleration. You will be verifying a powerful physical law well known as Newton's second law. F = ma You will also be comparing the gravitational mass of an object with its inertial mass. Where: m=W/g (gravitati ...
ConcepTest 4.1a Newton`s First Law I 1) there is a net force but the
... Mass is the measure of inertia of an object. In the SI system, mass is measured in kilograms. Mass is not weight: Mass is a property of an object. Weight is the force exerted on that object by gravity. If you go to the moon, whose gravitational acceleration is about 1/6 g, you will weigh much less. ...
... Mass is the measure of inertia of an object. In the SI system, mass is measured in kilograms. Mass is not weight: Mass is a property of an object. Weight is the force exerted on that object by gravity. If you go to the moon, whose gravitational acceleration is about 1/6 g, you will weigh much less. ...
Physics: Principles and Applications, 6e Giancoli
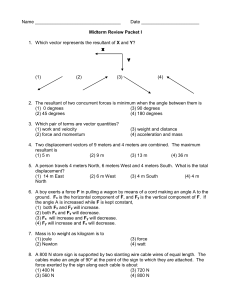
... 2) The resultant of two vectors is the smallest when the angle between them is A) 0°. B) 45°. C) 90°. D) 180°. 3) Two displacement vectors have magnitudes of 5.0 m and 7.0 m, respectively. When these two vectors are added, the magnitude of the sum A) is 2.0 m. B) could be as small as 2.0 m, or as la ...
... 2) The resultant of two vectors is the smallest when the angle between them is A) 0°. B) 45°. C) 90°. D) 180°. 3) Two displacement vectors have magnitudes of 5.0 m and 7.0 m, respectively. When these two vectors are added, the magnitude of the sum A) is 2.0 m. B) could be as small as 2.0 m, or as la ...