force
... cafeteria. Mac says that if he throws his jello with a greater speed, it will have greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend on speed, but rather on mass. With whom do you agree? Tosh ...
... cafeteria. Mac says that if he throws his jello with a greater speed, it will have greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend on speed, but rather on mass. With whom do you agree? Tosh ...
Physics of Rocket Flight
... In physics it normal to cal the distance between two points in a straight line the displacement. The term “displacement” not only considers the distance between the points but also the direction, thus it is a vector quantity. Speed also has an associate direction in physics, and is thus a vector qua ...
... In physics it normal to cal the distance between two points in a straight line the displacement. The term “displacement” not only considers the distance between the points but also the direction, thus it is a vector quantity. Speed also has an associate direction in physics, and is thus a vector qua ...
Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces 5
... Example 5-9: Moon’s centripetal acceleration. The Moon’s nearly circular orbit about the Earth has a radius of about 384,000 km and a period T of 27.3 days. Determine the acceleration of the Moon toward the Earth. ...
... Example 5-9: Moon’s centripetal acceleration. The Moon’s nearly circular orbit about the Earth has a radius of about 384,000 km and a period T of 27.3 days. Determine the acceleration of the Moon toward the Earth. ...
determination of the acceleration of an elevator.
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...
force=mass times acceleration
... 11. Inertia: the tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion 12. Inexhaustible: incapable of being entirely consumed or used up; renewable 13. Joule: SI unit of energy 14. Kinetic energy: The energy of a moving object 15. Law of Conservation of Energy: That energy can neither be created n ...
... 11. Inertia: the tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion 12. Inexhaustible: incapable of being entirely consumed or used up; renewable 13. Joule: SI unit of energy 14. Kinetic energy: The energy of a moving object 15. Law of Conservation of Energy: That energy can neither be created n ...
Physics
... 1. You walk 45m south and 45m east. Compute the resultant. 2. A ship leaves its home port expecting to travel to a port 750km due south. A severe storm comes up and blows the ship 175km due east off course. How far is the ship from its destination? 3. Bill rows a boat at 12.0 m/s directly across a r ...
... 1. You walk 45m south and 45m east. Compute the resultant. 2. A ship leaves its home port expecting to travel to a port 750km due south. A severe storm comes up and blows the ship 175km due east off course. How far is the ship from its destination? 3. Bill rows a boat at 12.0 m/s directly across a r ...
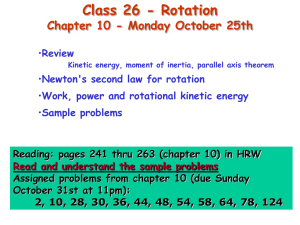
Class26
... •It is essential that these axes are parallel; as you can see from table 10-2, the moments of inertia can be different for different axes. ...
... •It is essential that these axes are parallel; as you can see from table 10-2, the moments of inertia can be different for different axes. ...
Lesson 20 questions – moments and torque - science
... distance = …813…(allow 810)…………….. m (2) c) The length of runways at some airports is less than the required distance for take-off by this aircraft in (b)(iii). State and explain one method that could be adopted for this aircraft so that it could reach the required take-off speed on shorter runways. ...
... distance = …813…(allow 810)…………….. m (2) c) The length of runways at some airports is less than the required distance for take-off by this aircraft in (b)(iii). State and explain one method that could be adopted for this aircraft so that it could reach the required take-off speed on shorter runways. ...
Centripetal Motion - San Diego Mesa College
... 8. Do not cut the string (leave the string attached to the bob), but remove the spring and mass hanger. Now change the radius marker to the largest possible radius. Be sure that the upper arm and the radius marker are adjusted such that the bob is directly over the marker when the bob hangs straigh ...
... 8. Do not cut the string (leave the string attached to the bob), but remove the spring and mass hanger. Now change the radius marker to the largest possible radius. Be sure that the upper arm and the radius marker are adjusted such that the bob is directly over the marker when the bob hangs straigh ...
Force, Mass, Acceleration, and Friction
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion – the net force acting on an object causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the net force. The acceleration of an object is determined by the size of the net force and the mass of the object. a = F / m, where F is measured in Newtons (N) and mass is measured ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion – the net force acting on an object causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the net force. The acceleration of an object is determined by the size of the net force and the mass of the object. a = F / m, where F is measured in Newtons (N) and mass is measured ...
Net Force
... accelerate. By pushing or pulling an object you are applying a force to the object. Force are measured in units of Newtons (N) o 1 “Newton” is the amount of force needed to accelerate a 1 kg mass at 1 m/s2 It’s hard to talk about acceleration without stating the “thing” that caused the accelerat ...
... accelerate. By pushing or pulling an object you are applying a force to the object. Force are measured in units of Newtons (N) o 1 “Newton” is the amount of force needed to accelerate a 1 kg mass at 1 m/s2 It’s hard to talk about acceleration without stating the “thing” that caused the accelerat ...
Lecture-06-09
... of about 2.5 m/s2 upward e) experiencing a constant acceleration of about 2.5 m/s2 downward ...
... of about 2.5 m/s2 upward e) experiencing a constant acceleration of about 2.5 m/s2 downward ...
Physics 9 - Sports: Chapter 2
... Newton's Second Law of Motion 1. If there is an unbalanced force acting on an object, what happens to the object? ____________ In what direction will the object accelerate in respect to the direction of the net force? _________ What did we do in class to demonstrate this? __________________________ ...
... Newton's Second Law of Motion 1. If there is an unbalanced force acting on an object, what happens to the object? ____________ In what direction will the object accelerate in respect to the direction of the net force? _________ What did we do in class to demonstrate this? __________________________ ...
Lecture8 (Equilibrium)
... Instantaneous Velocity vs Average Velocity instantaneous velocity at t=2 is 1 ms-1 Instantaneous velocity at t=3 is 0 ms-1 Instantaneous velocity at t=4 is __________ Instantaneous velocity at t=8 is __________ Instantaneous velocity at t=2 is undefined since it is different at 2+ (slightly > 2) an ...
... Instantaneous Velocity vs Average Velocity instantaneous velocity at t=2 is 1 ms-1 Instantaneous velocity at t=3 is 0 ms-1 Instantaneous velocity at t=4 is __________ Instantaneous velocity at t=8 is __________ Instantaneous velocity at t=2 is undefined since it is different at 2+ (slightly > 2) an ...