Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion Conclusion
... • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The atom in a molecule carries energy (chemical) • The molecule in a hot gas carries energy (thermal) • The nucleus of an atom carries energy (nuclear) (The energy carried by radi ...
... • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The atom in a molecule carries energy (chemical) • The molecule in a hot gas carries energy (thermal) • The nucleus of an atom carries energy (nuclear) (The energy carried by radi ...
4.11 Equilibrium Application of Newton`s Laws of Motion
... a tension in the rope that passes around the pulleys. Therefore, tension forces T1 and T2 are applied to the pulley on the foot. (It may seem surprising that the rope applies a force to either side of the foot pulley. Ignoring the weight of the foot, find the magnitude of F? ...
... a tension in the rope that passes around the pulleys. Therefore, tension forces T1 and T2 are applied to the pulley on the foot. (It may seem surprising that the rope applies a force to either side of the foot pulley. Ignoring the weight of the foot, find the magnitude of F? ...
Rotation
... We know that if an object is in (translational) equilibrium then it does not accelerate. We can say that SF = 0 An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
... We know that if an object is in (translational) equilibrium then it does not accelerate. We can say that SF = 0 An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
Unit 8 force - Kowenscience.com
... Friction The force that opposes the motion of an object, It is a force that two surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other. Friction acts in the direction opposite to motion. and is the force that brings an object to rest Without friction or other unbalanced forces, an object will ...
... Friction The force that opposes the motion of an object, It is a force that two surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other. Friction acts in the direction opposite to motion. and is the force that brings an object to rest Without friction or other unbalanced forces, an object will ...
File - Phy 2048-0002
... body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and direction. Principle of superposition: when two or more forces act on a body, the net force can be obtained by adding the individual forces vectorially. Inertial reference frame: where Newton’s laws hold. ...
... body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and direction. Principle of superposition: when two or more forces act on a body, the net force can be obtained by adding the individual forces vectorially. Inertial reference frame: where Newton’s laws hold. ...
Momentum - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... net force acts on an object, its velocity is constant. Its mass will not change. Therefore, in this situation, momentum is constant. Momentum is conserved. Newton's second law describes how the velocity of a body changes if a net force acts on it. ...
... net force acts on an object, its velocity is constant. Its mass will not change. Therefore, in this situation, momentum is constant. Momentum is conserved. Newton's second law describes how the velocity of a body changes if a net force acts on it. ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 6, Mar 24, 2005
... θ is the angle between the force vector and the displacement vector (see figure). The work done on the mass m equals the change in kinetic energy. The expression relating this is given by ∆K = W. ...
... θ is the angle between the force vector and the displacement vector (see figure). The work done on the mass m equals the change in kinetic energy. The expression relating this is given by ∆K = W. ...
By Newton`s second law
... zero, it will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed. Does the skateboard keep moving with constant speed after it leaves your hand? Why or why not? ...
... zero, it will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed. Does the skateboard keep moving with constant speed after it leaves your hand? Why or why not? ...
document
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
force - washburnhoogheem
... One way forces act is the result of direct contact. A contact force is transmitted by matter directly touching other matter such as wind acting to slow a parachute. ...
... One way forces act is the result of direct contact. A contact force is transmitted by matter directly touching other matter such as wind acting to slow a parachute. ...
Review Answers
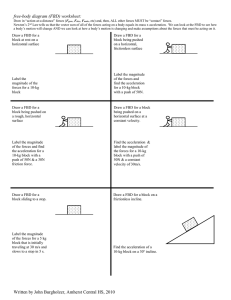
... Draw free-body diagrams for the following problems. Be sure to draw all the forces with arrows that are of appropriate length to reflect the given descriptions. a) Object slides across a horizontal surface at constant speed without friction. Fn up; equal Fg down b) A sky diver falls downward through ...
... Draw free-body diagrams for the following problems. Be sure to draw all the forces with arrows that are of appropriate length to reflect the given descriptions. a) Object slides across a horizontal surface at constant speed without friction. Fn up; equal Fg down b) A sky diver falls downward through ...