Circular Motion Notes
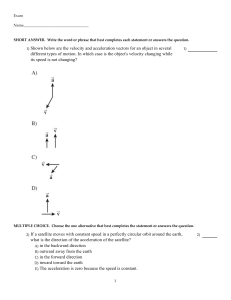
... motion of an object, we discuss its velocity (speed and direction), its acceleration, and any path it would follow. In this case, the ball would simply move straight upward, accelerating at – 10 m/s2 and decreasing its speed, reach a maximum height where its velocity is instantaneously zero, then ac ...
... motion of an object, we discuss its velocity (speed and direction), its acceleration, and any path it would follow. In this case, the ball would simply move straight upward, accelerating at – 10 m/s2 and decreasing its speed, reach a maximum height where its velocity is instantaneously zero, then ac ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 300 years ago Newton summarised all motion by three laws. Newtons 1st law of motion If an object has zero net force acting on it, it will remain at rest, or continue moving with an unchanged velocity. Newtons 2nd law of motion A constant force leads to a constant acceleration. This law relates to th ...
... 300 years ago Newton summarised all motion by three laws. Newtons 1st law of motion If an object has zero net force acting on it, it will remain at rest, or continue moving with an unchanged velocity. Newtons 2nd law of motion A constant force leads to a constant acceleration. This law relates to th ...
Physics Benchmark Exam #1 2008-2009
... A red ball and a green ball are simultaneously thrown horizontally from the same height. The red ball has an initial speed of 40 meters per second and the green ball has an initial speed of 20 meters per second. Compared to the time it takes the red ball to reach the ground, the time it takes the gr ...
... A red ball and a green ball are simultaneously thrown horizontally from the same height. The red ball has an initial speed of 40 meters per second and the green ball has an initial speed of 20 meters per second. Compared to the time it takes the red ball to reach the ground, the time it takes the gr ...
Chia Teck Chee and Chia Yee Fei The first part of Newton`s First
... acting on the moving body and it is initially in motion. The apparatus set-up for the demonstration is shown in Figure I. In a, the net force acting on the system (M + M + m) is mg. The system is accelerating until the mass M on the left of the pulley rises to position y2. In b, the net force acting ...
... acting on the moving body and it is initially in motion. The apparatus set-up for the demonstration is shown in Figure I. In a, the net force acting on the system (M + M + m) is mg. The system is accelerating until the mass M on the left of the pulley rises to position y2. In b, the net force acting ...
G = 6.67 10 -11 m 3 s -2 kg -1
... We will know analyze the motion of terrestrial falling bodies and orbiting planets in more detail. We will analyze both phenomenon in the same way and show that Newton’s theory explains both. The plan is to combine Newton’s second law with Newton’s law of gravitation to determine the acceleration. ...
... We will know analyze the motion of terrestrial falling bodies and orbiting planets in more detail. We will analyze both phenomenon in the same way and show that Newton’s theory explains both. The plan is to combine Newton’s second law with Newton’s law of gravitation to determine the acceleration. ...
and the Normal Force
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
work - ruthedradan
... (theta) is defined as: -the angle between the force and the displacement vector, which means it is not just any angle, but rather a very specific angle. ...
... (theta) is defined as: -the angle between the force and the displacement vector, which means it is not just any angle, but rather a very specific angle. ...
Review- some Forces, CF, Friction
... • The contact force between the tires and the road is the static friction force (for most normal drivers). It is this force that provides the acceleration required to reduce the speed of your car. • The maximum static friction force is larger than the kinetic friction force. As a result, your are mu ...
... • The contact force between the tires and the road is the static friction force (for most normal drivers). It is this force that provides the acceleration required to reduce the speed of your car. • The maximum static friction force is larger than the kinetic friction force. As a result, your are mu ...
Slides - Nuffield Foundation
... a Vertical R = 1200g the carforces: is skidding? F = m R = 0.8 1200g = 9408 N ...
... a Vertical R = 1200g the carforces: is skidding? F = m R = 0.8 1200g = 9408 N ...
4-3 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accelerate. At the same time, by Newton's third law, the tool is pushing back against you in the opposite ...
... can directly away from the shuttle. Then, with the help of Newton's second and third laws, you will accelerate back towards the shuttle. As you throw the tool, you push against it, causing it to accelerate. At the same time, by Newton's third law, the tool is pushing back against you in the opposite ...
Newton`s Law of Gravitation
... matter for objects that are fairly compact. Over short distances such objects fall at the same rate even in air. ...
... matter for objects that are fairly compact. Over short distances such objects fall at the same rate even in air. ...
From our equations of motion for constant acceleration we have
... direction of the acceleration is the same as the net force. The consequences of this law are very familiar from our everyday experiences. If we slide a book across a table we can do it quite easily and achieve a reasonable acceleration. Try pushing on a whole bookcase and the result is quite differe ...
... direction of the acceleration is the same as the net force. The consequences of this law are very familiar from our everyday experiences. If we slide a book across a table we can do it quite easily and achieve a reasonable acceleration. Try pushing on a whole bookcase and the result is quite differe ...
psaa forces worksheet
... Force can be mathematically described as mass times acceleration. Often in the form of a push or a pull, force is any influence that can cause a massive body to be accelerated (deformed). Sources of forces include gravity, electricity, magnets, or simple muscular effort. 2. What are the effects of f ...
... Force can be mathematically described as mass times acceleration. Often in the form of a push or a pull, force is any influence that can cause a massive body to be accelerated (deformed). Sources of forces include gravity, electricity, magnets, or simple muscular effort. 2. What are the effects of f ...