Chow, Lu-Ping 周綠蘋 - 臺大基因體醫學研究中心
... 3. Identification of protein/peptide molecular weight by mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) 4. Identification of peptide sequence and posttranslational modification (LC-MS/MS) 5. Prediction of unknown protein by mass spectrometry database search with MASCOT software (MALDI-TOF, LC-MS/MS) ...
... 3. Identification of protein/peptide molecular weight by mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) 4. Identification of peptide sequence and posttranslational modification (LC-MS/MS) 5. Prediction of unknown protein by mass spectrometry database search with MASCOT software (MALDI-TOF, LC-MS/MS) ...
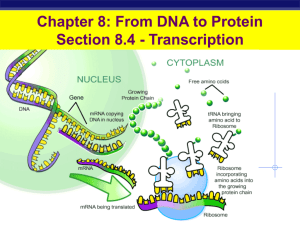
Protein Synthesis
... What controls inherited traits? What controls the production of proteins? Define a gene. Diagram the central dogma of biology. What is the purpose of transcription? What type of RNA is used in transcription? What nitrogen base in RNA is used as a substitution ...
... What controls inherited traits? What controls the production of proteins? Define a gene. Diagram the central dogma of biology. What is the purpose of transcription? What type of RNA is used in transcription? What nitrogen base in RNA is used as a substitution ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
... Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
Biochemistry
... Levels of Protein Structure • Primary protein structure – linear arrangement of amino acids in the polypeptide (like beads on a string) – exact sequence of amino acids determines overall protein structure (analogy: different arrangements of letters spell out words with different meanings) – all ...
... Levels of Protein Structure • Primary protein structure – linear arrangement of amino acids in the polypeptide (like beads on a string) – exact sequence of amino acids determines overall protein structure (analogy: different arrangements of letters spell out words with different meanings) – all ...
1,2basicchemnoaudio
... 3 Main groups of living things 1. Eukarya More complicated than the last two groups Animals and plants are examples of this group 2. Bacteria- some can make you sick 3. Archaea- similar to bacteria, harmless ...
... 3 Main groups of living things 1. Eukarya More complicated than the last two groups Animals and plants are examples of this group 2. Bacteria- some can make you sick 3. Archaea- similar to bacteria, harmless ...
syllabus - Hudson Area Schools
... an individual, and a single gene can influence more than one trait. Before a cell divides, this genetic information must be copied and apportioned evenly into the daughter cells. B4.2 DNA The genetic information encoded in DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. Genes a ...
... an individual, and a single gene can influence more than one trait. Before a cell divides, this genetic information must be copied and apportioned evenly into the daughter cells. B4.2 DNA The genetic information encoded in DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. Genes a ...
bch425 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... the contributors do not in any way claim authorship or ownership of them. The materials are also not to be used for any commercial purpose. ...
... the contributors do not in any way claim authorship or ownership of them. The materials are also not to be used for any commercial purpose. ...
Cells - SchoolRack
... sequence (order) of bases are changed because it has not been copied exactly. For example, the sequence of nitrogen bases provides instruction for the abnormal protein that causes the sickle-cell anemia. ...
... sequence (order) of bases are changed because it has not been copied exactly. For example, the sequence of nitrogen bases provides instruction for the abnormal protein that causes the sickle-cell anemia. ...
effective: september 2003 curriculum guidelines
... There will be one midterm in week 7. The final examination will cover the entire course. If the student achieves a higher mark on the final than on the mid-term, the mid-term grade will be raised to equal that achieved on the ...
... There will be one midterm in week 7. The final examination will cover the entire course. If the student achieves a higher mark on the final than on the mid-term, the mid-term grade will be raised to equal that achieved on the ...
AP Biology Unit 1- The Chemistry of Life
... (b) Predict how the normal function of the plasma membrane would be altered if all phospholipids were saturated, resulting in fatty acid tails without kinks or bends. Explain the effect this would have on plants located in very cold regions. (c) Proteins are an important component of the cell membra ...
... (b) Predict how the normal function of the plasma membrane would be altered if all phospholipids were saturated, resulting in fatty acid tails without kinks or bends. Explain the effect this would have on plants located in very cold regions. (c) Proteins are an important component of the cell membra ...
Amino acids and prot..
... teeth, cartilage, tendons, skin and blood vessels. • Collagen may be present as gel e.g. in extracellular matrix or in vitreous humor of the eye. • Collagens are the most important protein in mammals. They form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most c ...
... teeth, cartilage, tendons, skin and blood vessels. • Collagen may be present as gel e.g. in extracellular matrix or in vitreous humor of the eye. • Collagens are the most important protein in mammals. They form about 30% of total body proteins. • There are more than 20 types of collagens, the most c ...
Transcription/translation
... Also area where the “Gene” sequence begins. Operator – area of DNA that turns gene “on” or “off”. It’s the switch ...
... Also area where the “Gene” sequence begins. Operator – area of DNA that turns gene “on” or “off”. It’s the switch ...
Chemistry of Life
... Chemical reactions also depend on the pH of the environment within the organism. ...
... Chemical reactions also depend on the pH of the environment within the organism. ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Lakewood City Schools
... Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
... Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
File
... 43. What type of sensory information foes the Pacinian Corpuscle detect? 44. What type of sensory information does the free nerve endings detect? 45. What sensory information does the Meissner’s corpuscle detect? 46. What are the seven bones that constitute the orbit? ...
... 43. What type of sensory information foes the Pacinian Corpuscle detect? 44. What type of sensory information does the free nerve endings detect? 45. What sensory information does the Meissner’s corpuscle detect? 46. What are the seven bones that constitute the orbit? ...
13 Protein Synthesis Making a Sentence Activity Key
... 3. The m-RNA leaves the nucleus with the transcribed code and goes to the cytoplasm (the rest of the classroom) to find the ribosome (the student desks). (1 point) 4. The m-RNA and the ribosome tell the t-RNA which anti-codons are needed (cards around the room). The ribosome writes the anti-codon in ...
... 3. The m-RNA leaves the nucleus with the transcribed code and goes to the cytoplasm (the rest of the classroom) to find the ribosome (the student desks). (1 point) 4. The m-RNA and the ribosome tell the t-RNA which anti-codons are needed (cards around the room). The ribosome writes the anti-codon in ...
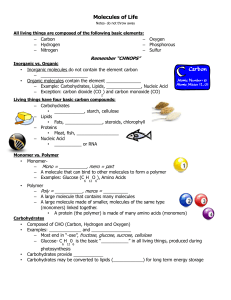
Molecules of Life
... Some types of proteins can contain other elements like S, P, Fe, and Cu (Sulfur, Phosphorous, Iron, Copper) Made of small units (monomers) called ____________ __________. Examples: – Proteins make up muscle, __________ and hair – Hemoglobin (______________) is a protein that carries oxygenated blood ...
... Some types of proteins can contain other elements like S, P, Fe, and Cu (Sulfur, Phosphorous, Iron, Copper) Made of small units (monomers) called ____________ __________. Examples: – Proteins make up muscle, __________ and hair – Hemoglobin (______________) is a protein that carries oxygenated blood ...
BIOL 246 - Marine Biology - American University of Beirut
... be on roles in which nucleic acids are not mere vessels of protein coding sequence, but rather in which their structures function in regulation and catalysis. Experimental methods will be discussed as appropriate, but not unduly emphasized. Each week will consist of at least one lecture and one grou ...
... be on roles in which nucleic acids are not mere vessels of protein coding sequence, but rather in which their structures function in regulation and catalysis. Experimental methods will be discussed as appropriate, but not unduly emphasized. Each week will consist of at least one lecture and one grou ...
Lab Techniques for Systems Biology
... •How are we going to get there? – Use all scientific tools at hand, including complete sequenced genomes ...
... •How are we going to get there? – Use all scientific tools at hand, including complete sequenced genomes ...
Biology Standards Checklist
... e. Sexual selection 1. Mechanisms: f. Evolution is the consequence of four interaction types 1. Mechanisms: g. History of life on Earth: fossil record, common ancestors, cladograms ...
... e. Sexual selection 1. Mechanisms: f. Evolution is the consequence of four interaction types 1. Mechanisms: g. History of life on Earth: fossil record, common ancestors, cladograms ...
(EXAMPLES: DNA and RNA) NUCLEIC ACIDS contain atoms of
... DNA and RNA have more structural & functional differences that will be discussed in later units. How many nucleotides are joined together to form this portion of a DNA molecule?_______________________ What is the cellular process (reaction) that combines monomers into polymers?______________________ ...
... DNA and RNA have more structural & functional differences that will be discussed in later units. How many nucleotides are joined together to form this portion of a DNA molecule?_______________________ What is the cellular process (reaction) that combines monomers into polymers?______________________ ...
HW and review worksheet
... blocks (Fig 5.15); dehydration synthesis forms a peptide bond between two adjacent amino acids; many amino acids linked together is called a polypeptide. Is a polypeptide the same as a protein? Know the general structure of amino acids and how to recognize a peptide bond 2. Amino acids differ from e ...
... blocks (Fig 5.15); dehydration synthesis forms a peptide bond between two adjacent amino acids; many amino acids linked together is called a polypeptide. Is a polypeptide the same as a protein? Know the general structure of amino acids and how to recognize a peptide bond 2. Amino acids differ from e ...
Introduction to Cells
... reaction that links monomers together via covalent bonding. The chemical mechanism cells use for making polymers is similar for all macromolecules. ...
... reaction that links monomers together via covalent bonding. The chemical mechanism cells use for making polymers is similar for all macromolecules. ...