HW13_Answers
... 1) List the three main components of a disk galaxy and describe the difference between the stars that are present in the components. The three main components are the disk, the bulge and the halo. The disk has stars, gas and dust. It is the location where star formation is occurring. Because of this ...
... 1) List the three main components of a disk galaxy and describe the difference between the stars that are present in the components. The three main components are the disk, the bulge and the halo. The disk has stars, gas and dust. It is the location where star formation is occurring. Because of this ...
Slide 1
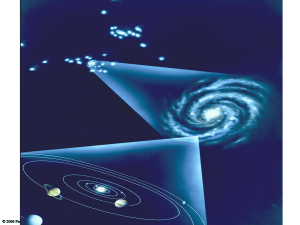
... Big Bang…explanation of formation of galaxies • 15 billion years ago mass of hydrogen ...
... Big Bang…explanation of formation of galaxies • 15 billion years ago mass of hydrogen ...
Lec12
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
BYOG: Build Your Own Galaxy
... The purpose of this labette is to illustrate the major features of spiral galaxies. Those features are not accidents – they are the result of the way the galaxy was formed, and they help explain how the galaxy behaves. First, read the following description of galaxies (adapted from InfoPlease): A ty ...
... The purpose of this labette is to illustrate the major features of spiral galaxies. Those features are not accidents – they are the result of the way the galaxy was formed, and they help explain how the galaxy behaves. First, read the following description of galaxies (adapted from InfoPlease): A ty ...
2. Universe and galaxies
... • I. have spiral arms that wind outward from the center. • II. consist of bright stars, planets, moons, dust, and gas. ...
... • I. have spiral arms that wind outward from the center. • II. consist of bright stars, planets, moons, dust, and gas. ...
Ay 1 – Homework #6
... C. They are mostly dark-matter dominated. D. Over-densities created by spiral density waves (i.e. spiral arms) are necessary to create sites of star formation. 5. What is the physical significance of the Tully-Fisher relation for spiral galaxies? A. It implies a link between the dark matter halos of ...
... C. They are mostly dark-matter dominated. D. Over-densities created by spiral density waves (i.e. spiral arms) are necessary to create sites of star formation. 5. What is the physical significance of the Tully-Fisher relation for spiral galaxies? A. It implies a link between the dark matter halos of ...
The Universe – Powerpoint
... Galaxies that don’t fit into the spiral or elliptical galaxies are considered irregular galaxies. They have a wide variety of shape and characteristics, and are frequently the result of when two or more galaxies collide. ...
... Galaxies that don’t fit into the spiral or elliptical galaxies are considered irregular galaxies. They have a wide variety of shape and characteristics, and are frequently the result of when two or more galaxies collide. ...
Galaxies: 33.1
... observations. This picture was taken with light from the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
... observations. This picture was taken with light from the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. ...
CH 15 SEC 4 STAR SYSTEMS AND GALAXIES
... KEY- EACH GALAXY CONTAINS BILLIONS OF STARS AND THE LARGER ONES TRILLIONS OF STARS. KEY- SCIENTIST ARE DISCOVERING MORE EARTHLIKE PLANETS ALL THE TIME. ...
... KEY- EACH GALAXY CONTAINS BILLIONS OF STARS AND THE LARGER ONES TRILLIONS OF STARS. KEY- SCIENTIST ARE DISCOVERING MORE EARTHLIKE PLANETS ALL THE TIME. ...
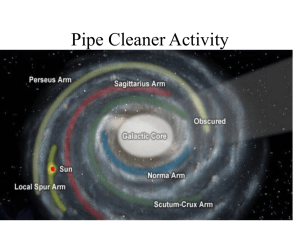
20.2 The Milky Way and Other Galaxies
... -RECOGNIZE THAT AT THE CENTER OF THE MILKY WAY THERE IS A BULGE STARS, FROM WHICH ARE SPIRAL ARMS OF GAS, DUST AND MOST OF THE YOUNG STARS. -RECOGNIZE THAT THE SOLAR SYSTEM IS PART OF THE MILKY WAY GALAXY. K -DEMONSTRATE THAT HUBBLE’S LAW THAT GALAXIES THAT ARE FARTHER AWAY HAVE A GREATER RED SHIFT, ...
... -RECOGNIZE THAT AT THE CENTER OF THE MILKY WAY THERE IS A BULGE STARS, FROM WHICH ARE SPIRAL ARMS OF GAS, DUST AND MOST OF THE YOUNG STARS. -RECOGNIZE THAT THE SOLAR SYSTEM IS PART OF THE MILKY WAY GALAXY. K -DEMONSTRATE THAT HUBBLE’S LAW THAT GALAXIES THAT ARE FARTHER AWAY HAVE A GREATER RED SHIFT, ...
Galaxies - Wallkill Valley Regional High School
... - A spherical “halo” of stars, including many in globular clusters - A super-massive black hole at the center of the central bulge ...
... - A spherical “halo” of stars, including many in globular clusters - A super-massive black hole at the center of the central bulge ...
Star Systems and Galaxies
... • A galaxy is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters,dust, and gas bound together by gravity • The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: • Spiral Galaxies • Elliptical Galaxies • Irregular Galaxies ...
... • A galaxy is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters,dust, and gas bound together by gravity • The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: • Spiral Galaxies • Elliptical Galaxies • Irregular Galaxies ...
Where is the Solar System in the Universe?
... • These are medium sized galaxies with very old stars. ...
... • These are medium sized galaxies with very old stars. ...
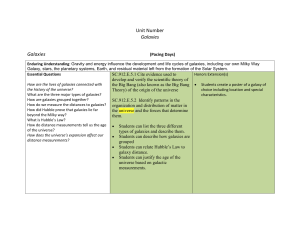
galaxies
... Enduring Understanding: Gravity and energy influence the development and life cycles of galaxies, including our own Milky Way Galaxy, stars, the planetary systems, Earth, and residual material left from the formation of the Solar System. Essential Questions Honors Extension(s) SC.912.E.5.1 Cite evid ...
... Enduring Understanding: Gravity and energy influence the development and life cycles of galaxies, including our own Milky Way Galaxy, stars, the planetary systems, Earth, and residual material left from the formation of the Solar System. Essential Questions Honors Extension(s) SC.912.E.5.1 Cite evid ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
... galaxies are outlying members. Here galaxies are so numerous that they seem to outnumber the visible stars. Estimates of the total number are between 1,200 and 2,000 and the average distance is 53 million light years (a light year is about 10 trillion kilometres). As with virtually all clusters of g ...
... galaxies are outlying members. Here galaxies are so numerous that they seem to outnumber the visible stars. Estimates of the total number are between 1,200 and 2,000 and the average distance is 53 million light years (a light year is about 10 trillion kilometres). As with virtually all clusters of g ...
Page 25 - Types of Galaxies
... • They tend to be smaller objects that are without definite shape and tend to have very hot newer stars mixed in with lots of gas and dust. • These galaxies often have active regions of star formation. Sometimes the irregular shape of these galaxies results from interactions or collisions between ga ...
... • They tend to be smaller objects that are without definite shape and tend to have very hot newer stars mixed in with lots of gas and dust. • These galaxies often have active regions of star formation. Sometimes the irregular shape of these galaxies results from interactions or collisions between ga ...
Section 4 Galaxies and the Universe
... 1. Steady state theory—universe has always existed just as it is now 2. Oscillating model—universe expands and contracts repeatedly over time D. Universe is expanding 1. Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object a. Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end o ...
... 1. Steady state theory—universe has always existed just as it is now 2. Oscillating model—universe expands and contracts repeatedly over time D. Universe is expanding 1. Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object a. Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end o ...
633 infrared, ultraviolet, x-ray, and gamma
... Lower-luminosity active galaxies also exist. Astronomers suspect they may be weaker versions of quasars or may be powered by star formation rather than supermassive black holes. Active galaxies are the subject of much debate among astronomers. The study of these distant objects is one of astronomy’s ...
... Lower-luminosity active galaxies also exist. Astronomers suspect they may be weaker versions of quasars or may be powered by star formation rather than supermassive black holes. Active galaxies are the subject of much debate among astronomers. The study of these distant objects is one of astronomy’s ...
Star Systems and Galaxies
... Galaxies • A Radio Telescope is a device used to detect long radio waves coming from objects in space. • A galaxy is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters,dust, and gas bound together by gravity • The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: • Spiral Gal ...
... Galaxies • A Radio Telescope is a device used to detect long radio waves coming from objects in space. • A galaxy is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters,dust, and gas bound together by gravity • The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: • Spiral Gal ...
Irregular Galaxies
... 3) Irregular Galaxies- galaxies that don’t fit into the other classes. a) Many of these galaxies may have their shape distorted by neighboring galaxies’ gravity. ...
... 3) Irregular Galaxies- galaxies that don’t fit into the other classes. a) Many of these galaxies may have their shape distorted by neighboring galaxies’ gravity. ...
The Universe - greenslime.info
... of galaxies are known to exist galaxies can contain from hundreds of thousands to one trillion stars 3 major types ...
... of galaxies are known to exist galaxies can contain from hundreds of thousands to one trillion stars 3 major types ...
File - The World of Astronomy
... million to over a trillion stars and can range in size from a few thousand to several hundred thousand light-years across. There are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the universe. Galaxies come in many different sizes, shapes and brightnesses and, like stars, are found alone, in pairs, or in larg ...
... million to over a trillion stars and can range in size from a few thousand to several hundred thousand light-years across. There are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the universe. Galaxies come in many different sizes, shapes and brightnesses and, like stars, are found alone, in pairs, or in larg ...
Galaxies ppt
... • Speed of light is 186,000 miles per second. • 5,878,499,810,000 miles (5.87849981 x 1012 miles) • It takes the sunlight 9 minutes to reach Earth. – (distance of 93 million miles) ...
... • Speed of light is 186,000 miles per second. • 5,878,499,810,000 miles (5.87849981 x 1012 miles) • It takes the sunlight 9 minutes to reach Earth. – (distance of 93 million miles) ...
Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies

The Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies is a catalog of peculiar galaxies produced by Halton Arp. A total of 338 galaxies are presented in the atlas, which was originally published in 1966 by the California Institute of Technology.The primary goal of the catalog was to present photographs of examples of the different kinds of peculiar structures found among nearby galaxies. Arp realized that the reason why galaxies formed into spiral or elliptical shapes was not well understood. He perceived peculiar galaxies as small ""experiments"" that astronomers could use to understand the physical processes that distort spiral or elliptical galaxies. With this atlas, astronomers had a sample of peculiar galaxies that they could study in more detail. The atlas does not present a complete overview of every peculiar galaxy in the sky but instead provides examples of the different phenomena as observed in nearby galaxies.Because little was known at the time of publication about the physical processes that caused the different shapes, the galaxies in the atlas are sorted based on their appearance. Objects 1–101 are individual peculiar spiral galaxies or spiral galaxies that apparently have small companions. Objects 102–145 are elliptical and elliptical-like galaxies. Individual or groups of galaxies with neither elliptical nor spiral shapes are listed as objects 146–268. Objects 269–327 are double galaxies. Finally, objects that simply do not fit into any of the above categories are listed as objects 332–338. Most objects are best known by their other designations, but a few galaxies are best known by their Arp numbers (such as Arp 220).Today, the physical processes that lead to the peculiarities seen in the Arp atlas are now well understood. A large number of the objects are interacting galaxies, including M51 (Arp 85), Arp 220, and the Antennae Galaxies (NGC 4038/NGC 4039, or Arp 244). A few of the galaxies are simply dwarf galaxies that do not have enough mass to produce enough gravity to allow the galaxies to form any cohesive structure. NGC 1569 (Arp 210) is an example of one of the dwarf galaxies in the atlas. A few other galaxies are radio galaxies. These objects contain active galactic nuclei that produce powerful jets of gas called radio jets. The atlas includes the nearby radio galaxies M87 (Arp 152) and Centaurus A (Arp 153).