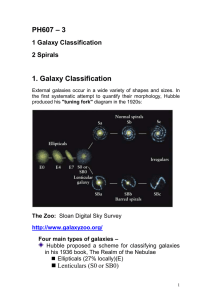
galaxies
... 5. (2 pts.) Why can’t galaxies evolve from elliptical to spiral? Why can’t they evolve from spiral to elliptical? ...
... 5. (2 pts.) Why can’t galaxies evolve from elliptical to spiral? Why can’t they evolve from spiral to elliptical? ...
PH607lec12-3gal1
... A large fraction of disk galaxies have bars: narrow linear structures crossing the face of the galaxy. In barred S0 galaxies the bar is often the only structure visible in the disc. In types SBa and later the bar often connects to a spiral pattern extending to larger radii (e.g. NGC 1300). Viewed fa ...
... A large fraction of disk galaxies have bars: narrow linear structures crossing the face of the galaxy. In barred S0 galaxies the bar is often the only structure visible in the disc. In types SBa and later the bar often connects to a spiral pattern extending to larger radii (e.g. NGC 1300). Viewed fa ...
Galaxies
... Newton's law of gravity, the rotational velocity would steadily decrease for stars further away from the galactic center. Analogously, inner planets within the Solar System travel more quickly about the Sun than do the outer planets (e.g. the Earth travels around the sun at about 100,000 km/hr while ...
... Newton's law of gravity, the rotational velocity would steadily decrease for stars further away from the galactic center. Analogously, inner planets within the Solar System travel more quickly about the Sun than do the outer planets (e.g. the Earth travels around the sun at about 100,000 km/hr while ...
Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies
... Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and show no evidence of ongoing star formation. Many do, however, have large clouds of hot gas, extending far beyond the visible boundaries of the galaxy. ...
... Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and show no evidence of ongoing star formation. Many do, however, have large clouds of hot gas, extending far beyond the visible boundaries of the galaxy. ...
AY1 Homework for Quiz 3: Spring 2017
... ____ Mass transfer from a close companion onto a white dwarf ____ The collapse of a white dwarf whose mass exceeds 1.4MSun ____ The iron core of a massive star reaches the Chandrasekar limit ...
... ____ Mass transfer from a close companion onto a white dwarf ____ The collapse of a white dwarf whose mass exceeds 1.4MSun ____ The iron core of a massive star reaches the Chandrasekar limit ...
Astronomy Galaxies Quiz – Study Guide You will be given a set of
... 13. Describe two reasons why galaxies (even the same types) look different. 14. Where is the center of the universe? 15. How does the Doppler Shift relate to the expanding universe? 16. Old galaxies are ______________ (what color?) and contain (a little or a lot) of dust. 17. Compare open and globul ...
... 13. Describe two reasons why galaxies (even the same types) look different. 14. Where is the center of the universe? 15. How does the Doppler Shift relate to the expanding universe? 16. Old galaxies are ______________ (what color?) and contain (a little or a lot) of dust. 17. Compare open and globul ...
Dark Matter
... we are made of only comprises about 5% (the remaining 70% of the universe is called “Dark Energy”). ...
... we are made of only comprises about 5% (the remaining 70% of the universe is called “Dark Energy”). ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
Galaxies Quiz – Study Guide KEY You will be given a set of images
... a. Where do you find NEW stars in spiral galaxies? _______ARMS___ b. Which type of galaxy has the most NEW stars? ___IRREGULAR____ c. Which type of galaxy has the most OLD stars? __ELLIPTICAL__ d. Which type of galaxy has the most dust and gas? ___IRREGULAR__ e. Which type of galaxy is the largest ( ...
... a. Where do you find NEW stars in spiral galaxies? _______ARMS___ b. Which type of galaxy has the most NEW stars? ___IRREGULAR____ c. Which type of galaxy has the most OLD stars? __ELLIPTICAL__ d. Which type of galaxy has the most dust and gas? ___IRREGULAR__ e. Which type of galaxy is the largest ( ...
Galaxies - science9atsouthcarletonhs
... – Lenticular galaxies are disc galaxies (like spiral galaxies) which have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing star formation.[2] As a result, they consist mainly of aging stars (like elliptical galaxies). The dust in most lenticular galaxies is ge ...
... – Lenticular galaxies are disc galaxies (like spiral galaxies) which have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing star formation.[2] As a result, they consist mainly of aging stars (like elliptical galaxies). The dust in most lenticular galaxies is ge ...
Rich and Poor Galaxy Clusters
... • The Local Supercluster is heading toward a region of space known as the Great Attractor, where there are a large number of massive superclusters • There may be super-superclusters! ...
... • The Local Supercluster is heading toward a region of space known as the Great Attractor, where there are a large number of massive superclusters • There may be super-superclusters! ...
Universe, Galaxies, Solar System
... are made of stars and dust. • Spiral Galaxies have a central bulge, a disk, a halo, and some may have a “bar” of stars passing through the center. These types of galaxies are called barred spirals. • Spiral galaxies are huge, and contain large amounts of gas and dust. • Spiral galaxies have both you ...
... are made of stars and dust. • Spiral Galaxies have a central bulge, a disk, a halo, and some may have a “bar” of stars passing through the center. These types of galaxies are called barred spirals. • Spiral galaxies are huge, and contain large amounts of gas and dust. • Spiral galaxies have both you ...
Welcome to the Milky Way Galaxy: Student Notes
... • A galaxy is a “system of _________________________, together with dust and gas, held together by ______________________ attraction.” • There are 3 types of galaxies: Elliptical, Spiral, and Irregular • Elliptical galaxies are ______________ __________________ • Spiral galaxies have a spherical sha ...
... • A galaxy is a “system of _________________________, together with dust and gas, held together by ______________________ attraction.” • There are 3 types of galaxies: Elliptical, Spiral, and Irregular • Elliptical galaxies are ______________ __________________ • Spiral galaxies have a spherical sha ...
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within Comparison to
... • SBa galaxies have a bright bulge and bar with faint, tightly wound spiral arms. • SBb galaxies have fainter bulges and looser spiral arms. • SBc galaxies have faint bulges, and loose spiral arms. ...
... • SBa galaxies have a bright bulge and bar with faint, tightly wound spiral arms. • SBb galaxies have fainter bulges and looser spiral arms. • SBc galaxies have faint bulges, and loose spiral arms. ...
PX269 Galaxies - University of Warwick
... the Milky Way, nebulous stars, but especially about four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which, unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name MEDICEAN STARS ...
... the Milky Way, nebulous stars, but especially about four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which, unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name MEDICEAN STARS ...
Section 28.2 - CPO Science
... Astronomers classify galaxies according to their shape. 1. Spiral galaxies consist of a central, dense area surrounded by spiraling arms. 2. Barred spiral galaxies have a bar-shaped structure in the center. 3. Elliptical galaxies look like the central portion of a spiral galaxy without the arms. 4. ...
... Astronomers classify galaxies according to their shape. 1. Spiral galaxies consist of a central, dense area surrounded by spiraling arms. 2. Barred spiral galaxies have a bar-shaped structure in the center. 3. Elliptical galaxies look like the central portion of a spiral galaxy without the arms. 4. ...
File - 5th Grade Science Almost done!!!!!!!!!
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
UniverseofGalaxies
... divided into SBa, SBb, SBc, with similar characteristics to regular spirals, except for a centrallyoriented bar ...
... divided into SBa, SBb, SBc, with similar characteristics to regular spirals, except for a centrallyoriented bar ...
PX269 Galaxies - University of Warwick
... about the face of the Moon, countless fixed stars, the Milky Way, nebulous stars, but especially about four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which, unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to ...
... about the face of the Moon, countless fixed stars, the Milky Way, nebulous stars, but especially about four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which, unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to ...
1 - WordPress.com
... A galaxy is an enormous collection of gas, dust and billions of stars held together by gravity. 3. List the three basic shapes of galaxies. Spiral, Elliptical (like a football or cigar), Irregular 4. What characteristics do all galaxies share? The have millions of stars, dust and gas – all held toge ...
... A galaxy is an enormous collection of gas, dust and billions of stars held together by gravity. 3. List the three basic shapes of galaxies. Spiral, Elliptical (like a football or cigar), Irregular 4. What characteristics do all galaxies share? The have millions of stars, dust and gas – all held toge ...
Organizing the cosmos
... There is still uncertainty on exactly how the universe and our solar system formed. There are many theories but no one knows for sure. By studying distant galaxies astronomers may one day determine how the universe was ...
... There is still uncertainty on exactly how the universe and our solar system formed. There are many theories but no one knows for sure. By studying distant galaxies astronomers may one day determine how the universe was ...
Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies

The Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies is a catalog of peculiar galaxies produced by Halton Arp. A total of 338 galaxies are presented in the atlas, which was originally published in 1966 by the California Institute of Technology.The primary goal of the catalog was to present photographs of examples of the different kinds of peculiar structures found among nearby galaxies. Arp realized that the reason why galaxies formed into spiral or elliptical shapes was not well understood. He perceived peculiar galaxies as small ""experiments"" that astronomers could use to understand the physical processes that distort spiral or elliptical galaxies. With this atlas, astronomers had a sample of peculiar galaxies that they could study in more detail. The atlas does not present a complete overview of every peculiar galaxy in the sky but instead provides examples of the different phenomena as observed in nearby galaxies.Because little was known at the time of publication about the physical processes that caused the different shapes, the galaxies in the atlas are sorted based on their appearance. Objects 1–101 are individual peculiar spiral galaxies or spiral galaxies that apparently have small companions. Objects 102–145 are elliptical and elliptical-like galaxies. Individual or groups of galaxies with neither elliptical nor spiral shapes are listed as objects 146–268. Objects 269–327 are double galaxies. Finally, objects that simply do not fit into any of the above categories are listed as objects 332–338. Most objects are best known by their other designations, but a few galaxies are best known by their Arp numbers (such as Arp 220).Today, the physical processes that lead to the peculiarities seen in the Arp atlas are now well understood. A large number of the objects are interacting galaxies, including M51 (Arp 85), Arp 220, and the Antennae Galaxies (NGC 4038/NGC 4039, or Arp 244). A few of the galaxies are simply dwarf galaxies that do not have enough mass to produce enough gravity to allow the galaxies to form any cohesive structure. NGC 1569 (Arp 210) is an example of one of the dwarf galaxies in the atlas. A few other galaxies are radio galaxies. These objects contain active galactic nuclei that produce powerful jets of gas called radio jets. The atlas includes the nearby radio galaxies M87 (Arp 152) and Centaurus A (Arp 153).