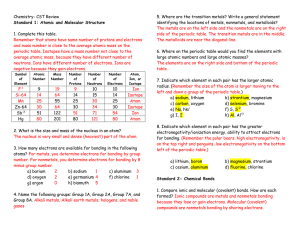
CP Chemistry Practice Mid
... 25. Water has a specific heat of 4.184 J/g°C while glass (Pyrex) has a specific heat of 0.780 J/g°C. If 10.0 J of heat is added to 1.00 g of each of these, which will experience the larger increase of temperature? a. glass b. water c. They both will experience the same change in temperature since on ...
... 25. Water has a specific heat of 4.184 J/g°C while glass (Pyrex) has a specific heat of 0.780 J/g°C. If 10.0 J of heat is added to 1.00 g of each of these, which will experience the larger increase of temperature? a. glass b. water c. They both will experience the same change in temperature since on ...
Chapter 3 Part 2 Review
... Mass to mass stoichiometric relationships: Ex 1. The food we eat is degraded in our bodies to provide energy for growth and function. A general equation for this very complex process is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O If 856 g of C6H12O6 is consumed by a person over a certain period, what is the mass ...
... Mass to mass stoichiometric relationships: Ex 1. The food we eat is degraded in our bodies to provide energy for growth and function. A general equation for this very complex process is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O If 856 g of C6H12O6 is consumed by a person over a certain period, what is the mass ...
Ductility-the ability to be stretched into wires
... return to its original form after being stretched (__.P) ...
... return to its original form after being stretched (__.P) ...
physics/0010052 PDF
... Pay attention that if P=const and A is the work of expansion then dQ and dA=PdV are exact differentials. Let's consider heat exchange, one introduces the quantity of heat ∆Q in the system (∆V=0): ∆Q=∆U. Now let's suppose ∆V>0. Let's find out, is it necessary to write ∆Q=∆U-P∆V or ∆Q=∆U+P∆V. It is ne ...
... Pay attention that if P=const and A is the work of expansion then dQ and dA=PdV are exact differentials. Let's consider heat exchange, one introduces the quantity of heat ∆Q in the system (∆V=0): ∆Q=∆U. Now let's suppose ∆V>0. Let's find out, is it necessary to write ∆Q=∆U-P∆V or ∆Q=∆U+P∆V. It is ne ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... temperature affect the gas pressure? Gas pressure increases when the amount of gas and temperature increases but the volume is decreased. For Q’s #9-14, name the gas law and show all your work. 7. The pressure on 2.00 L of anesthetic gas changes from 100 kPa to 40 kPa. What will be the new volume if ...
... temperature affect the gas pressure? Gas pressure increases when the amount of gas and temperature increases but the volume is decreased. For Q’s #9-14, name the gas law and show all your work. 7. The pressure on 2.00 L of anesthetic gas changes from 100 kPa to 40 kPa. What will be the new volume if ...
B. The Physical Properties of Matter
... space. (Matter is what makes up everything other than energy.) Hence, chemistry may be better described as the science concerned with the properties, composition, and behaviour of matter. ...
... space. (Matter is what makes up everything other than energy.) Hence, chemistry may be better described as the science concerned with the properties, composition, and behaviour of matter. ...
The Physical Properties And Physical Changes of Substances
... space. (Matter is what makes up everything other than energy.) Hence, chemistry may be better described as the science concerned with the properties, composition, and behaviour of matter. ...
... space. (Matter is what makes up everything other than energy.) Hence, chemistry may be better described as the science concerned with the properties, composition, and behaviour of matter. ...
Chapter 2 Power Point
... A: If the composition of a material is fixed, the material is a substance. If the composition of the substance may vary, the material is a mixture. ...
... A: If the composition of a material is fixed, the material is a substance. If the composition of the substance may vary, the material is a mixture. ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... As = Adessolved In the case that the gas phase is a complex mixture of species (for example, MoO3(s) Æ Mo3O9(g), Mo4O12(g), Mo5O15(g)) it is necessary to measure the individual gaseous components, which is commonly very difficult. Static Methods for the Determination of Vapor Pressures i) Applicatio ...
... As = Adessolved In the case that the gas phase is a complex mixture of species (for example, MoO3(s) Æ Mo3O9(g), Mo4O12(g), Mo5O15(g)) it is necessary to measure the individual gaseous components, which is commonly very difficult. Static Methods for the Determination of Vapor Pressures i) Applicatio ...
WELCOME TO AP CHEMISTRY
... him/her a favor because the ability to explain a concept to someone else is a measure of that person’s true understanding. Use the text book as your primary resource. Please memorize nomenclature rules for ionic compounds, covalent compounds, as well as for acids and bases. You will be expected to k ...
... him/her a favor because the ability to explain a concept to someone else is a measure of that person’s true understanding. Use the text book as your primary resource. Please memorize nomenclature rules for ionic compounds, covalent compounds, as well as for acids and bases. You will be expected to k ...
2014-15 FINAL REVIEW Nomenclature: Chemical Name Chemical
... nitrate. What mass of magnesium hydroxide is formed? What is/are the concentration of any ions remaining in the solution? Heat of Reaction: 1. Hg has a specific heat of 0.139 J/goC. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of a 22.80 g sample from 16.1oC to 32.5oC? 2. Some water is heated ...
... nitrate. What mass of magnesium hydroxide is formed? What is/are the concentration of any ions remaining in the solution? Heat of Reaction: 1. Hg has a specific heat of 0.139 J/goC. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of a 22.80 g sample from 16.1oC to 32.5oC? 2. Some water is heated ...
Unit 1: Matter and Energy HW Packet
... Part 8: Decide whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. 1. __________ Both elements and compounds are pure substances. 2. __________ A heterogeneous substance has at least two pure substances in it. 3. __________ Pure substances have variable composition. 4. __________ Compounds have vari ...
... Part 8: Decide whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. 1. __________ Both elements and compounds are pure substances. 2. __________ A heterogeneous substance has at least two pure substances in it. 3. __________ Pure substances have variable composition. 4. __________ Compounds have vari ...
How to Make a Collage
... of general chemistry prior to taking the course, (4) stay after school for help where your knowledge base is weak or the subject area is difficult, (5) minimize absences (whether they are an approved school activity, vacation or illness) as they will greatly affect your work load and understanding, ...
... of general chemistry prior to taking the course, (4) stay after school for help where your knowledge base is weak or the subject area is difficult, (5) minimize absences (whether they are an approved school activity, vacation or illness) as they will greatly affect your work load and understanding, ...
國立嘉義大學九十二學年度
... 3.Calculate the density in g/L of chlorine gas at STP (A) 2.13 × 10-2 g/L (B) 46.9 g/L (C) 1.58 g/L (D) 3.16 g/L (E) 0.316 kg/L 4.Which statement is false? (A) The average kinetic energies of molecules from samples of different "ideal" gases is the same at the same temperature. (B) The molecules of ...
... 3.Calculate the density in g/L of chlorine gas at STP (A) 2.13 × 10-2 g/L (B) 46.9 g/L (C) 1.58 g/L (D) 3.16 g/L (E) 0.316 kg/L 4.Which statement is false? (A) The average kinetic energies of molecules from samples of different "ideal" gases is the same at the same temperature. (B) The molecules of ...
matter and - cloudfront.net
... INTENSIVE physical property Does NOT depend on the amount of material present (e.g. color, melting point, freezing point, density) ...
... INTENSIVE physical property Does NOT depend on the amount of material present (e.g. color, melting point, freezing point, density) ...
Haley CHM2045 Final Review
... 5. Based on the diagram, classify each as a physical or chemical change. ...
... 5. Based on the diagram, classify each as a physical or chemical change. ...
Chapter 2 - Cloudfront.net
... Gas: Term used for substances that exists in the gaseous state at room temperature. Vapor: Term used for the gaseous state of a substance that is usually a liquid or a solid at room ...
... Gas: Term used for substances that exists in the gaseous state at room temperature. Vapor: Term used for the gaseous state of a substance that is usually a liquid or a solid at room ...
Monitoring Reactions by TLC The fastest and most commonly used
... (3) TLC solvents - A binary mixture of miscible solvents usually works best. TLC solvents are conveniently made up in the TLC chamber just before analysis from solvents kept in dropping bottles. Common TLC solvent combinations are: • For neutral organic molecules: hexanes (bp 68-70 °C) as the non-po ...
... (3) TLC solvents - A binary mixture of miscible solvents usually works best. TLC solvents are conveniently made up in the TLC chamber just before analysis from solvents kept in dropping bottles. Common TLC solvent combinations are: • For neutral organic molecules: hexanes (bp 68-70 °C) as the non-po ...
I Examen I Trim Science
... Applied: focuses on developing these applications. Ex. Shampoo, Tosty food, Panadol. ...
... Applied: focuses on developing these applications. Ex. Shampoo, Tosty food, Panadol. ...
Gas chromatography

Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture (the relative amounts of such components can also be determined). In some situations, GC may help in identifying a compound. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture.In gas chromatography, the mobile phase (or ""moving phase"") is a carrier gas, usually an inert gas such as helium or an unreactive gas such as nitrogen. The stationary phase is a microscopic layer of liquid or polymer on an inert solid support, inside a piece of glass or metal tubing called a column (a homage to the fractionating column used in distillation). The instrument used to perform gas chromatography is called a gas chromatograph (or ""aerograph"", ""gas separator"").The gaseous compounds being analyzed interact with the walls of the column, which is coated with a stationary phase. This causes each compound to elute at a different time, known as the retention time of the compound. The comparison of retention times is what gives GC its analytical usefulness.Gas chromatography is in principle similar to column chromatography (as well as other forms of chromatography, such as HPLC, TLC), but has several notable differences. First, the process of separating the compounds in a mixture is carried out between a liquid stationary phase and a gas mobile phase, whereas in column chromatography the stationary phase is a solid and the mobile phase is a liquid. (Hence the full name of the procedure is ""Gas–liquid chromatography"", referring to the mobile and stationary phases, respectively.) Second, the column through which the gas phase passes is located in an oven where the temperature of the gas can be controlled, whereas column chromatography (typically) has no such temperature control. Finally, the concentration of a compound in the gas phase is solely a function of the vapor pressure of the gas.Gas chromatography is also similar to fractional distillation, since both processes separate the components of a mixture primarily based on boiling point (or vapor pressure) differences. However, fractional distillation is typically used to separate components of a mixture on a large scale, whereas GC can be used on a much smaller scale (i.e. microscale).Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Strictly speaking, GLPC is the most correct terminology, and is thus preferred by many authors.