Force and Inertia
... • A) a steadily decreasing upward force from the initial toss. • B) an increasing downward force of gravity and a steadily decreasing upward force. • C) an almost constant downward force of gravity and a steadily decreasing upward force. • D) an almost constant downward force of gravity. • E) a natu ...
... • A) a steadily decreasing upward force from the initial toss. • B) an increasing downward force of gravity and a steadily decreasing upward force. • C) an almost constant downward force of gravity and a steadily decreasing upward force. • D) an almost constant downward force of gravity. • E) a natu ...
Newton`s 1st Law
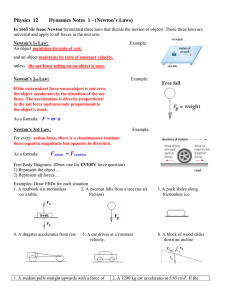
... The force needed to keep an object sliding is equal to but opposite in direction of the frictional force – the vector sum is zero Inertia - what Galileo called the tendency of an object to maintain its initial state ...
... The force needed to keep an object sliding is equal to but opposite in direction of the frictional force – the vector sum is zero Inertia - what Galileo called the tendency of an object to maintain its initial state ...
Dr. Zeemo has a brief guide to Newton`s Three Laws of Motion.
... is tossed in the air, gravity pulls it back down so it can be caught and tossed again. ...
... is tossed in the air, gravity pulls it back down so it can be caught and tossed again. ...
Definitions
... but not always. Consider an elevator cab. How does the normal force compare to weight if the cab is moving at a constant velocity? Accelerating upward? Accelerating downward? ...
... but not always. Consider an elevator cab. How does the normal force compare to weight if the cab is moving at a constant velocity? Accelerating upward? Accelerating downward? ...
Tonight`s PowerPoint Presentation
... circle is called speed are not the centripetal accelerating force ...
... circle is called speed are not the centripetal accelerating force ...
physics140-f07-lecture5 - Open.Michigan
... where S F represents the sum of all external forces acting on an object with velocity v. A valid inertial reference frame is one in which objects move at constant velocity unless forced to do otherwise. ...
... where S F represents the sum of all external forces acting on an object with velocity v. A valid inertial reference frame is one in which objects move at constant velocity unless forced to do otherwise. ...
KD-4 power point review
... This is a FAKE force Outward force is a misconception due to inertia ...
... This is a FAKE force Outward force is a misconception due to inertia ...