Newton`s Laws Powerpoint
... The acceleration (change of speed or direction) of a truck will be less than the acceleration of a golf ball if the same force is applied. ...
... The acceleration (change of speed or direction) of a truck will be less than the acceleration of a golf ball if the same force is applied. ...
Newton`s Second Law 1 PPT
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
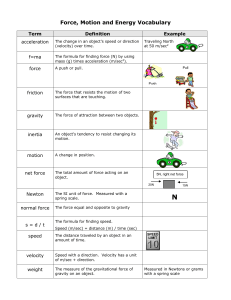
FORCE and MOTION UNIT VOCABULARY
... The formula for finding force (N) by using mass (g) times acceleration (m/sec2). ...
... The formula for finding force (N) by using mass (g) times acceleration (m/sec2). ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation Notes 1 – Centripetal Acceleration
... This unit we will investigate the special case of kinematics and dynamics of objects in uniform circular motion. First let’s consider a mass on a string being twirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed. Let’s determine the speed of the object. Remember that speed is defined as: We define the ...
... This unit we will investigate the special case of kinematics and dynamics of objects in uniform circular motion. First let’s consider a mass on a string being twirled in a horizontal circle at a constant speed. Let’s determine the speed of the object. Remember that speed is defined as: We define the ...
Circular Motion
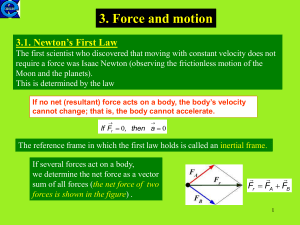
... 1. If the force exerted by a horse on a cart is equal and opposite to the force exerted by a cart on the horse, as required by Newton’s third law, how does the horse manage to move a cart? 2. A soft-drink sits at rest on a table. Which of the Newton’s laws explains why the upward force of the table ...
... 1. If the force exerted by a horse on a cart is equal and opposite to the force exerted by a cart on the horse, as required by Newton’s third law, how does the horse manage to move a cart? 2. A soft-drink sits at rest on a table. Which of the Newton’s laws explains why the upward force of the table ...
The Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when
... rotation axis and to the velocity of the body in the rotating frame. It is proportional to the object's speed in the rotating frame. These additional forces are termed inertial forces, fictitious forces, or pseudo-forces. They allow theapplication of Newton's laws to a rotating system. They are corr ...
... rotation axis and to the velocity of the body in the rotating frame. It is proportional to the object's speed in the rotating frame. These additional forces are termed inertial forces, fictitious forces, or pseudo-forces. They allow theapplication of Newton's laws to a rotating system. They are corr ...
Air Pressure, Forces, and Motion
... to resist changes in motion) Mass is a measure of an object’s inertia Mass is also a measure of the amount of an object’s matter content. (i.e. protons, neutrons, and electrons) ...
... to resist changes in motion) Mass is a measure of an object’s inertia Mass is also a measure of the amount of an object’s matter content. (i.e. protons, neutrons, and electrons) ...
Connecting Motion with Force
... Force- a push or pull one body exerts on another. -Force does not always change velocity. Balanced forces- forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. Ex: Tug of War. ...
... Force- a push or pull one body exerts on another. -Force does not always change velocity. Balanced forces- forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. Ex: Tug of War. ...
Part II
... reference frame of the car, there is an apparent force, pointed away from the center of the curve & pushing you to the door. ...
... reference frame of the car, there is an apparent force, pointed away from the center of the curve & pushing you to the door. ...
Newton`s Second and Third Laws of Motion
... has more mass it accelerates at a lower rate because mass has inertia. ...
... has more mass it accelerates at a lower rate because mass has inertia. ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Types of forces Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
... Types of forces Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
Warm-up
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...