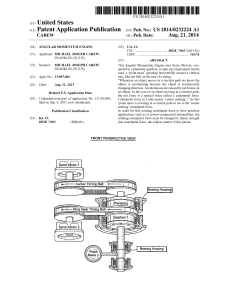
Engineering mechanics "Static"
... into, two vector components F1 and F2 with the specified directions by completing the parallelogram as shown to obtain the magnitudes of F1and F2. The relationship between a force and its vector components along given axes must not be contused with the relationship between a force and its perpendicu ...
... into, two vector components F1 and F2 with the specified directions by completing the parallelogram as shown to obtain the magnitudes of F1and F2. The relationship between a force and its vector components along given axes must not be contused with the relationship between a force and its perpendicu ...
Friction Intro - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... During the winter, owners of pickup trucks often place sandbags in the rear of their vehicles. Calculate the increased static force of friction between the rubber tires and wet concrete resulting from the addition of 200. kg of sandbags in the back of the truck. ...
... During the winter, owners of pickup trucks often place sandbags in the rear of their vehicles. Calculate the increased static force of friction between the rubber tires and wet concrete resulting from the addition of 200. kg of sandbags in the back of the truck. ...
WebAssign Practice Exam 2 Answers
... adequate stopping distance at all times. It takes about a second to react to the brake lights of the car in front of you. On a high-speed highway, your car may travel more than 30 meters before you can engage the brakes. Bumper-to-bumper traffic at high speed, as often exists on the highways near bi ...
... adequate stopping distance at all times. It takes about a second to react to the brake lights of the car in front of you. On a high-speed highway, your car may travel more than 30 meters before you can engage the brakes. Bumper-to-bumper traffic at high speed, as often exists on the highways near bi ...
Circular Motion Chapter
... Uniform Circular Motion From Newton’s first law we know that if there is no net force acting on an object, it will travel in a straight line at constant speed. Whenever an object fails to travel in this way it is, by definition accelerating. By Newton’s second law we can also conclude that there mus ...
... Uniform Circular Motion From Newton’s first law we know that if there is no net force acting on an object, it will travel in a straight line at constant speed. Whenever an object fails to travel in this way it is, by definition accelerating. By Newton’s second law we can also conclude that there mus ...
Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
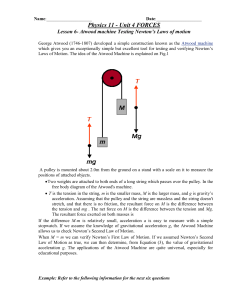
... Example: A concrete block is lifted by hoisting mechanism in which the cables are securely wrapped around the respective drums. The drums are fastened together and rotate as a single unit @ their mass center at O. Combined mass of drum is 150 kg, and radius of gyration @ O is 450 mm. A constant tens ...
... Example: A concrete block is lifted by hoisting mechanism in which the cables are securely wrapped around the respective drums. The drums are fastened together and rotate as a single unit @ their mass center at O. Combined mass of drum is 150 kg, and radius of gyration @ O is 450 mm. A constant tens ...
Lesson 10 notes - Angular Measurement - science
... For a circle, 1 complete circumference is 2r and T is the Time period for one rotation (T) So ...
... For a circle, 1 complete circumference is 2r and T is the Time period for one rotation (T) So ...
Dynamics Chapter
... thus changing its velocity from nothing to something. Acceleration is just the change in velocity over a period of time. So if pushing something can make it start moving then a net force must result in acceleration. Note, however, that only a net force results in acceleration. If I push on an object ...
... thus changing its velocity from nothing to something. Acceleration is just the change in velocity over a period of time. So if pushing something can make it start moving then a net force must result in acceleration. Note, however, that only a net force results in acceleration. If I push on an object ...
TEKS 8.7 A
... other hand—if the motion is changing slowly the acceleration is small. If the motion of the object is not changing at all, the acceleration is exactly equal to zero, no matter what the speed or direction of the motion. Newton’s Second Law connects the size of the force, the mass or amount of materia ...
... other hand—if the motion is changing slowly the acceleration is small. If the motion of the object is not changing at all, the acceleration is exactly equal to zero, no matter what the speed or direction of the motion. Newton’s Second Law connects the size of the force, the mass or amount of materia ...
Chapter 4- wrap up
... • The magnitude of the frictional force depends on the normal force and the material of the two objects in contact. Wood on wood would have a different frictional force than steel on wood, and so on. Heavy objects have more friction than very light ones, etc. • When an object is at rest, it takes a ...
... • The magnitude of the frictional force depends on the normal force and the material of the two objects in contact. Wood on wood would have a different frictional force than steel on wood, and so on. Heavy objects have more friction than very light ones, etc. • When an object is at rest, it takes a ...