chapter15 - AppServ Open Project 2.4.9
... exerted by a fluid on any immersed object The object is in equilibrium There must be an upward force to balance the downward force ...
... exerted by a fluid on any immersed object The object is in equilibrium There must be an upward force to balance the downward force ...
4 Newton`s Third Law
... your pencil. Gravity pulls the pencil downward. At the same time, the pencil pulls Earth upward with an equal and opposite reaction force. You don’t see Earth accelerate toward the pencil because Earth’s inertia is so great that its acceleration is too small to notice. ...
... your pencil. Gravity pulls the pencil downward. At the same time, the pencil pulls Earth upward with an equal and opposite reaction force. You don’t see Earth accelerate toward the pencil because Earth’s inertia is so great that its acceleration is too small to notice. ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... • For each example above, answer the following: • Is the circular motion caused by a force? • If so, in what direction is that force acting? • What is the source of the force acting on each object? © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company ...
... • For each example above, answer the following: • Is the circular motion caused by a force? • If so, in what direction is that force acting? • What is the source of the force acting on each object? © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company ...
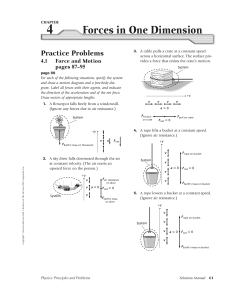
Honors Physics: Newton`s Laws Exam Review A crate rests on very
... arranged as they are, we can see that the heavy weight will move downward and the lighter mass will move up. We will treat the as if they are in one dimension, however. As we have two bodies, we must draw a FBD for each of them. Each body experiences two forces; the tension in the string (T) which h ...
... arranged as they are, we can see that the heavy weight will move downward and the lighter mass will move up. We will treat the as if they are in one dimension, however. As we have two bodies, we must draw a FBD for each of them. Each body experiences two forces; the tension in the string (T) which h ...
F35 AIS Krumenacker SAE 081016
... sink rate (altitude-hold), so some other means of low-workload height hold was required – solution was a pilot-engageable “gripper” mode, in which an altitude-hold augmentation could be quickly engaged and disengaged – with gripper engaged, longitudinal stick breakout force is significantly increase ...
... sink rate (altitude-hold), so some other means of low-workload height hold was required – solution was a pilot-engageable “gripper” mode, in which an altitude-hold augmentation could be quickly engaged and disengaged – with gripper engaged, longitudinal stick breakout force is significantly increase ...
MAE 241 –Statics Fall 2006 Jacky C. Prucz
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle ...
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle ...
CHAPTER 1 Forces in action
... After completing this chapter, you should be able to: ■ apply algebraic and graphical methods to the analysis of changes in motion ■ apply Newton’s three laws of motion to situations in which two or more coplanar forces act in a straight line and two dimensions ■ analyse the motion of projectiles ne ...
... After completing this chapter, you should be able to: ■ apply algebraic and graphical methods to the analysis of changes in motion ■ apply Newton’s three laws of motion to situations in which two or more coplanar forces act in a straight line and two dimensions ■ analyse the motion of projectiles ne ...
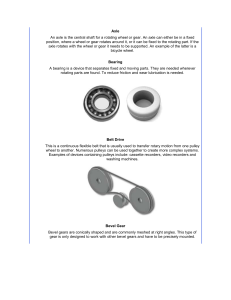
Axle
... The gear (or velocity) ratio can relate to many types of mechanism. For example: 1. The comparison between the number of teeth of two meshed gears. 2. The comparison between the circumferences of two pulleys which are connected together by a belt drive. 3. The relationship between the movement of a ...
... The gear (or velocity) ratio can relate to many types of mechanism. For example: 1. The comparison between the number of teeth of two meshed gears. 2. The comparison between the circumferences of two pulleys which are connected together by a belt drive. 3. The relationship between the movement of a ...
Newton*s First Law
... Glenveau, and Warren Peace are discussing the problem. Glen suggests that the normal force is 50 N; Olive suggests that the normal force in the diagram is 75 N; and Warren suggests that the normal force is 100 N. While all three answers may seem reasonable, only one is correct. Who is ...
... Glenveau, and Warren Peace are discussing the problem. Glen suggests that the normal force is 50 N; Olive suggests that the normal force in the diagram is 75 N; and Warren suggests that the normal force is 100 N. While all three answers may seem reasonable, only one is correct. Who is ...