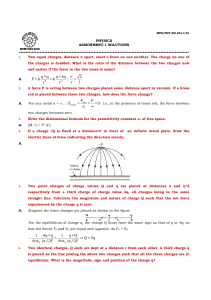
Key Learning(s) - East Pennsboro Area School District
... The Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy, which states that the total amount of mechanical energy in system must remain constant, is an alternative method to Newtonian Dynamics for describing, explaining and predicting motion. All of the energy in a system must be accounted for whether it is tra ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy, which states that the total amount of mechanical energy in system must remain constant, is an alternative method to Newtonian Dynamics for describing, explaining and predicting motion. All of the energy in a system must be accounted for whether it is tra ...
Chapter 13
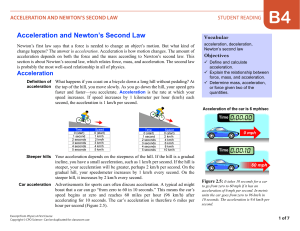
... static friction force and the box starts to move (Figure 13.6). The force of static friction balances your force up to a limit. The limit of the friction force depends on the types of surfaces and the weight of the object you are pushing. ...
... static friction force and the box starts to move (Figure 13.6). The force of static friction balances your force up to a limit. The limit of the friction force depends on the types of surfaces and the weight of the object you are pushing. ...
Chapter 5
... yields FN = 2.0 N. (a) By Newton’s third law, the force exerted by the block on the surface has that same magnitude but opposite direction: 2.0 N. (b) The direction is down. 15. (a) – (c) In all three cases the scale is not accelerating, which means that the two cords exert forces of equal magnitude ...
... yields FN = 2.0 N. (a) By Newton’s third law, the force exerted by the block on the surface has that same magnitude but opposite direction: 2.0 N. (b) The direction is down. 15. (a) – (c) In all three cases the scale is not accelerating, which means that the two cords exert forces of equal magnitude ...
Chapter 2
... Some scalars can have negative values. Examples are temperature, Temp = –10 °F (units are degrees Fahrenheit), sound intensity, I = –10 dB (the units are decibels), and an altitude, A = –45 ft (the units are feet). Some arbitrary choice for zero, e.g., sea level for altitude, determined the sign of ...
... Some scalars can have negative values. Examples are temperature, Temp = –10 °F (units are degrees Fahrenheit), sound intensity, I = –10 dB (the units are decibels), and an altitude, A = –45 ft (the units are feet). Some arbitrary choice for zero, e.g., sea level for altitude, determined the sign of ...
File
... Push a cart along a track so that twice as much net force acts on it. If the acceleration remains the same, what is a reasonable explanation? A. The mass of the cart doubles when the force is doubled. B. The cart experiences a force that it didn't before. C. The track is not level. D. Friction rever ...
... Push a cart along a track so that twice as much net force acts on it. If the acceleration remains the same, what is a reasonable explanation? A. The mass of the cart doubles when the force is doubled. B. The cart experiences a force that it didn't before. C. The track is not level. D. Friction rever ...
Chapter 5 - Force and Motion
... An object with twice the amount of matter accelerates only half as much in response to the same force. The more matter an object has, the more it resists accelerating in response to the same force. The tendency of an object to resist a change in its velocity is called inertia. The mass used ...
... An object with twice the amount of matter accelerates only half as much in response to the same force. The more matter an object has, the more it resists accelerating in response to the same force. The tendency of an object to resist a change in its velocity is called inertia. The mass used ...