s - Nuffield Foundation
... 5 One end of a light inextensible string is attached to a tool box of mass 2.5 kg which is lying on a horizontal table. The string passes over a smooth pulley and is tied at the other end to a bag of mass 1.4 kg. a Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the tool box. b If the tool box is just o ...
... 5 One end of a light inextensible string is attached to a tool box of mass 2.5 kg which is lying on a horizontal table. The string passes over a smooth pulley and is tied at the other end to a bag of mass 1.4 kg. a Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the tool box. b If the tool box is just o ...
Anonymous-VibrationTheoryFundamentals.pdf
... Mechanical vibrating systems consist of elements such as a spring for storing potential energy, mass and inertia for kinetic energy, and damper for dissipating mechanical energy. The vibration process alternatively converts energy between its potential and kinetic forms. In its general sense the vib ...
... Mechanical vibrating systems consist of elements such as a spring for storing potential energy, mass and inertia for kinetic energy, and damper for dissipating mechanical energy. The vibration process alternatively converts energy between its potential and kinetic forms. In its general sense the vib ...
Gr. 11 Physics Forces
... the interactions present at some moment in time. An ID lists all the objects that are interacting with one another and has lines representing each interaction. The lines are labelled with a single letter describing the type of interaction: a = applied (a person’s contact), g = gravitational, n = nor ...
... the interactions present at some moment in time. An ID lists all the objects that are interacting with one another and has lines representing each interaction. The lines are labelled with a single letter describing the type of interaction: a = applied (a person’s contact), g = gravitational, n = nor ...
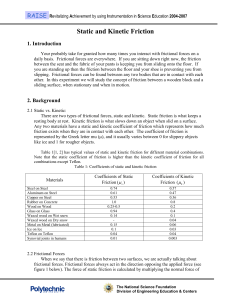
Static and Kinetic Friction
... you are standing up then the friction between the floor and your shoe is preventing you from slipping. Frictional forces can be found between any two bodies that are in contact with each other. In this experiment we will study the concept of friction between a wooden block and a sliding surface, whe ...
... you are standing up then the friction between the floor and your shoe is preventing you from slipping. Frictional forces can be found between any two bodies that are in contact with each other. In this experiment we will study the concept of friction between a wooden block and a sliding surface, whe ...
Chapter 4
... • What’s given and what’s asked for? • Usually every word is important! Draw rough picture, showing the forces and masses. • Which are the external forces? What is the system that the problem is referring to? Draw free-body diagrams showing the external forces on each body. Choose a convenient coord ...
... • What’s given and what’s asked for? • Usually every word is important! Draw rough picture, showing the forces and masses. • Which are the external forces? What is the system that the problem is referring to? Draw free-body diagrams showing the external forces on each body. Choose a convenient coord ...
Section 1 Force and Motion: Practice Problems
... Yes, for a while the diver is accelerating upward because there is an additional upward force due to air resistance on the parachute. The upward acceleration causes the diver’s downward velocity to decrease. Newton’s second law says that a net force in a certain direction will result in an accelerat ...
... Yes, for a while the diver is accelerating upward because there is an additional upward force due to air resistance on the parachute. The upward acceleration causes the diver’s downward velocity to decrease. Newton’s second law says that a net force in a certain direction will result in an accelerat ...
Rotary Homework #1
... 11. A certain light truck can go around a flat curve having a radius of 150 m with a maximum speed of 32.0 m/s. With what maximum speed can it go around a curve having a radius of 75.0 m? {Hint: Assume the same centripetal acceleration for each case.} 12. A 55.0-kg ice-skater is moving at 4.00 m/s w ...
... 11. A certain light truck can go around a flat curve having a radius of 150 m with a maximum speed of 32.0 m/s. With what maximum speed can it go around a curve having a radius of 75.0 m? {Hint: Assume the same centripetal acceleration for each case.} 12. A 55.0-kg ice-skater is moving at 4.00 m/s w ...
Vlasov Simulations of Thermal Plasma Waves
... √ for plasma wave simulations with a driver with γp = 7.25. Contour plots are used here so that direct comparison of transformed distributions can be performed. All calculations are shown close to a laboratory frame time tf = 20π. Fig. 3a is performed in a frame moving at vp at slightly later than t ...
... √ for plasma wave simulations with a driver with γp = 7.25. Contour plots are used here so that direct comparison of transformed distributions can be performed. All calculations are shown close to a laboratory frame time tf = 20π. Fig. 3a is performed in a frame moving at vp at slightly later than t ...
Part V Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms_printer
... only one or two reactions are desired, it is relatively easy to apply. If all reactions are desired, it makes more sense to apply the techniques of kinetostatic analysis (to be covered in upcoming topics). ...
... only one or two reactions are desired, it is relatively easy to apply. If all reactions are desired, it makes more sense to apply the techniques of kinetostatic analysis (to be covered in upcoming topics). ...
Unit 9 Summary
... Newton’s 1st Law holds that an object in motion will continue moving in the same manner (no velocity change) unless acted on by an unbalanced force. (Fnet=0N : constant velocity or Fnet≠0N : uniform acceleration) Newton’s 2nd Law describes this change in motion by quantifying the relationship betwee ...
... Newton’s 1st Law holds that an object in motion will continue moving in the same manner (no velocity change) unless acted on by an unbalanced force. (Fnet=0N : constant velocity or Fnet≠0N : uniform acceleration) Newton’s 2nd Law describes this change in motion by quantifying the relationship betwee ...
7thMotionfinal_Oct
... Sir Isaac Newton is credited with describing laws of gravity and motion. His three laws of motion explain objects at rest, constant motion, and acceleration due to balanced or unbalanced forces exerted on objects. The first law describes inertia, the tendency of an object to remain in motion or stay ...
... Sir Isaac Newton is credited with describing laws of gravity and motion. His three laws of motion explain objects at rest, constant motion, and acceleration due to balanced or unbalanced forces exerted on objects. The first law describes inertia, the tendency of an object to remain in motion or stay ...