16. Elevator worksheet 1
... 3. Upon reaching the top of the building, the elevator accelerates downward at 3.0 m/s2. a. Construct a force diagram for the man. ...
... 3. Upon reaching the top of the building, the elevator accelerates downward at 3.0 m/s2. a. Construct a force diagram for the man. ...
R - IBPhysicsLund
... Topic 2: Mechanics 2.4 Uniform circular motion 2.4.1 Draw a vector diagram to illustrate that the acceleration of a particle moving with constant speed in a circle is directed towards the center of the circle. 2.4.2 Apply the expressions for centripetal acceleration. 2.4.3 Identify the force produci ...
... Topic 2: Mechanics 2.4 Uniform circular motion 2.4.1 Draw a vector diagram to illustrate that the acceleration of a particle moving with constant speed in a circle is directed towards the center of the circle. 2.4.2 Apply the expressions for centripetal acceleration. 2.4.3 Identify the force produci ...
Polygon of Forces
... Force and Newton's First Law If the resultant force acting on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest (if originally at rest) or will move with constant speed in a straight line (if originally in motion). To understand and use the First Law it is helpful to first develop a concept of a ...
... Force and Newton's First Law If the resultant force acting on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest (if originally at rest) or will move with constant speed in a straight line (if originally in motion). To understand and use the First Law it is helpful to first develop a concept of a ...
P - UniMAP Portal
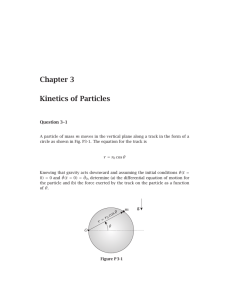
... (a) the tension in each rope given α = 45, (b) the value of α for which the tension in rope 2 is minimum. ...
... (a) the tension in each rope given α = 45, (b) the value of α for which the tension in rope 2 is minimum. ...
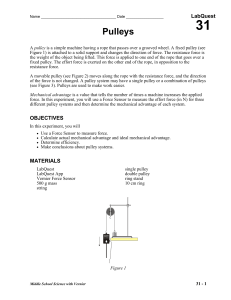
31 Pulleys
... 1. Set the range switch on the Force Sensor to 10 N. Connect the Force Sensor to LabQuest. Choose New from the File menu. If you have an older sensor that does not auto-ID, manually set up the sensor. 2. Zero the Force Sensor with its hook pointing down. a. Hold the Force Sensor in a vertical positi ...
... 1. Set the range switch on the Force Sensor to 10 N. Connect the Force Sensor to LabQuest. Choose New from the File menu. If you have an older sensor that does not auto-ID, manually set up the sensor. 2. Zero the Force Sensor with its hook pointing down. a. Hold the Force Sensor in a vertical positi ...
5.5 Equilibrum
... of objects for which there are no changes in motion. In accord with Newton's first law, if at rest, the state of rest persists. If moving, motion continues without Change (slow down, speed up, stop or change direction). Mechanical Equilibrium Rule: For any object or system of objects in equilibrium, ...
... of objects for which there are no changes in motion. In accord with Newton's first law, if at rest, the state of rest persists. If moving, motion continues without Change (slow down, speed up, stop or change direction). Mechanical Equilibrium Rule: For any object or system of objects in equilibrium, ...
Types of Friction - AustinMeehanAcademy3
... Weight is related to mass, but they are not the same. ◦Weight changes when gravitational force changes. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. ◦The amount of mass in an object does not change. This can get confusing… because weight and mass are “constant” on Earth, the terms weight and mass are of ...
... Weight is related to mass, but they are not the same. ◦Weight changes when gravitational force changes. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. ◦The amount of mass in an object does not change. This can get confusing… because weight and mass are “constant” on Earth, the terms weight and mass are of ...
Document
... motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Explanation: A glass of water placed on a table remains there unless a force is applied to remove it. Similarly, if a car is moving with uniform velocity, it goes on moving with the uni ...
... motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Explanation: A glass of water placed on a table remains there unless a force is applied to remove it. Similarly, if a car is moving with uniform velocity, it goes on moving with the uni ...
MODULE 5 STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS
... subjected to some action. This action can be in the form of load due to the weight of things such as people, furniture, wind, snow, etc. or some other kind of excitation such as an earthquake, shaking of the ground due to a blast nearby, etc. In essence all these loads are dynamic, including the sel ...
... subjected to some action. This action can be in the form of load due to the weight of things such as people, furniture, wind, snow, etc. or some other kind of excitation such as an earthquake, shaking of the ground due to a blast nearby, etc. In essence all these loads are dynamic, including the sel ...