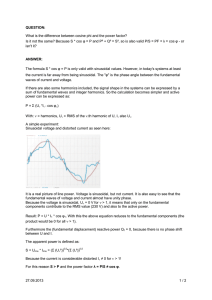
PQ Overview – Practical Aspect
... process. However dips caused due to faults in power system can’t be avoided. In highly meshed integrated power network, faults in one part of system causes voltage dips in other neighbouring parts of system. The first step towards mitigation is to measure the dips. Reliance supplies power to Mumbai ...
... process. However dips caused due to faults in power system can’t be avoided. In highly meshed integrated power network, faults in one part of system causes voltage dips in other neighbouring parts of system. The first step towards mitigation is to measure the dips. Reliance supplies power to Mumbai ...
*60129 covers/backs 4.30
... The VK-150 monoblock The monoblock version of the VK-75, the VK-150 supplies a prodigious 150 watts of output power. The stereo VK-75 can be fully upgraded to VK-150 monoblock status, maintaining the commitment to a rational upgrade path that has won BAT unprecedented customer loyalty. In addition, ...
... The VK-150 monoblock The monoblock version of the VK-75, the VK-150 supplies a prodigious 150 watts of output power. The stereo VK-75 can be fully upgraded to VK-150 monoblock status, maintaining the commitment to a rational upgrade path that has won BAT unprecedented customer loyalty. In addition, ...
Sélectivité et anisotropie des Filtres Spatiaux :
... control, in order to ensure constant switching frequency and tight control of the position of modulation pulses. This allows high accuracy in tracking highly distorted current waveforms, and minimises the ripple in three-phase systems. This technique is very simple and robust, its implementation emp ...
... control, in order to ensure constant switching frequency and tight control of the position of modulation pulses. This allows high accuracy in tracking highly distorted current waveforms, and minimises the ripple in three-phase systems. This technique is very simple and robust, its implementation emp ...
100 HVT Series AC Hipot Tester FEATURES
... • Continuously adjustable output from zero to full voltage • Compact design • Single end grounded high voltage test transformer • Separate guard and return • Triple range current meter • Triple range voltmeter • Hand cart mounted • Zero start interlock • External interlock provision • Input power ci ...
... • Continuously adjustable output from zero to full voltage • Compact design • Single end grounded high voltage test transformer • Separate guard and return • Triple range current meter • Triple range voltmeter • Hand cart mounted • Zero start interlock • External interlock provision • Input power ci ...
PSPICE Slides
... • For resistors, capacitors – category is ANALOG • For voltage/current supplies – category is SOURCE • For specified device with code such as D1N4148 (Silicon Diode) – EVAL ...
... • For resistors, capacitors – category is ANALOG • For voltage/current supplies – category is SOURCE • For specified device with code such as D1N4148 (Silicon Diode) – EVAL ...
Slide 1
... superior power performance for the majority of the region examined – Near fop,max, pseudo-NMOS inverters dissipate less power than CMOS inverters – CMOS inverters are shown to vary significantly with clock frequency while the pseudo-NMOS inverters change very little with clock frequency ...
... superior power performance for the majority of the region examined – Near fop,max, pseudo-NMOS inverters dissipate less power than CMOS inverters – CMOS inverters are shown to vary significantly with clock frequency while the pseudo-NMOS inverters change very little with clock frequency ...
power transmission activity
... To get a basic overview of how electrical energy makes it from the power generating station to your home, read the article on “How Power Grids Work” at http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/energy/power.htm and answer the following questions. 1. Identify each of the main parts of the power ...
... To get a basic overview of how electrical energy makes it from the power generating station to your home, read the article on “How Power Grids Work” at http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/energy/power.htm and answer the following questions. 1. Identify each of the main parts of the power ...
Problem 1 Find out how much power the 2 A source delivers to the
... ELEC 300 — Linear Circuits: II — Spring 2017 ...
... ELEC 300 — Linear Circuits: II — Spring 2017 ...
Metering all your needs
... > Activate and test meter disconnection device Token Entry lockout > Protection against fraudulent token attacks Delayed reconnection > In rush current protection of utility assets > Protects appliances from surge due to load shedding ...
... > Activate and test meter disconnection device Token Entry lockout > Protection against fraudulent token attacks Delayed reconnection > In rush current protection of utility assets > Protects appliances from surge due to load shedding ...
Lab 8
... Notice that in this subtle new world of the op amp, we also specify a Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR), which for the LM1458 is 70 dB. What ratio of voltages does this represent between the out-ofphase to the in-phase amplification of the op amp? (G) To power the op amp, you will make use of the B ...
... Notice that in this subtle new world of the op amp, we also specify a Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR), which for the LM1458 is 70 dB. What ratio of voltages does this represent between the out-ofphase to the in-phase amplification of the op amp? (G) To power the op amp, you will make use of the B ...
What does the “PASSIVE” device mean
... for high voltage and high frequency applications (low power losses needed), as charge accumulators thanks to big specific capacity, as variable capacitors for tuned RF applications, for filtering in AC/DC converters, in power sources. ...
... for high voltage and high frequency applications (low power losses needed), as charge accumulators thanks to big specific capacity, as variable capacitors for tuned RF applications, for filtering in AC/DC converters, in power sources. ...
Mains electricity
Mains electricity is the general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. In the US, electric power is referred to by several names including household power, household electricity, house current, powerline, domestic power, wall power, line power, AC power, city power, street power, and grid power.The two principal properties of the electric power supply, voltage and frequency, differ between regions. A voltage of (nominally) 230 V and a frequency of 50 Hz is used in Europe, most of Asia, most of South America and Australia. In North America, the most common combination is 120 V and a frequency of 60 Hz. Other voltages exist, and some countries may have, for example, 230 V but 60 Hz. This is a concern to travelers, since portable appliances designed for one voltage and frequency combination may not operate or may be destroyed by another.The use of different plugs and sockets in different regions provides some protection from accidental use of appliances with incompatible voltage and frequency requirements.