Homework 5
... http://www.ieee.org/organizations/pubs/newsletters/sscs/oct04/jssc.pdf. Thus, we can express the maximum clock frequency of a circuit as f = K(V – Vth )α/V, where V is the supply voltage, Vth is threshold voltage assumed to be the same for p and n devices, and K and α are constants specific to the c ...
... http://www.ieee.org/organizations/pubs/newsletters/sscs/oct04/jssc.pdf. Thus, we can express the maximum clock frequency of a circuit as f = K(V – Vth )α/V, where V is the supply voltage, Vth is threshold voltage assumed to be the same for p and n devices, and K and α are constants specific to the c ...
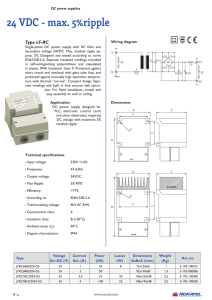
24 V AC Power Supply (Rev0): FA24AC/50, FA24AC/60
... 100 - 240 V AC input 12 V DC output, 24 W High efficiency ...
... 100 - 240 V AC input 12 V DC output, 24 W High efficiency ...
Microelectronics… - Oakland University
... water wave motion to create electricity • Electrical energy is conditioned and stored for later use ...
... water wave motion to create electricity • Electrical energy is conditioned and stored for later use ...
What causes the electrical faults or voltage dips? These electrical
... on lower voltage networks, by various factors including wildlife and lightning. ...
... on lower voltage networks, by various factors including wildlife and lightning. ...
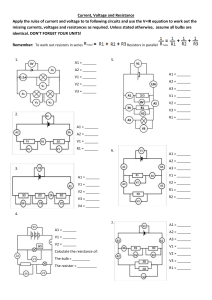
Current, Voltage and Resistance
... Current, Voltage and Resistance Apply the rules of current and voltage to to following circuits and use the V=IR equation to work out the missing currents, voltages and resistances as required. Unless stated otherwise, assume all bulbs are identical. DON’T FORGET YOUR UNITS! Remember: To work out re ...
... Current, Voltage and Resistance Apply the rules of current and voltage to to following circuits and use the V=IR equation to work out the missing currents, voltages and resistances as required. Unless stated otherwise, assume all bulbs are identical. DON’T FORGET YOUR UNITS! Remember: To work out re ...
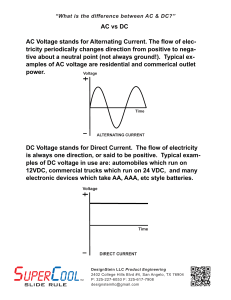
AC DC
... Easier to convert from AC to DC when needed than vice versa (stuff that runs on batteries can be plugged in to an outlet) ...
... Easier to convert from AC to DC when needed than vice versa (stuff that runs on batteries can be plugged in to an outlet) ...
AC vs DC AC Voltage stands for Alternating Current. The flow of elec
... “What is the difference between AC & DC?” ...
... “What is the difference between AC & DC?” ...
Mains electricity
Mains electricity is the general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. In the US, electric power is referred to by several names including household power, household electricity, house current, powerline, domestic power, wall power, line power, AC power, city power, street power, and grid power.The two principal properties of the electric power supply, voltage and frequency, differ between regions. A voltage of (nominally) 230 V and a frequency of 50 Hz is used in Europe, most of Asia, most of South America and Australia. In North America, the most common combination is 120 V and a frequency of 60 Hz. Other voltages exist, and some countries may have, for example, 230 V but 60 Hz. This is a concern to travelers, since portable appliances designed for one voltage and frequency combination may not operate or may be destroyed by another.The use of different plugs and sockets in different regions provides some protection from accidental use of appliances with incompatible voltage and frequency requirements.