Electrostatics - Coulomb`s Law
... The three main branches of classical physics are Mechanics, Thermal Physics and Electromagnetism. The first part of this module concerns electrostatics (charges at rest). Electrical current is simply the rate of flow of charge over time. Electrical current is the source of magnetism. ...
... The three main branches of classical physics are Mechanics, Thermal Physics and Electromagnetism. The first part of this module concerns electrostatics (charges at rest). Electrical current is simply the rate of flow of charge over time. Electrical current is the source of magnetism. ...
AP PHYSICS 1
... classical mechanics) concerned with the study of forces and torques and their effect on motion, as opposed to kinematics, which studies the motion of objects without reference to its causes. In addition, Isaac Newton established the undergirding physical laws which govern dynamics in physics. By stu ...
... classical mechanics) concerned with the study of forces and torques and their effect on motion, as opposed to kinematics, which studies the motion of objects without reference to its causes. In addition, Isaac Newton established the undergirding physical laws which govern dynamics in physics. By stu ...
Circular Motion 2
... Which of the following statements are true of an object moving in a circle at a constant speed? A. The object experiences a force which has a component directed parallel to the direction of ...
... Which of the following statements are true of an object moving in a circle at a constant speed? A. The object experiences a force which has a component directed parallel to the direction of ...
Chapter 4 - Nicholls State University
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. ...
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. ...
force
... ◦ The weight of the ball acting vertically down. ◦ A horizontal force that maintains the motion. ◦ A force whose direction changes as the direction of motion changes. ◦ The weight of the ball and a horizontal force. ◦ The weight of the ball and a force in the direction of motion. © 2015 Pearson Educ ...
... ◦ The weight of the ball acting vertically down. ◦ A horizontal force that maintains the motion. ◦ A force whose direction changes as the direction of motion changes. ◦ The weight of the ball and a horizontal force. ◦ The weight of the ball and a force in the direction of motion. © 2015 Pearson Educ ...
CH04.AST1001.F16.EDS
... • The force of the car on the truck is equal and opposite to the force of the truck on the car. T • The momentum transferred from the truck to the car is equal and opposite to the momentum transferred from the car to the truck. T • The change of velocity of the car is the same as the change of veloc ...
... • The force of the car on the truck is equal and opposite to the force of the truck on the car. T • The momentum transferred from the truck to the car is equal and opposite to the momentum transferred from the car to the truck. T • The change of velocity of the car is the same as the change of veloc ...
08 Rotation
... You go in a circle (turn with the car), because of the centripetal (center seeking) force of the door on you. If you open the door – you will not move radially outward ...
... You go in a circle (turn with the car), because of the centripetal (center seeking) force of the door on you. If you open the door – you will not move radially outward ...
Tension is a reaction force applied by a stretched string (rope or a
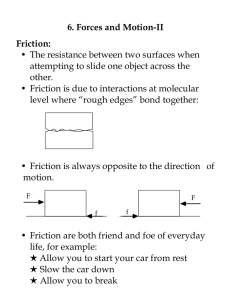
... Friction always acts in the opposite direction of motion. Friction is NOT a conservative force. This means the energy used during the frictional force cannot go back into the object, the energy is used in sound, heat, light, etc… that is given off to the environment. ...
... Friction always acts in the opposite direction of motion. Friction is NOT a conservative force. This means the energy used during the frictional force cannot go back into the object, the energy is used in sound, heat, light, etc… that is given off to the environment. ...
Chapter 11 Hand Tool Design Guidelines
... Center of gravity • The speed and angle of takeoff primarily determine the trajectory of the performer's CG during the jump. • The only other influencing factor is air resistance, which exerts an extremely small effect on performance in the jumping ...
... Center of gravity • The speed and angle of takeoff primarily determine the trajectory of the performer's CG during the jump. • The only other influencing factor is air resistance, which exerts an extremely small effect on performance in the jumping ...
1st Term Exam
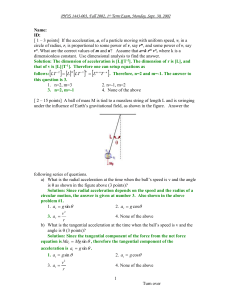
... 3. Horizontal when flying straight and down when coming down 4. None of the above g) What is each acceleration component? ( 3 points) Solution: Since the only force in this motion is gravitational force exerting on the bomb by the planet P, the acceleration is only on negative y direction, downward. ...
... 3. Horizontal when flying straight and down when coming down 4. None of the above g) What is each acceleration component? ( 3 points) Solution: Since the only force in this motion is gravitational force exerting on the bomb by the planet P, the acceleration is only on negative y direction, downward. ...
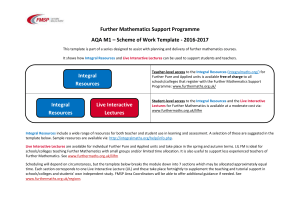
AQA M1 - The Further Mathematics Support Programme
... Integral Resources include a wide range of resources for both teacher and student use in learning and assessment. A selection of these are suggested in the template below. Sample resources are available via: http://integralmaths.org/help/info.php. Live Interactive Lectures are available for individu ...
... Integral Resources include a wide range of resources for both teacher and student use in learning and assessment. A selection of these are suggested in the template below. Sample resources are available via: http://integralmaths.org/help/info.php. Live Interactive Lectures are available for individu ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.