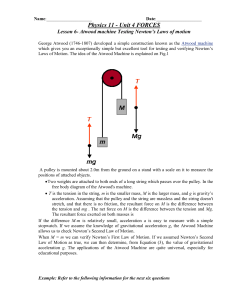
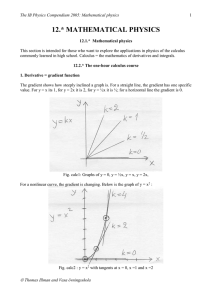
Lecture 20.TorqueRot..
... Which of the arrangements below is least effective in loosening the nut? Force is proportional to length of vector. ...
... Which of the arrangements below is least effective in loosening the nut? Force is proportional to length of vector. ...
Everybody has been told that Earth rotates on its axis once each day
... Question Where would the ball land if the van was slowing down? Answer It would land forward of the release point because the ball continues moving with the horizontal velocity it had when released, whereas the van is slowing down. As before, the descriptions of the ball's motion are different. But ...
... Question Where would the ball land if the van was slowing down? Answer It would land forward of the release point because the ball continues moving with the horizontal velocity it had when released, whereas the van is slowing down. As before, the descriptions of the ball's motion are different. But ...
Previous solved assignments physics PHY101
... For your information: Choice “d” is partly correct; although it turns out that there is a net force on the sphere from the balloon. Because the electrons in the balloon are closer to the attractive positive charges in the sphere, and farther away from the repelling negative charges, there is a net f ...
... For your information: Choice “d” is partly correct; although it turns out that there is a net force on the sphere from the balloon. Because the electrons in the balloon are closer to the attractive positive charges in the sphere, and farther away from the repelling negative charges, there is a net f ...
PROBLEMS
... to reach an apple in a tree without climbing the tree. Sitting in a chair connected to a rope that passes over a frictionless pulley (Fig. P5.51), Pat pulls on the loose end of the rope with such a force that the spring scale reads 250 N. Pat's true weight is 320 N, and the chair weighs 160 N. (a) D ...
... to reach an apple in a tree without climbing the tree. Sitting in a chair connected to a rope that passes over a frictionless pulley (Fig. P5.51), Pat pulls on the loose end of the rope with such a force that the spring scale reads 250 N. Pat's true weight is 320 N, and the chair weighs 160 N. (a) D ...
More than Gravity
... There are complicated theories about black holes that have never been seen, densities of planets that have never been measured, and subatomic particles that have never been detected. However, it is simpler than all of that and right in front of us. The Sun and the solar wind are the most powerful fo ...
... There are complicated theories about black holes that have never been seen, densities of planets that have never been measured, and subatomic particles that have never been detected. However, it is simpler than all of that and right in front of us. The Sun and the solar wind are the most powerful fo ...
Notes on Fluid Dynamics These notes are meant for my PHY132
... In this introductory class, we will limit our treatment to moving fluids whose density doesn’t change and ones that are at steady state. There are two main relationships that we will derive and apply. The first one is called the ”continuity equation”, and the second one Bernouli’s equation. By stead ...
... In this introductory class, we will limit our treatment to moving fluids whose density doesn’t change and ones that are at steady state. There are two main relationships that we will derive and apply. The first one is called the ”continuity equation”, and the second one Bernouli’s equation. By stead ...
Tension, Continuous Systems and Differential Equations
... between two trees. The ends of the rope are at the same height and they make an angle θ with the trees. a) What is the tension at the ends of the rope where it is connected to the trees? b) What is the tension in the rope at a point midway between the trees? Be sure you show any free body force diag ...
... between two trees. The ends of the rope are at the same height and they make an angle θ with the trees. a) What is the tension at the ends of the rope where it is connected to the trees? b) What is the tension in the rope at a point midway between the trees? Be sure you show any free body force diag ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion for a Particle Moving in One Dimension
... anything is happening, no matter how fast the elevator is traveling or whether you are going up or down. In both car and elevator examples, when you feel as if you are at rest you are moving in a straight line at a constant rate. This kind of motion is called constant velocity. Constant velocity fee ...
... anything is happening, no matter how fast the elevator is traveling or whether you are going up or down. In both car and elevator examples, when you feel as if you are at rest you are moving in a straight line at a constant rate. This kind of motion is called constant velocity. Constant velocity fee ...
charged geosynchronous debris perturbation
... magnetic field, as well as the absolute charge level. The Lorentz force, acting orthogonal to the orbital velocity, would be able to change the momentum without changing the orbit energy or mean motion. Wiesel recently reported in [5] some near-GEO debris objects which appear to accelerate towards t ...
... magnetic field, as well as the absolute charge level. The Lorentz force, acting orthogonal to the orbital velocity, would be able to change the momentum without changing the orbit energy or mean motion. Wiesel recently reported in [5] some near-GEO debris objects which appear to accelerate towards t ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.