PROPERTIES OF MATTER Question 1 (8 marks) Two metal balls
... (7 marks) A zebra first sees a lion when the lion is 12.5 m away and moving towards the zebra with a velocity of 5 ms-1. The zebra begins to accelerate away from the lion; at the same time the lion accelerates towards the zebra at 2 ms-2. (a) If the lion takes 15 seconds to catch the zebra, how far ...
... (7 marks) A zebra first sees a lion when the lion is 12.5 m away and moving towards the zebra with a velocity of 5 ms-1. The zebra begins to accelerate away from the lion; at the same time the lion accelerates towards the zebra at 2 ms-2. (a) If the lion takes 15 seconds to catch the zebra, how far ...
An Introduction to Gravity in the Solar System
... cores. The details of the interactions between the cores and the planetesimal swarm are very complicated and the subject of much activity. But we do think the cores somehow emerge from the process on stable orbits. How it all sorts out to get to that state is a bit fuzzy at present. In the inner sol ...
... cores. The details of the interactions between the cores and the planetesimal swarm are very complicated and the subject of much activity. But we do think the cores somehow emerge from the process on stable orbits. How it all sorts out to get to that state is a bit fuzzy at present. In the inner sol ...
How do forces affect the motion of an object? A force is a push or a
... • Fluid friction opposes the motion of an object through a fluid. • Fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air is known as air resistance. • Fluid friction increases as the speed of the object moving through the fluid increases. ...
... • Fluid friction opposes the motion of an object through a fluid. • Fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air is known as air resistance. • Fluid friction increases as the speed of the object moving through the fluid increases. ...
RP 3P1 Force and Motion - NC Science Wiki
... Since everything is moving, there is no fixed reference point against which the motion of things can be described. All motion is relative to whatever point or object we choose. Thus, a parked bus has no motion with reference to the earth's surface; but since the earth spins on its axis, the bus is m ...
... Since everything is moving, there is no fixed reference point against which the motion of things can be described. All motion is relative to whatever point or object we choose. Thus, a parked bus has no motion with reference to the earth's surface; but since the earth spins on its axis, the bus is m ...
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (30 marks)
... e) there is no air resistance in the region where the astronaut is orbiting ...
... e) there is no air resistance in the region where the astronaut is orbiting ...
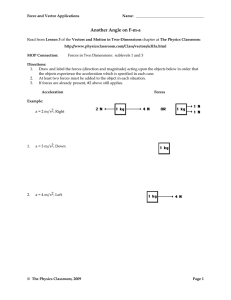
Net Force Net force is the sum of the forces acting
... Predict if the following objects are speeding up, slowing down, or moving at constant velocity. F net a) ...
... Predict if the following objects are speeding up, slowing down, or moving at constant velocity. F net a) ...
Theory of Forces Adding Forces Review Forces and Motion Vector
... Contact pushes by a surface are usually called normal forces Normal is an old fashioned word for perpendicular One more relevant Object: the Earth ...
... Contact pushes by a surface are usually called normal forces Normal is an old fashioned word for perpendicular One more relevant Object: the Earth ...
Do Now - Hicksville Public Schools
... An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in straight line motion will remain in straight line motion, unless Newton’s 1st law – What is inertia? Inertia is ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in straight line motion will remain in straight line motion, unless Newton’s 1st law – What is inertia? Inertia is ...
NewtonsLaws - University of Colorado Boulder
... Remember, the philosophy of science is this: "The final test of the validity of any idea is experiment." In Physics, the only statements that are true always are definitions (like a ...
... Remember, the philosophy of science is this: "The final test of the validity of any idea is experiment." In Physics, the only statements that are true always are definitions (like a ...
Gravitational Induction and the Gyroscopic Force
... moving particle actually moves through rotating aether. The Coriolis/gyroscopic force appears as parts (3) and (4) of equation (5) in Maxwell’s 1861 paper. The second tangential component is determined by angular acceleration of the aether relative to a particle and it appears to be missing a counte ...
... moving particle actually moves through rotating aether. The Coriolis/gyroscopic force appears as parts (3) and (4) of equation (5) in Maxwell’s 1861 paper. The second tangential component is determined by angular acceleration of the aether relative to a particle and it appears to be missing a counte ...
Question:
... An astronaut is preparing calculations for a flight to the Moon. The combined mass of the crew, all equipment, fuel, and the rocket is 2.8106 kg on the launch pad. a. The rocket’s engines produce a combined 35106 N of thrust. Is this enough to lift the rocket and its payload? What if the engines p ...
... An astronaut is preparing calculations for a flight to the Moon. The combined mass of the crew, all equipment, fuel, and the rocket is 2.8106 kg on the launch pad. a. The rocket’s engines produce a combined 35106 N of thrust. Is this enough to lift the rocket and its payload? What if the engines p ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.