Questions and Solutions - Physics and Engineering Physics
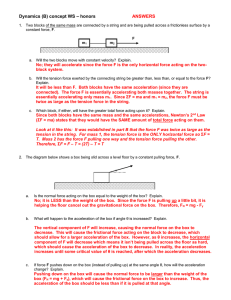
... Calculate the net work done by the normal force on the rider between points B and D. (2 marks) ...
... Calculate the net work done by the normal force on the rider between points B and D. (2 marks) ...
What is the Centrifugal Force?
... particles in the field, and are thus called centrifugal fertilizers. Their accuracy depends first and foremost on the spacing between the traversals of the spreader. The larger the spacing, the less overlap there is. The amount of overlap largely determines the quality of the fertilizer dispersion t ...
... particles in the field, and are thus called centrifugal fertilizers. Their accuracy depends first and foremost on the spacing between the traversals of the spreader. The larger the spacing, the less overlap there is. The amount of overlap largely determines the quality of the fertilizer dispersion t ...
Forces - Wsfcs
... The SI unit of force is the newton (N). One newton is the amount of force that causes a mass of 1 kilogram to accelerate at 1 m/s2 . Thus, the newton can also be expressed as kg·m/s2 . The newton was named for the scientist Sir Isaac Newton, who is famous for his law of gravity. You’ll learn more ab ...
... The SI unit of force is the newton (N). One newton is the amount of force that causes a mass of 1 kilogram to accelerate at 1 m/s2 . Thus, the newton can also be expressed as kg·m/s2 . The newton was named for the scientist Sir Isaac Newton, who is famous for his law of gravity. You’ll learn more ab ...
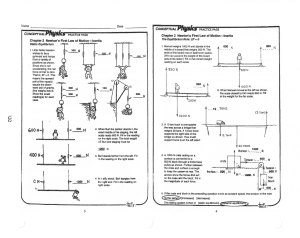
Chapter 12: Forces in Motion
... • There are four main types of friction: static friction, sliding friction, rolling friction, and fluid friction. Static Friction • is the friction force that acts on objects that are ____ moving. • Static friction always acts in the direction ____________ to that of the applied force. • You experi ...
... • There are four main types of friction: static friction, sliding friction, rolling friction, and fluid friction. Static Friction • is the friction force that acts on objects that are ____ moving. • Static friction always acts in the direction ____________ to that of the applied force. • You experi ...
PES 1110 Fall 2013, Spendier Lecture 9/Page 1 Today
... This is how we honor great Physicists – we name units after them. 1N = 0.22 lb (on Earth) if you go some place else your weight is different Just for fun, go to burger king and you ask for “one Newton Burger” and see what they will do In can only think of one problem in this term were there is only ...
... This is how we honor great Physicists – we name units after them. 1N = 0.22 lb (on Earth) if you go some place else your weight is different Just for fun, go to burger king and you ask for “one Newton Burger” and see what they will do In can only think of one problem in this term were there is only ...
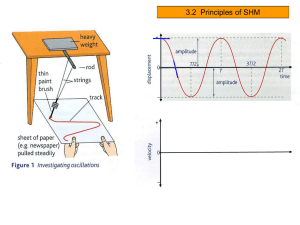
Simple Harmonic Motion 2
... body moves repeatedly over the same path in equal time intervals. Examples: uniform circular motion and simple harmonic motion. ...
... body moves repeatedly over the same path in equal time intervals. Examples: uniform circular motion and simple harmonic motion. ...
Two Dimensional Motion 2
... Acceleration that causes a change in direction. An object in circular motion has a centripetal acceleration. Centripetal (means “center-seeking”) Acceleration always acts towards the center of the circle. ...
... Acceleration that causes a change in direction. An object in circular motion has a centripetal acceleration. Centripetal (means “center-seeking”) Acceleration always acts towards the center of the circle. ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.