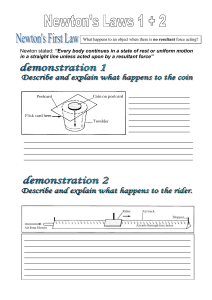
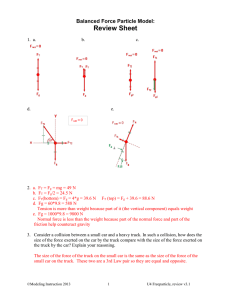
Principles of Animation Physics
... Figure 3: (Left) Character demonstrating the Law of Inertia by standing on a bus when it comes to a sudden stop. (Right) This character is seated when the bus stops; notice how her hair flies forward due to the Law of Inertia. At first this all seems purely academic until you realize that follow-throu ...
... Figure 3: (Left) Character demonstrating the Law of Inertia by standing on a bus when it comes to a sudden stop. (Right) This character is seated when the bus stops; notice how her hair flies forward due to the Law of Inertia. At first this all seems purely academic until you realize that follow-throu ...
Class Notes
... A force causes an object that is not moving to move or changes the velocity of an object. The change in velocity can be a change in its speed or its direction or both. The unit of force is the Newton, symbol N. Friction is a force that opposes the motion of objects when they are in contact. ...
... A force causes an object that is not moving to move or changes the velocity of an object. The change in velocity can be a change in its speed or its direction or both. The unit of force is the Newton, symbol N. Friction is a force that opposes the motion of objects when they are in contact. ...
Section 8-2 Center of Mass
... i. (+) When rotation is counterclockwise ii. (-) When rotation is clockwise e. When more than 1 force causes rotation then net torque is the sum of all torques involved. 4. Center of Mass – point at which all of the mass of the body can be considered to be concentrated when analyzing transitional mo ...
... i. (+) When rotation is counterclockwise ii. (-) When rotation is clockwise e. When more than 1 force causes rotation then net torque is the sum of all torques involved. 4. Center of Mass – point at which all of the mass of the body can be considered to be concentrated when analyzing transitional mo ...
CENTRIPETAL FORCE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
... b.) The net centripetal force is generated by the normal and gravity. c.) The frictional force is static and its directed in the normal direction. d.) The frictional force is static and its directed up the incline. 8.) A car travels with constant speed around the track shown to the right. At which p ...
... b.) The net centripetal force is generated by the normal and gravity. c.) The frictional force is static and its directed in the normal direction. d.) The frictional force is static and its directed up the incline. 8.) A car travels with constant speed around the track shown to the right. At which p ...
Generation of Gravitational Force
... other property of Gravitational field is known. If there is a direct sensor of gravity which is not based on the force applied on mass, then it will give an opening to produce Gravitational Force (using gravity motor). Visualize a DC motor without fundamentals of Electrical Engineering : Let us once ...
... other property of Gravitational field is known. If there is a direct sensor of gravity which is not based on the force applied on mass, then it will give an opening to produce Gravitational Force (using gravity motor). Visualize a DC motor without fundamentals of Electrical Engineering : Let us once ...
Slides - uchicago hep
... Quantum field theory tells us that there is a smallest possible excitation of a field, the quanta of this field or a particle. When we say “particles interact”, what we really mean is: One field ...
... Quantum field theory tells us that there is a smallest possible excitation of a field, the quanta of this field or a particle. When we say “particles interact”, what we really mean is: One field ...
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
... rims. Why does this allow a racer to achieve greater accelerations than would an identical reduction in the mass of the bicycle’s frame? Describe the energy transformations involved when a yo-yo is thrown downward and then climbs back up its string to be caught in the user’s hand. Calculate the mome ...
... rims. Why does this allow a racer to achieve greater accelerations than would an identical reduction in the mass of the bicycle’s frame? Describe the energy transformations involved when a yo-yo is thrown downward and then climbs back up its string to be caught in the user’s hand. Calculate the mome ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.