* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slides - uchicago hep
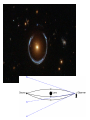
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
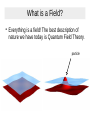
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup