AP Exam Study Overview (Without Rotational Dynamics)
... There is a height difference from top to bottom, but the object has speed at the top as well. And the bottom may not necessarily be the lowest point in the problem ...
... There is a height difference from top to bottom, but the object has speed at the top as well. And the bottom may not necessarily be the lowest point in the problem ...
Standard Grade work booklet
... application of this circuit). 4. A clock pulse generator circuit is shown below. A LED monitor circuit is to be connected between the output Y of the generator and Z (the +5 V supply rail). The generator produces pulses which are fed to the LED monitor causing the LED to flash on and off. (a) The LE ...
... application of this circuit). 4. A clock pulse generator circuit is shown below. A LED monitor circuit is to be connected between the output Y of the generator and Z (the +5 V supply rail). The generator produces pulses which are fed to the LED monitor causing the LED to flash on and off. (a) The LE ...
UNIT 4 Lab
... If one object exerts a force on a second object, then the second object exerts a force back on the first object that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to that exerted on it by the first object. j. Is this consistent with your observations above? When two objects are in contact with eac ...
... If one object exerts a force on a second object, then the second object exerts a force back on the first object that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to that exerted on it by the first object. j. Is this consistent with your observations above? When two objects are in contact with eac ...
hsc syllabus - HSC Guru
... identify absences of electrons in a nearly full band as holes, and recognise that both electrons and holes help to carry current compare qualitatively the relative number of free electrons that can drift from atom to atom in conductors, semiconductors and insulators identify that the use of ge ...
... identify absences of electrons in a nearly full band as holes, and recognise that both electrons and holes help to carry current compare qualitatively the relative number of free electrons that can drift from atom to atom in conductors, semiconductors and insulators identify that the use of ge ...
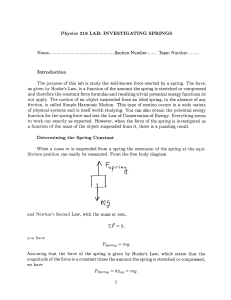
Physics 218 LAB: INVESTIGATING SPRINGS Name Section
... The purpose of this lab is study the well-known force exerted by a spring. The force, as given by Hooke’s Law, is a function of the amount the spring is stretched or compressed and therefore the constant force formulae and resulting trivial potential energy functions do not apply. The motion of an o ...
... The purpose of this lab is study the well-known force exerted by a spring. The force, as given by Hooke’s Law, is a function of the amount the spring is stretched or compressed and therefore the constant force formulae and resulting trivial potential energy functions do not apply. The motion of an o ...
IIT Paper 2010 - auroraclasses.org
... A block of mass m is on an inclined plane of angle θ. The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is μ and tan θ > μ. The block is held stationary by applying a force P parallel to the plane. The direction of force pointing up the plane is taken to be positive. As P is varied from P1 ...
... A block of mass m is on an inclined plane of angle θ. The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is μ and tan θ > μ. The block is held stationary by applying a force P parallel to the plane. The direction of force pointing up the plane is taken to be positive. As P is varied from P1 ...
Simple Machines PPT
... What is a simple machine? A machine should assist you in doing work however, the amount of work done overall is the same The most basic objects that redirect force are called simple machines ...
... What is a simple machine? A machine should assist you in doing work however, the amount of work done overall is the same The most basic objects that redirect force are called simple machines ...
Coning Angle
... the spring constant k= I2 and the mass m = I. Thus, the natural frequency of the blade in flapping is just . That is, the blade will have a natural tendency to flap up and down exactly once per revolution. The right hand side of equation (1) is called the forcing function and will contain a steady ...
... the spring constant k= I2 and the mass m = I. Thus, the natural frequency of the blade in flapping is just . That is, the blade will have a natural tendency to flap up and down exactly once per revolution. The right hand side of equation (1) is called the forcing function and will contain a steady ...