College Physics (Etkina) Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics 2.1
... 32) The acceleration due to gravity is lower on the Moon than on Earth. Which one of the following statements is true about the mass and weight of an astronaut on the Moon's surface, compared to Earth? A) Mass is less, weight is the same. B) Mass is the same, weight is less. C) Both mass and weight ...
... 32) The acceleration due to gravity is lower on the Moon than on Earth. Which one of the following statements is true about the mass and weight of an astronaut on the Moon's surface, compared to Earth? A) Mass is less, weight is the same. B) Mass is the same, weight is less. C) Both mass and weight ...
FE ANS
... downwards then a is negative and N is less than its usual value. The person's "apparent weight" is less than mg . If the downward acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity, then N is zero. This is "weightlessness". "Weightlessness" also occurs in an orbiting spacecraft. The astronaut ...
... downwards then a is negative and N is less than its usual value. The person's "apparent weight" is less than mg . If the downward acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity, then N is zero. This is "weightlessness". "Weightlessness" also occurs in an orbiting spacecraft. The astronaut ...
Chapter 7 - Cloudfront.net
... same angular motion. Every point on the rotating object does not have the same linear motion. ...
... same angular motion. Every point on the rotating object does not have the same linear motion. ...
Tension, Continuous Systems and Differential Equations
... between two trees. The ends of the rope are at the same height and they make an angle θ with the trees. a) What is the tension at the ends of the rope where it is connected to the trees? b) What is the tension in the rope at a point midway between the trees? Be sure you show any free body force diag ...
... between two trees. The ends of the rope are at the same height and they make an angle θ with the trees. a) What is the tension at the ends of the rope where it is connected to the trees? b) What is the tension in the rope at a point midway between the trees? Be sure you show any free body force diag ...
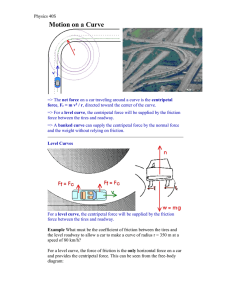
Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
... • The force of gravity causes the speed of an object in a vertical circular path to vary. The object accelerates on the downward portion of its circular path and decelerates on the upward portion of the circular path. • At the top and bottom of a vertical circular path, the weight and the normal for ...
... • The force of gravity causes the speed of an object in a vertical circular path to vary. The object accelerates on the downward portion of its circular path and decelerates on the upward portion of the circular path. • At the top and bottom of a vertical circular path, the weight and the normal for ...
Phy221 Lab 2
... Clearly, if you apply a horizontal force to a block on a horizontal surface and the block does not move then the static frictional force has the same magnitude as the applied force. But, how would you actually measure the maximum static frictional force, fsmax? Discuss this with your lab partners an ...
... Clearly, if you apply a horizontal force to a block on a horizontal surface and the block does not move then the static frictional force has the same magnitude as the applied force. But, how would you actually measure the maximum static frictional force, fsmax? Discuss this with your lab partners an ...
Solution - Jobworks Physics
... Now k is slightly different for situations in either air or a vacuum, but for us we will round this value off to be 9.0 x 109 Nm2/C2 Coulomb's Law is sometimes also written as: F = (1/4πεo)(q1q2/r2) The quantity εo is called the permittivity of free space. For a deeper explanation of what this is an ...
... Now k is slightly different for situations in either air or a vacuum, but for us we will round this value off to be 9.0 x 109 Nm2/C2 Coulomb's Law is sometimes also written as: F = (1/4πεo)(q1q2/r2) The quantity εo is called the permittivity of free space. For a deeper explanation of what this is an ...
pdf x1
... Numeric Examples: Electric Force Is Strong Electric force between two 1C charges 1 meter apart: F=8.99x109N Proton and electron in a hydrogen atom: qelectron= -1.6x10-19 C, qproton= 1.6x10-19 C, r=5.3x10-11m à Electric force F= 8.2 x10-8 N. This force is large: Compared to the mass of p ...
... Numeric Examples: Electric Force Is Strong Electric force between two 1C charges 1 meter apart: F=8.99x109N Proton and electron in a hydrogen atom: qelectron= -1.6x10-19 C, qproton= 1.6x10-19 C, r=5.3x10-11m à Electric force F= 8.2 x10-8 N. This force is large: Compared to the mass of p ...