Possibility of the Space Propulsion System Utilizing
... (electron’s mass), N = 1026 , vd = 108 m/s for the value of the vacuum arc (Boxman, Martin and Sanders, 1996), and M ≈ M ′ . Assuming that the electro-dynamical damping factor has the value on the order of the Abraham-Lorenz damping constant, it can be seen from the calculation result that this spac ...
... (electron’s mass), N = 1026 , vd = 108 m/s for the value of the vacuum arc (Boxman, Martin and Sanders, 1996), and M ≈ M ′ . Assuming that the electro-dynamical damping factor has the value on the order of the Abraham-Lorenz damping constant, it can be seen from the calculation result that this spac ...
Gravity and Inertia (Rec. 1.23.14) (* file)
... aether--to the intimately local aether at that--not some distant aether. In our aether model, relative mass increase comes about due to the temporary change of the permittivity of space in the transverse direction due to the altered speed of light in that direction. In order to affect the mass of th ...
... aether--to the intimately local aether at that--not some distant aether. In our aether model, relative mass increase comes about due to the temporary change of the permittivity of space in the transverse direction due to the altered speed of light in that direction. In order to affect the mass of th ...
Uniform Circular Motion - K
... together, Δv is directed more and more toward the exact center of the circular path. Since when we have the instantaneous acceleration, v1 and v2 should be about a fraction of a second apart, at that moment the direction is in fact directed directly toward the center of the circle. ...
... together, Δv is directed more and more toward the exact center of the circular path. Since when we have the instantaneous acceleration, v1 and v2 should be about a fraction of a second apart, at that moment the direction is in fact directed directly toward the center of the circle. ...
Presentation Lesson 09 Newton Second Law of Motion
... Usually called the law of inertia Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force exerted upon it ...
... Usually called the law of inertia Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force exerted upon it ...
Newton’s Second Law of Motion – Force & Acceleration
... Usually called the law of inertia Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force exerted upon it ...
... Usually called the law of inertia Every object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by an unbalanced force exerted upon it ...
Question Paper - Revision Science
... Assuming that air resistance is negligible, which of the following would produce a more reliable value of g? A Drop the card from a greater height. B Ensure that the card is dropped from rest. C Make the card shorter. D Move the light gates further apart. (Total for Question 10 = 1 mark) TOTAL FOR S ...
... Assuming that air resistance is negligible, which of the following would produce a more reliable value of g? A Drop the card from a greater height. B Ensure that the card is dropped from rest. C Make the card shorter. D Move the light gates further apart. (Total for Question 10 = 1 mark) TOTAL FOR S ...
posted
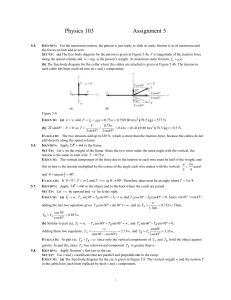
... IDENTIFY: Apply Newton’s second law to the rocket plus its contents and to the power supply. Both the rocket and the power supply have the same acceleration. SET UP: The free-body diagrams for the rocket and for the power supply are given in Figures 5.12a and b. Since the highest altitude of the roc ...
... IDENTIFY: Apply Newton’s second law to the rocket plus its contents and to the power supply. Both the rocket and the power supply have the same acceleration. SET UP: The free-body diagrams for the rocket and for the power supply are given in Figures 5.12a and b. Since the highest altitude of the roc ...
W - Cloudfront.net
... Work & Energy A rock is dropped from a distance RE above the surface of the earth, and is observed to have kinetic energy K1 when it hits the ground. An identical rock is dropped from twice the height (2RE) above the earth’s surface and has kinetic energy K2 when it hits. RE is the radius of the ...
... Work & Energy A rock is dropped from a distance RE above the surface of the earth, and is observed to have kinetic energy K1 when it hits the ground. An identical rock is dropped from twice the height (2RE) above the earth’s surface and has kinetic energy K2 when it hits. RE is the radius of the ...
(Springs) Scripted - UTeach Outreach
... Mass and weight are the same. Mass is an extensive, measurable physical property of matter – it is dependent on the amount of matter in a substance, but mass does not vary with location. Weight depends on how much gravity is acting on an object at the moment. This is why an object’s weight could be ...
... Mass and weight are the same. Mass is an extensive, measurable physical property of matter – it is dependent on the amount of matter in a substance, but mass does not vary with location. Weight depends on how much gravity is acting on an object at the moment. This is why an object’s weight could be ...