Chapter 6 Clickers
... a) The coefficient of kinetic friction is the same for all three blocks. b) The magnitude of the force of kinetic friction is greater for block 3. c) The normal force exerted by the surface is the same for all three blocks. d) Block 3 has the greatest apparent area in contact with the surface. e) If ...
... a) The coefficient of kinetic friction is the same for all three blocks. b) The magnitude of the force of kinetic friction is greater for block 3. c) The normal force exerted by the surface is the same for all three blocks. d) Block 3 has the greatest apparent area in contact with the surface. e) If ...
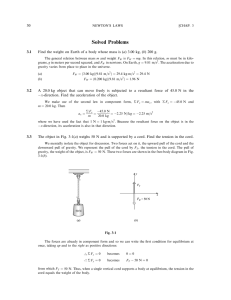
Gravitational and Anti-gravitational Applications
... Because that universal outward Flow originates at each particle and flows radially outward in all directions its density or concentration decreases inversely as the square of distance from the source of the Flow. At a large distance from the source the wave front of a very small portion of the total ...
... Because that universal outward Flow originates at each particle and flows radially outward in all directions its density or concentration decreases inversely as the square of distance from the source of the Flow. At a large distance from the source the wave front of a very small portion of the total ...
Printable Activities
... The easiest way to describe these types of fields is through lines representing the forces generated in these situations. In the case of an electric field, it can be considered as a point charge, or as an interaction between charges. ...
... The easiest way to describe these types of fields is through lines representing the forces generated in these situations. In the case of an electric field, it can be considered as a point charge, or as an interaction between charges. ...
Momentum
... The top graph represents the variation of displacement with time for a particle executing simple harmonic motion. Which curve in the bottom graph represents the variation of acceleration with time for the same particle? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) None of these is correct. Answer: B 28. A body moving in ...
... The top graph represents the variation of displacement with time for a particle executing simple harmonic motion. Which curve in the bottom graph represents the variation of acceleration with time for the same particle? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) None of these is correct. Answer: B 28. A body moving in ...
Ch. 7 PP - Lemon Bay High School
... • The gravitational forces that two masses exert on each other are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. • This is an example of Newton’s third law of motion. • One example is the Earth-moon system, shown on the next slide. • As a result of these forces, the moon and Earth each orbit ...
... • The gravitational forces that two masses exert on each other are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. • This is an example of Newton’s third law of motion. • One example is the Earth-moon system, shown on the next slide. • As a result of these forces, the moon and Earth each orbit ...
Momentum and Impulse
... 5. Impulse is defined as the force exerted on an object times the time it lasts. TRUE 6. Automobile seatbelts are used to lengthen the time of impact in case of a collision. TRUE 7. When a baseball player follows through when hitting the ball, the contact time with the ball is longer. TRUE 8. The mo ...
... 5. Impulse is defined as the force exerted on an object times the time it lasts. TRUE 6. Automobile seatbelts are used to lengthen the time of impact in case of a collision. TRUE 7. When a baseball player follows through when hitting the ball, the contact time with the ball is longer. TRUE 8. The mo ...
Gauss`s law, infinite homogenous charge distributions and
... everywhere which makes perfect sense, but this means that the electric flux through an arbitrary surface S enclosing a certain charge Q (S) is zero in conflict with the integral form of the Gauss’s law that states that the flux must be equal to Q (S) /²0 . In order to keep the symmetrical solution f ...
... everywhere which makes perfect sense, but this means that the electric flux through an arbitrary surface S enclosing a certain charge Q (S) is zero in conflict with the integral form of the Gauss’s law that states that the flux must be equal to Q (S) /²0 . In order to keep the symmetrical solution f ...
Physics Class Syllabus
... Learning Objectives: At the end of this unit the student should be able to: • Define and identify the following terms on displacement vs. time graph: equilibrium position, amplitude, period, and frequency • Define simple harmonic motion • Use the reference circle to describe the displacement, veloci ...
... Learning Objectives: At the end of this unit the student should be able to: • Define and identify the following terms on displacement vs. time graph: equilibrium position, amplitude, period, and frequency • Define simple harmonic motion • Use the reference circle to describe the displacement, veloci ...
Introduction
... student’s ability to understand a concept within a physical setting. For example, the set of line diagrams below focus on exploring a student’s understanding of the relationship between forces and motion. Whilst the strategy was originally used in interview situations between a single student and a ...
... student’s ability to understand a concept within a physical setting. For example, the set of line diagrams below focus on exploring a student’s understanding of the relationship between forces and motion. Whilst the strategy was originally used in interview situations between a single student and a ...
Chapter 02 Motion
... C. its mass remains the same, but its weight decreases. D. both its mass and weight decrease. Accessibility: Keyboard Navigation Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze Gradable: automatic Section: 02.06 Topic: Weight and mass ...
... C. its mass remains the same, but its weight decreases. D. both its mass and weight decrease. Accessibility: Keyboard Navigation Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze Gradable: automatic Section: 02.06 Topic: Weight and mass ...