* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fields - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
Nordström's theory of gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
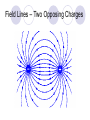
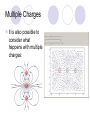
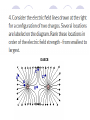
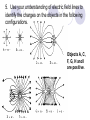
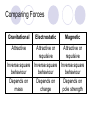
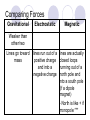
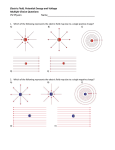
Field Theory Physics 12 Field Theory When forces exist without contact, it can be useful to use field theory to describe the force experienced by a particle at any point in space. We have previously considered gravitational fields and seen that gravitational fields are the result of mass creating the field and the distance an object is placed from the mass. Draw a diagram of what you think a gravitational field on Earth would look like. Use rays to show direction. Fields There are three common forces that act without contact between objects: Gravitational Electrostatic Magnetic Since these forces do not require contact, field theory is often used to describe the force that results on an object within the field (ie, not touching). How do we know what a field looks like then??? Electric Field Mapping To map an electric field, a small test charge is placed in the field and the magnitude and direction of the force is recorded. The test charge is then moved throughout the electric field and a map of the field is created. The force experienced by the test charge will be the result of Coulomb’s Law. Test charge is a positive charge (and small – so as not to affect the overall charge too much). Test Charge The test charge that is used must be small compared to the charge creating the field. If not, the test charge’s field will change the field that is being investigated. The electric field should be the same regardless of the test charge used. Imagine a positively charged particle… Electric Field Mapping If a positive charge was put in this field, it would repel (outward arrows). As you get farther from the charged particle, the repulsion gets less and less. The arrows represent the FORCE. What would a negatively charged particle’s field look like? *** NOTES More dense field lines means greater charge Electric field lines never cross each other Multiple charges in a field What would a field look like for one positively and one negatively charged particle? Field Lines – Two Opposing Charges What do you think… Will happen when two positive charges of equal strength are put together? What will the field look like? Field Lines – Two Positive Charges What do you think… Will happen when two negative charges are put together? What will the field look like? Problem What are the relative magnitudes of the charges in the diagram? What is the polarity of each of the charges? The left one is larger strength as there are more lines from it. It is a positive charge as the arrows go away from it. The right charge is weaker and negative. Multiple Charges It is also possible to consider what happens with multiple charges: Check Your Understanding 1.Several electric field line patterns are shown in the diagrams below. Which of these patterns are incorrect? Why? C, D, E Check Your Understanding 2. What is wrong with this diagram? Field lines are crossed d DAECB 5. Use your understanding of electric field lines to identify the charges on the objects in the following configurations. Objects A, C, F, G, H and I are positive. 6. Observe the electric field lines below for various configurations. Rank the objects according to which has the greatest magnitude of electric charge, beginning with the smallest charge. B<A C<D G<E<F J<H<I Test Charge – Electric Field Intensity Formula kqqt q is the charge of the source Fe 2 qt is the charge of the test r charge Fe kqqt 2 qt qt r Divide your electrostatic force formula by the test charge E = Fe/qt This is the electric field intensity Fe kq 2 qt r Fe E qt Where … E = electric field intensity (N/C) FQ = Fe = electric force (N) qt = Electric charge (C) of test charge Field Intensity at a Point Example 1: A positive charge of 3.2 x 10-5 C experiences a force of 4.8N right when placed in an electric field. Find the magnitude and direction of the field, at that location. Draw a picture of what this might look like. Hint… there are 2 answers Example 2 A positive test charge, qt = + 2.0 x 10-9 C, is placed in an electric field and experiences a force of F = 4.0 x 10-9 N [W]. A) What is the electric field intensity (magnitude) at the location of the test charge? B) Predict the force that would be experienced by a charge of +9.0 x 10-6 C if it replaced the test charge. Answer Practice Problems Page 646 Questions 12-14 So what do you think would happen… If we wanted a diagram of Earth and Moon (gravitational charge instead of electrostatic)? What do you think… A field would look like around a “regular” magnet (one North and one South pole)? Consider North as positive. Comparing Forces Gravitational Electrostatic Magnetic Attractive Attractive or repulsive Inverse square behaviour Depends on charge Attractive or repulsive Inverse square behaviour Depends on pole strength Inverse square behaviour Depends on mass Comparing Forces Gravitational Electrostatic Magnetic lines run out of a positive charge and into a negative charge lines are actually closed loops running out of a north pole and into a south pole (if a dipole magnet) - North is like + if monopole *** Weaker than other two Lines go toward mass Field Lines Summary Graphical representation of the field surrounding a point charge/mass or series of charges/poles Electric fields: lines run out of a positive charge and into a negative charge Gravitational fields: lines all go toward a mass Magnetic field lines: lines are actually closed loops running out of a north pole and into a south pole Gravitational Field The strength of a gravitational field can be determined using a test mass Like with a test charge, the test mass should be small In a manner similar to the electric field, we will divide out the test mass Gmmt Fg 2 r Fg Gmmt mt r 2 mt Fg Gm 2 r mt Fg g mt Practice Problems Page 649 Questions 15-17