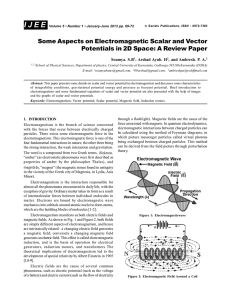
1. Activity #1: Calibrating Force sensors
... object accelerates with acceleration a m/s2. In other words, forces cause accelerations, and F = ma is the relation between the total force on an object and the object’s acceleration. 0.6 Weight Every object near the surface of the earth is subject to the gravitational attraction of the earth. When ...
... object accelerates with acceleration a m/s2. In other words, forces cause accelerations, and F = ma is the relation between the total force on an object and the object’s acceleration. 0.6 Weight Every object near the surface of the earth is subject to the gravitational attraction of the earth. When ...
Student 1 - Lon Capa
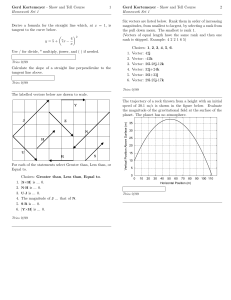
... A wrecking ball of mass M is suspended by a thin cable (of negligible mass). The ball’s position is recorded by a flash camera three times at intervals of 65 ms. For each of the sequences illustrated below, the tension remains constant. Indicate whether the tension in the cable, T, is Greater than, ...
... A wrecking ball of mass M is suspended by a thin cable (of negligible mass). The ball’s position is recorded by a flash camera three times at intervals of 65 ms. For each of the sequences illustrated below, the tension remains constant. Indicate whether the tension in the cable, T, is Greater than, ...
Study Guide
... The more momentum an object has, the more difficult it is to stop. Objects can transfer momentum to another object. Example: billiards, croquet Elastic collisions involve objects bouncing off each other with little heat or deformation. Inelastic collisions involve objects sticking together after a c ...
... The more momentum an object has, the more difficult it is to stop. Objects can transfer momentum to another object. Example: billiards, croquet Elastic collisions involve objects bouncing off each other with little heat or deformation. Inelastic collisions involve objects sticking together after a c ...
File - PHYSICS WORLD
... Q7. A famous relation in physics relates moving mass m to the rest mass m 0 of a particle in terms of its speed v and the speed of the light c. A boy recalls the relation almost correctly but forgets where to put the constant c. He writes: m = mo / (1 – v2)1/2 Guess where to put the missing c. Q8. A ...
... Q7. A famous relation in physics relates moving mass m to the rest mass m 0 of a particle in terms of its speed v and the speed of the light c. A boy recalls the relation almost correctly but forgets where to put the constant c. He writes: m = mo / (1 – v2)1/2 Guess where to put the missing c. Q8. A ...
MCQs - Moalims.com
... (The choice of direction, Whether an object is speeding up or slowing down, The position of the object) 12. The acceleration due to gravity __________. (has the same value every where in space, has the same value every where on the earth, varies with the latitude on the earth) 13. Swimming is possib ...
... (The choice of direction, Whether an object is speeding up or slowing down, The position of the object) 12. The acceleration due to gravity __________. (has the same value every where in space, has the same value every where on the earth, varies with the latitude on the earth) 13. Swimming is possib ...
216KB - NZQA
... Draw and label forces. Forces acting are the weight downwards and air resistance upwards. Weight is greater than air resistance when she has just jumped. Net force Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towar ...
... Draw and label forces. Forces acting are the weight downwards and air resistance upwards. Weight is greater than air resistance when she has just jumped. Net force Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towar ...
NCEA Level 1 Science (90940) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... Draw and label forces. Forces acting are the weight downwards and air resistance upwards. Weight is greater than air resistance when she has just jumped. Net force Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towar ...
... Draw and label forces. Forces acting are the weight downwards and air resistance upwards. Weight is greater than air resistance when she has just jumped. Net force Net force is in the downwards direction and greater than zero. Forces are unbalanced. Explanation of motion Motion is acceleration towar ...