Chapter 7 - KFUPM Faculty List
... 052: Q#2: An object of mass 1.0 kg is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 0.50 m at a constant speed of 2.0 m/s. The work done on the object during one revolution is: (Ans: Zero-J). Q#3: A boy holds a 40-N weight at arm's length for 10 s. His arm is 1.5 m above the ground. The work done by the ...
... 052: Q#2: An object of mass 1.0 kg is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 0.50 m at a constant speed of 2.0 m/s. The work done on the object during one revolution is: (Ans: Zero-J). Q#3: A boy holds a 40-N weight at arm's length for 10 s. His arm is 1.5 m above the ground. The work done by the ...
Refraction
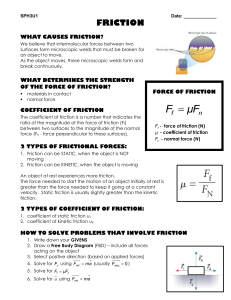
... 1. Friction can be STATIC, when the object is NOT moving 2. Friction can be KINETIC, when the object is moving An object at rest experiences more friction. The force needed to start the motion of an object initially at rest is greater than the force needed to keep it going at a constant velocity. St ...
... 1. Friction can be STATIC, when the object is NOT moving 2. Friction can be KINETIC, when the object is moving An object at rest experiences more friction. The force needed to start the motion of an object initially at rest is greater than the force needed to keep it going at a constant velocity. St ...
nuclear gravitation field theory
... apart. The need for additional Neutrons in the Nucleus is required to raise the Strong Nuclear Force to hold the Nucleus together. Note that for the heavier elements, the Neutron to Proton ratio rises from a 1 to 1 ratio for Light Nuclei to a 3 to 2 ratio for Heavy Nuclei. For stable Nuclei of the H ...
... apart. The need for additional Neutrons in the Nucleus is required to raise the Strong Nuclear Force to hold the Nucleus together. Note that for the heavier elements, the Neutron to Proton ratio rises from a 1 to 1 ratio for Light Nuclei to a 3 to 2 ratio for Heavy Nuclei. For stable Nuclei of the H ...
7thMotionfinal_Oct
... A force is a push or pull on an object that can either cause it to start moving, change direction or slow down until it finally stops. Forces always act in pairs. Balanced forces are opposite in direction and equal in size which causes no change in motion. Objects will either remain at rest or conti ...
... A force is a push or pull on an object that can either cause it to start moving, change direction or slow down until it finally stops. Forces always act in pairs. Balanced forces are opposite in direction and equal in size which causes no change in motion. Objects will either remain at rest or conti ...
Measurements - Singapore A Level Notes
... largest radius of orbit, objects located at the equator move with the greatest speed and kinetic energy compared to those located at other latitudes. Hence the total change in kinetic energy of the satellite between the Earth’s surface and in orbit will also be the lowest. Describe the concept of we ...
... largest radius of orbit, objects located at the equator move with the greatest speed and kinetic energy compared to those located at other latitudes. Hence the total change in kinetic energy of the satellite between the Earth’s surface and in orbit will also be the lowest. Describe the concept of we ...
Jeopardy_Science
... This force depends on the distance between objects and their masses. Gravity ...
... This force depends on the distance between objects and their masses. Gravity ...