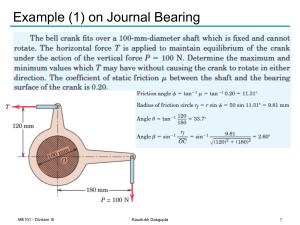
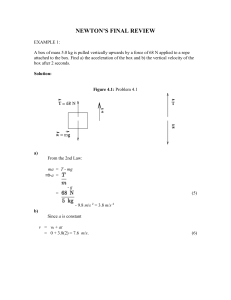
Momentum and Impulse (PowerPoint)
... Friction is an outside force that will change the momentum of an object In a collision between two objects the total momentum just before the collision will be the same just after the collision Total Momentum just before collision = ...
... Friction is an outside force that will change the momentum of an object In a collision between two objects the total momentum just before the collision will be the same just after the collision Total Momentum just before collision = ...
Centrifugation - UniMAP Portal
... At the end of the residence time of the particle in the fluid, the particle is at a distance rB m from the axis of rotation. If rB
... At the end of the residence time of the particle in the fluid, the particle is at a distance rB m from the axis of rotation. If rB
4.0 Mechanical systems use forces to transfer energy.
... classified as contact forces or action-at-a-distance forces. Contact forces must touch the object that they push or pull, for example, hitting a tennis ball (Figure 4.7). Another common contact force is friction. Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion of an object. If you slide a hocke ...
... classified as contact forces or action-at-a-distance forces. Contact forces must touch the object that they push or pull, for example, hitting a tennis ball (Figure 4.7). Another common contact force is friction. Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion of an object. If you slide a hocke ...
Electricity
... Both balls have a mass of 1kg. If the white ball continued in the same direction at 2m/s what was the velocity of the red ball? 2) A car of mass 1000kg heading up the M1 at 50m/s collides with a stationary truck of mass 8000kg and sticks to it. What velocity does the wreckage move forward at? 3) A d ...
... Both balls have a mass of 1kg. If the white ball continued in the same direction at 2m/s what was the velocity of the red ball? 2) A car of mass 1000kg heading up the M1 at 50m/s collides with a stationary truck of mass 8000kg and sticks to it. What velocity does the wreckage move forward at? 3) A d ...
Angular Kinetics II
... Q1. At the instant of takeoff, a 60-kg diver’s angular momentum about his transverse axis is 20 kg·m2/s. His radius of gyration about the transverse axis is 1.0 m at this instant. During the dive, the diver tucks and reduces his radius of gyration about the transverse axis is to 0.5 m. a. At takeof ...
... Q1. At the instant of takeoff, a 60-kg diver’s angular momentum about his transverse axis is 20 kg·m2/s. His radius of gyration about the transverse axis is 1.0 m at this instant. During the dive, the diver tucks and reduces his radius of gyration about the transverse axis is to 0.5 m. a. At takeof ...