ENGR-2150 SPRING 2008
... magnitudes were added because the fields were in the same direction and in (b) and (c) the field magnitudes were subtracted because the two fields were in opposite directions. In part (b) we could have used Coulomb's law to find the forces on the electron due to the two charges and then added these ...
... magnitudes were added because the fields were in the same direction and in (b) and (c) the field magnitudes were subtracted because the two fields were in opposite directions. In part (b) we could have used Coulomb's law to find the forces on the electron due to the two charges and then added these ...
how to classify flowering plants. Most people think that biological
... mind your commonsense knowledge of certain ordinary phenomena. For instance, we know that the gravitational attraction between us and the planet earth will act even if our feet momentarily leave the ground, and that although magnets have mass and are affected by gravity, most objects that have mass ...
... mind your commonsense knowledge of certain ordinary phenomena. For instance, we know that the gravitational attraction between us and the planet earth will act even if our feet momentarily leave the ground, and that although magnets have mass and are affected by gravity, most objects that have mass ...
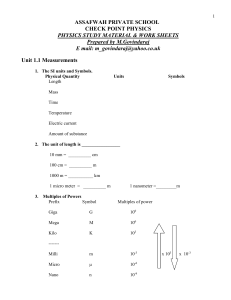
Measurements - Physicslocker Index
... (a) When the bell strikes for the sixth time, the wrist-watch is as shown in fig 2 (a)Calculate the time interval between the 1st strike and the 6th strike. time interval = ……………… s (b) Calculate the time interval between one strike and the next. time interval = ………………s (c) At precisely 11 o’clock, ...
... (a) When the bell strikes for the sixth time, the wrist-watch is as shown in fig 2 (a)Calculate the time interval between the 1st strike and the 6th strike. time interval = ……………… s (b) Calculate the time interval between one strike and the next. time interval = ………………s (c) At precisely 11 o’clock, ...
Physics Cycle 5 Worksheets.docx
... 20.The most common force on a ______________ is an object’s ________________. When an object is on a surface its weight pushes _____________ and the surface exerts a _________________ up equal to ___________________. If the surface is __________________ then: a. The forces are ______________________ ...
... 20.The most common force on a ______________ is an object’s ________________. When an object is on a surface its weight pushes _____________ and the surface exerts a _________________ up equal to ___________________. If the surface is __________________ then: a. The forces are ______________________ ...
HSC 2003 - Board of Studies
... The apparatus described in this first-hand investigation was used to carry out an identical experiment on another planet where the acceleration due to gravity is less than that on Earth. The horizontal speed of the ball as it left the table on the planet was the same as in part (a). Compare the rang ...
... The apparatus described in this first-hand investigation was used to carry out an identical experiment on another planet where the acceleration due to gravity is less than that on Earth. The horizontal speed of the ball as it left the table on the planet was the same as in part (a). Compare the rang ...
General Relativity: An Informal Primer 1 Introduction
... General relativity, and its application to cosmological models such as inflation, is a remarkably beautiful and elegant theory. Yet newcomers to the field often face at least three types of challenges: conceptual, mathematical, and notational. Over the past century, physicists and mathematicians hav ...
... General relativity, and its application to cosmological models such as inflation, is a remarkably beautiful and elegant theory. Yet newcomers to the field often face at least three types of challenges: conceptual, mathematical, and notational. Over the past century, physicists and mathematicians hav ...
Questions
... We step on the brakes of our Ferrari, providing a constant decelerating force force F and the car comes to rest in 8 s. If the car travels 50 m during the first 4 s, what total distance x is required to stop the car? (A) 100 m > x < 200 m (B) 100 m ...
... We step on the brakes of our Ferrari, providing a constant decelerating force force F and the car comes to rest in 8 s. If the car travels 50 m during the first 4 s, what total distance x is required to stop the car? (A) 100 m > x < 200 m (B) 100 m ...
Partial solutions from Ch1 to Ch6
... 6.3 Centripetal Force ................................................................................................................. 50 6.5 Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation .............................................................................. 51 6.6 Satellites and Kepler’s Laws: An ...
... 6.3 Centripetal Force ................................................................................................................. 50 6.5 Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation .............................................................................. 51 6.6 Satellites and Kepler’s Laws: An ...
A STRAIGHTFORWARD SET UP OF
... which strikingly turns out to be the exact Dirac solution were (the second term at the RHS of Eq.(31) neglected, and) the spin-orbit interaction not taken into account [1]. We can right away estimate that, in this case the magnitude of E R is larger than that of the corresponding Schrodinger eigenv ...
... which strikingly turns out to be the exact Dirac solution were (the second term at the RHS of Eq.(31) neglected, and) the spin-orbit interaction not taken into account [1]. We can right away estimate that, in this case the magnitude of E R is larger than that of the corresponding Schrodinger eigenv ...
Chapter 5 - Force and Motion
... B. The rope tension equals the object’s weight. C. The rope tension is less than the object’s weight. D. The rope tension can’t be compared to the object’s weight. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... B. The rope tension equals the object’s weight. C. The rope tension is less than the object’s weight. D. The rope tension can’t be compared to the object’s weight. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Lecture 20.TorqueRot..
... Which of the arrangements below is least effective in loosening the nut? Force is proportional to length of vector. ...
... Which of the arrangements below is least effective in loosening the nut? Force is proportional to length of vector. ...