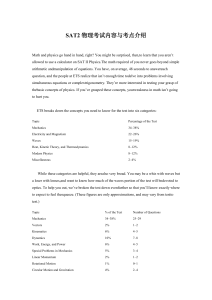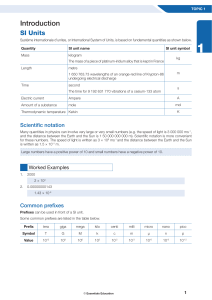
SAT2物理词汇完整版
... If ρ1 = 2ρ2, l1 = 2l2 and r1 = 2r2, what is the ratio R1/R2? ρ1, ρ2 are the resistivities of the two wires, l1, l2 are the lengths of the two wires, r1, r2 are the radii of the of the cross-sectional areas of the two wires. ...
... If ρ1 = 2ρ2, l1 = 2l2 and r1 = 2r2, what is the ratio R1/R2? ρ1, ρ2 are the resistivities of the two wires, l1, l2 are the lengths of the two wires, r1, r2 are the radii of the of the cross-sectional areas of the two wires. ...
Momentum and Collisions
... lasts for a certain amount of time; in terms of dots, the collision lasts for a time equivalent to approximately nine dots. In the halfbackdefensive back collision, the halfback experiences a force that lasts for a certain amount of time to change his momentum. Since the collision causes the rightwa ...
... lasts for a certain amount of time; in terms of dots, the collision lasts for a time equivalent to approximately nine dots. In the halfbackdefensive back collision, the halfback experiences a force that lasts for a certain amount of time to change his momentum. Since the collision causes the rightwa ...
Survival Needs… Food
... a) 5 kg of water with a temperature of 150°C b) 8 kg of water with a temperature of 110°C c) 10 kg of water with a temperature of 90°C d) 100 kg of water with a temperature of 28°C D… temperature measures the average kinetic energy. To determine the greatest amount of energy, you need to consider ma ...
... a) 5 kg of water with a temperature of 150°C b) 8 kg of water with a temperature of 110°C c) 10 kg of water with a temperature of 90°C d) 100 kg of water with a temperature of 28°C D… temperature measures the average kinetic energy. To determine the greatest amount of energy, you need to consider ma ...
CHAPTERONE(1D2)
... shown in great detail in the UFT papers to relate a vector, V a defined by a given curvilinear coordinate system to the same vector defined in another curvilinear coordinate system, for example cylindrical polar and Cartesian, or complex circular and Cartesian. The spin connection has one upper and ...
... shown in great detail in the UFT papers to relate a vector, V a defined by a given curvilinear coordinate system to the same vector defined in another curvilinear coordinate system, for example cylindrical polar and Cartesian, or complex circular and Cartesian. The spin connection has one upper and ...
Chapter2 Laws of Motion
... property of an object that resists changes in its motion. To understand inertia, imagine trying to move a bowling ball and a golf ball. Which requires more force? Of course, the bowling ball needs more force to get it moving at the same speed as the golf ball (assuming the forces act for the same le ...
... property of an object that resists changes in its motion. To understand inertia, imagine trying to move a bowling ball and a golf ball. Which requires more force? Of course, the bowling ball needs more force to get it moving at the same speed as the golf ball (assuming the forces act for the same le ...
Document
... one object is pushed against the other, the greater the force of friction that results. ...
... one object is pushed against the other, the greater the force of friction that results. ...
Dynamics Chapter
... However, there are some properties of mass that you will need to understand. 1. Mass is intrinsic to an object. It does not depend on where the object is located. No matter whether it is; on earth, in outer space or deep under the ocean, the mass of an object will not change. 2. An object’s accelera ...
... However, there are some properties of mass that you will need to understand. 1. Mass is intrinsic to an object. It does not depend on where the object is located. No matter whether it is; on earth, in outer space or deep under the ocean, the mass of an object will not change. 2. An object’s accelera ...
Unit 4 Fields and Further Mechanics - complete
... 250 J kg–1 K–1. Assuming that all the lost kinetic energy becomes internal energy in the bullet, calculate its temperature rise during the collision. ...
... 250 J kg–1 K–1. Assuming that all the lost kinetic energy becomes internal energy in the bullet, calculate its temperature rise during the collision. ...
Chapter 14
... speed and/or elevation above the Earth’s surface changes, the pressure in the fluid varies with these changes The relationship between fluid speed, pressure and elevation was first derived by ...
... speed and/or elevation above the Earth’s surface changes, the pressure in the fluid varies with these changes The relationship between fluid speed, pressure and elevation was first derived by ...
Lecture slides with notes - University of Toronto Physics
... A long straight wire is carrying current from left to right. Near the wire is a charge g q with velocity y v. C Compare p the strength g of the magnetic g force on q in (a) vs. (b) a) (a) has the larger force b) (b) has the larger force c) force is the same for (a) and (b) a) ...
... A long straight wire is carrying current from left to right. Near the wire is a charge g q with velocity y v. C Compare p the strength g of the magnetic g force on q in (a) vs. (b) a) (a) has the larger force b) (b) has the larger force c) force is the same for (a) and (b) a) ...