Slides
... A plane surface in a horizontal position in a fluid at rest is subjected to a constant pressure. The magnitude of the force acting on one side of the surface is The elemental forces pdA acting on A are all parallel and in the same sense a scalar summation of all such elements yields the magnitude ...
... A plane surface in a horizontal position in a fluid at rest is subjected to a constant pressure. The magnitude of the force acting on one side of the surface is The elemental forces pdA acting on A are all parallel and in the same sense a scalar summation of all such elements yields the magnitude ...
Electrostatics Practice Test
... 8. When a charged body is brought close to an uncharged body without touching it, a(n) ____ charge may result on the uncharged body. When a charged body is brought into contact with an uncharged body and then is removed, a(n) ____ charge may result on the uncharged body. a. negative; positive c. ind ...
... 8. When a charged body is brought close to an uncharged body without touching it, a(n) ____ charge may result on the uncharged body. When a charged body is brought into contact with an uncharged body and then is removed, a(n) ____ charge may result on the uncharged body. a. negative; positive c. ind ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... the plane, including fuel and payload, is m = 45,200 kg. The following values are assumed for the widths bi of the sections: b1 = 1 m; b2 = 7 m; b3 = 3 m; b4 = 2 m, and for the corresponding basic lift forces: l1 = 0.3 N/m; l2 = 1.0 N/m; l3 = 0.7 N/m; l4 = 0.4 N/m. Using the gravity constant g = 9.8 ...
... the plane, including fuel and payload, is m = 45,200 kg. The following values are assumed for the widths bi of the sections: b1 = 1 m; b2 = 7 m; b3 = 3 m; b4 = 2 m, and for the corresponding basic lift forces: l1 = 0.3 N/m; l2 = 1.0 N/m; l3 = 0.7 N/m; l4 = 0.4 N/m. Using the gravity constant g = 9.8 ...
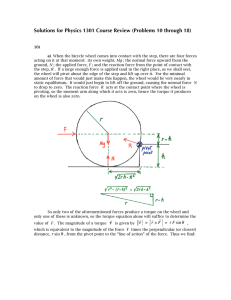
Static Equilibrium. Supports, Loads, Driven Oscillations
... block, and then place a small wedge 6” away from the end (board is 6’, remember). How much can we exert ...
... block, and then place a small wedge 6” away from the end (board is 6’, remember). How much can we exert ...
Document
... Friction is an outside force that will change the momentum of an object In a collision between two objects the total momentum just before the collision will be the same just after the collision Total Momentum just before collision = ...
... Friction is an outside force that will change the momentum of an object In a collision between two objects the total momentum just before the collision will be the same just after the collision Total Momentum just before collision = ...
Physical Science 1st Semester Exam Study Guide 2010 Introduction
... b. rate at which velocity changes. c. resistance of an object to a change in its velocity. d. speed of an object in a particular direction. 13. Weight is best described as a. an object’s resistance to acceleration. b. what causes an object to fall. c. the downward force exerted on objects due to gra ...
... b. rate at which velocity changes. c. resistance of an object to a change in its velocity. d. speed of an object in a particular direction. 13. Weight is best described as a. an object’s resistance to acceleration. b. what causes an object to fall. c. the downward force exerted on objects due to gra ...
Chapter 4
... that is stuck in the snow, you exert a force on it. A locomotive exerts a force on the train it is pulling or pushing, a steel cable exerts a force on the beam it is lifting at a construction site, and so on. Each of these examples shows that force, which is a push or a pull acting on an object, has ...
... that is stuck in the snow, you exert a force on it. A locomotive exerts a force on the train it is pulling or pushing, a steel cable exerts a force on the beam it is lifting at a construction site, and so on. Each of these examples shows that force, which is a push or a pull acting on an object, has ...
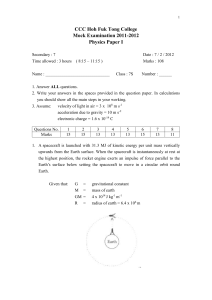
CCC Hoh Fuk Tong College
... The final mass m of the spacecraft ( with the astronaut ) when it is orbiting round the Earth is 5000kg. i. Find the orbiting speed v of the spacecraft ( with the astronaut ) in this circular orbit. ( 2 marks ) ...
... The final mass m of the spacecraft ( with the astronaut ) when it is orbiting round the Earth is 5000kg. i. Find the orbiting speed v of the spacecraft ( with the astronaut ) in this circular orbit. ( 2 marks ) ...
Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam
... to calculate the gravitational force on an object with mass m in a gravitational field of strength g in the context of the effects of a net force on objects and systems. 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. 3.B. ...
... to calculate the gravitational force on an object with mass m in a gravitational field of strength g in the context of the effects of a net force on objects and systems. 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. 3.B. ...
Ch 16: Electric Charge and Electric Field
... Charge is measured in units of Coulombs, C, after the inventor of Coulomb’s Law. 1C is the amount of charge which, if placed on each of 2 point objects 1 m apart, will result in each object exerting a force of 9.0 x 109 N on the other. This would be enormous force (almost 1 trillion tons) so w ...
... Charge is measured in units of Coulombs, C, after the inventor of Coulomb’s Law. 1C is the amount of charge which, if placed on each of 2 point objects 1 m apart, will result in each object exerting a force of 9.0 x 109 N on the other. This would be enormous force (almost 1 trillion tons) so w ...