Sixth Grade Science v. 2016
... and around one another; Expansion- a phase of matter that has no definite shape or volume. Particles of gas fly independently through space; Gas- an increase of volume; Mass- a subatomic particle with a positive charge; Mixture- to incorporate one substance uniformly into another substance at the pa ...
... and around one another; Expansion- a phase of matter that has no definite shape or volume. Particles of gas fly independently through space; Gas- an increase of volume; Mass- a subatomic particle with a positive charge; Mixture- to incorporate one substance uniformly into another substance at the pa ...
centripetal force and centrifugal force
... Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy) commonly known as the Principia, although this was not published until 1687. ...
... Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy) commonly known as the Principia, although this was not published until 1687. ...
SPH3U: What is a Force?
... move in circles and steep curves make you feel like you’re being pushed outwards. People call this the centripetal force. Do you think that’s the same force that keeps you from falling out of a roller coaster when it goes upside down? Find out with this quick activity. Make sure every member of your ...
... move in circles and steep curves make you feel like you’re being pushed outwards. People call this the centripetal force. Do you think that’s the same force that keeps you from falling out of a roller coaster when it goes upside down? Find out with this quick activity. Make sure every member of your ...
Gravity and Isostasy
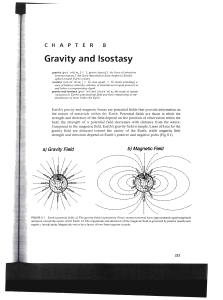
... mass of the object. c) Objects at Earth's surface (radius RI) have greater acceleration than objects some distance above the surface (radius R2)· ...
... mass of the object. c) Objects at Earth's surface (radius RI) have greater acceleration than objects some distance above the surface (radius R2)· ...
Inelastic Collisions
... When two objects collide they share a single interaction which creates equal sized forces directed in opposite directions. This interaction may speed-up one object and slow-down the other object, or, the interaction may slow-down both objects such as in a head-on collision of two cars. The force-tim ...
... When two objects collide they share a single interaction which creates equal sized forces directed in opposite directions. This interaction may speed-up one object and slow-down the other object, or, the interaction may slow-down both objects such as in a head-on collision of two cars. The force-tim ...
lecture 7 - friction and more Newton`s laws
... 1b. Divide forces into components if necessary. 1c. Group objects together if it seems convenient. 2. Use the Newton’s 2nd Law “blueprint equation” to get a “real equation” for each object. 2b. Do this for both x- and y-directions if necessary. 3. Plug what you know into the equations, and look at w ...
... 1b. Divide forces into components if necessary. 1c. Group objects together if it seems convenient. 2. Use the Newton’s 2nd Law “blueprint equation” to get a “real equation” for each object. 2b. Do this for both x- and y-directions if necessary. 3. Plug what you know into the equations, and look at w ...
Forces in Equilibrium
... Couple of a pair of equal and opposite forces defined as force x perpendicular distance between the lines of action of the forces. The principle of moments and its applications in simple balanced situations. Centre of mass; calculations of the position of the centre of mass of a regular lamina are n ...
... Couple of a pair of equal and opposite forces defined as force x perpendicular distance between the lines of action of the forces. The principle of moments and its applications in simple balanced situations. Centre of mass; calculations of the position of the centre of mass of a regular lamina are n ...
Chapter 12 ppt
... • Properties used to describe the motion of an object include a reference point, direction, speed, velocity, and acceleration. • Average speed can be calculated by dividing total distance by total time. • A change in velocity is due to a change in speed, direction, or both. • Speed and acceleration ...
... • Properties used to describe the motion of an object include a reference point, direction, speed, velocity, and acceleration. • Average speed can be calculated by dividing total distance by total time. • A change in velocity is due to a change in speed, direction, or both. • Speed and acceleration ...
Problem T2. Kelvin water dropper (8 points)
... to ∆E = σ/ε0 (which follows from the Gauss law); inside the enough to overcome the electrostatic push: The droplet starts droplet, there is no field due to the conductivity of the droplet: at the point where the electric potential is 0, which is the sum of Ē − 21 ∆E = 0; outside the droplet, there ...
... to ∆E = σ/ε0 (which follows from the Gauss law); inside the enough to overcome the electrostatic push: The droplet starts droplet, there is no field due to the conductivity of the droplet: at the point where the electric potential is 0, which is the sum of Ē − 21 ∆E = 0; outside the droplet, there ...
Wikipedia and Coriolis Force
... observed in cyclones. The Eötvös Effect on the other hand, along with its horizontal counterpart, is a real effect because it is compounded from the difference between two real inertial centrifugal forces. In this case, the Coriolislike term always acts radially outwards, except in a narrow band whe ...
... observed in cyclones. The Eötvös Effect on the other hand, along with its horizontal counterpart, is a real effect because it is compounded from the difference between two real inertial centrifugal forces. In this case, the Coriolislike term always acts radially outwards, except in a narrow band whe ...