Exam 2
... ____ 22. Two paths lead to the top of a big hill. One is steep and direct while the other is twice as long but less steep. How much more potential energy would you gain if you took the longer path? a. the same d. one-half as much b. you gain no potential energy e. four times as much c. twice as much ...
... ____ 22. Two paths lead to the top of a big hill. One is steep and direct while the other is twice as long but less steep. How much more potential energy would you gain if you took the longer path? a. the same d. one-half as much b. you gain no potential energy e. four times as much c. twice as much ...
Topic 9_2__Gravitational field, potential and energy
... Topic 9: Motion in fields 9.2 Gravitational field,potential,energy State and apply the formula relating gravitational field strength to gravitational potential gradient. The gravitational potential gradient is the change in gravitational potential per unit distance. Thus the GPG = ∆V/∆r. EXAMPLE: ...
... Topic 9: Motion in fields 9.2 Gravitational field,potential,energy State and apply the formula relating gravitational field strength to gravitational potential gradient. The gravitational potential gradient is the change in gravitational potential per unit distance. Thus the GPG = ∆V/∆r. EXAMPLE: ...
CHAPTER 4 - Dr. ZM Nizam
... 1) The first step is to draw a free body diagram of the body, labeling and directing all forces involved at each surface of contact. 2) The resultant, R exerted by a surface on a free body can be resolved into a normal component N and a tangential component F. F known as a friction force. When a bod ...
... 1) The first step is to draw a free body diagram of the body, labeling and directing all forces involved at each surface of contact. 2) The resultant, R exerted by a surface on a free body can be resolved into a normal component N and a tangential component F. F known as a friction force. When a bod ...
Generating Gravity and time. (Mahona Mercury engine and Mahona
... through an electrical wire. Since the velocity of these electrons can be considered as at or near the speed of light, we can assume that they are affected by both time dilation and length contraction, effects predicted by Albert Einstein’s famous theory of relativity. It is worth noting that Albert ...
... through an electrical wire. Since the velocity of these electrons can be considered as at or near the speed of light, we can assume that they are affected by both time dilation and length contraction, effects predicted by Albert Einstein’s famous theory of relativity. It is worth noting that Albert ...
Lesson 13 Moments – Turning forces
... • Dylan punches Henry in the face. If Henry’s head (mass 10 kg) was initially at rest and moves away from Dylans fist at 3 m/s, and the fist was in contact with the face for 0.2 seconds, what was the force of the punch? • m = 10kg, t = 0.2, u = 0, v = 3 • Ft = mv - mu ...
... • Dylan punches Henry in the face. If Henry’s head (mass 10 kg) was initially at rest and moves away from Dylans fist at 3 m/s, and the fist was in contact with the face for 0.2 seconds, what was the force of the punch? • m = 10kg, t = 0.2, u = 0, v = 3 • Ft = mv - mu ...
Forces and Motion Scripted - UTeach Outreach
... (3) Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses critical thinking, scientific reasoning, and problem solving to make informed decisions and knows the contributions of relevant scientists. The student is expected to: (D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, in ...
... (3) Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses critical thinking, scientific reasoning, and problem solving to make informed decisions and knows the contributions of relevant scientists. The student is expected to: (D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, in ...
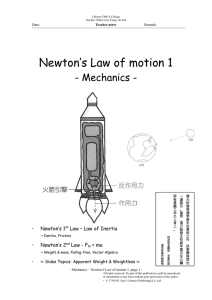
Newton`s Law of motion 1
... force (towards the centre of the Earth) acted on it. This is called weight of the object. This force comes from the Earth, and is called gravity. [Def.] Weight is the force of gravity on an object and is equal to the product of the mass of the object and Earth’s gravitational field strength (gravita ...
... force (towards the centre of the Earth) acted on it. This is called weight of the object. This force comes from the Earth, and is called gravity. [Def.] Weight is the force of gravity on an object and is equal to the product of the mass of the object and Earth’s gravitational field strength (gravita ...