* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Froehlich`s Physics
Pioneer anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
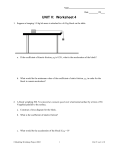
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
List of Static supporting characters wikipedia , lookup
Friction stir welding wikipedia , lookup
Physics Whiteboard – Forces with Friction 1. A 70 kg block is being pushed across a tabletop with a constant force of 350 N exerted in the direction of travel. If the coefficient of kinetic friction (µk) is 0.16, find the block’s acceleration. 2. A 10 kg box is being pushed by a 100 N force 30° above the horizontal. The acceleration of the box is 5 m/s2. What is the value of µk? 3. Two stacked boxes are being pulled at a constant velocity by a toy tractor. The coefficient of kinetic friction (µk) between the 10 kg box and the floor is 0.13. With what force must the tractor pull the boxes? 4. The same toy tractor from the problem above is attempting to pull a 20 kg box across a rough floor with a coefficient of static friction (µs) between the box and the floor of 0.40. If the tractor has a weight of 90 N, what must be the minimum coefficient of static friction between the tractor and the floor to get the box moving? 5. How large a force is necessary to pull out the 6.0 kg block with an acceleration of 1.5 m/s2 if its coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.40? 6. You push on a 20 kg box with a horizontal force of 50 N and the box slides along with a constant velocity. a. What would the acceleration be if you push with a 90 N force? b. What would happen if you suddenly stopped pushing? 7. A tow rope will break if the tension in it exceeds 1500 N. It is used to tow a 700 kg car along level ground. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. What is the largest acceleration the rope can give the car? whiteboard_friction.doc (173_wb_4a.doc) - froehlich 8. A crate of lab reports weighing 40.0 N rests on the floor of Al’s lab. The coefficient of static friction (µs) between the crate and the floor is 0.40, and the coefficient of kinetic friction (µk) is 0.20. a. If no horizontal force is applied to the crate and the crate is at rest, how large is the friction force applied to the crate? b. What is the magnitude of the friction force if Isaac comes in and applies a horizontal force of 6.0 N to the crate? c. What is the minimum horizontal force necessary to get the crate moving? d. Once Isaac gets the crate moving, what is the minimum horizontal force required to keep it moving? e. If Al helps Isaac and they apply a total horizontal force of 18.0 N, what is the magnitude of the friction force and what is the crate’s acceleration? 9. A 25.0 kg box of textbooks rests on a loading ramp that makes an angle θ with the horizon. The coefficient of kinetic friction (µk) is 0.25 and the coefficient of static friction (µs) is 0.35. a. As the angle θ slowly increases, find the minimum angle at which the box starts to slip. b. At the angle above, find the acceleration once the box begins to move. c. How fast will the box be moving once it has slid 5.0 m along the ramp? 10. In the illustration to the right, blocks A and B are connected by lightweight ropes to each other and to a wall. Block A weighs 60.0 N. The coefficient of static friction (µs) between block A and the tabletop on which it rests is 0.25. Weight B is 12.0 N, and the system is in static equilibrium. a. Find the friction force exerted on block A. b. Find the maximum weight of block B for which the system will remain in static equilibrium. 11. You are called as an expert witness in the trial of a traffic violation. The facts are these: A driver slammed on his brakes and came to a stop with constant acceleration. Measurements of his tires and the skid marks on the pavement indicate he locked his car’s wheels, and that the car traveled 192 ft (58.58 m) before stopping. The skid marks in the underwear were not measured. The coefficient of kinetic friction (µk) between the road and his tires was 0.75. The charge was that he was speeding in a 45 mph (20.115 m/s) zone. He pleads innocent. What is your conclusion? Is he guilty or innocent? How fast was he going when he hit the brakes? 12. If the coefficient of static friction between a table and a massive piece of rope is µs, what fraction of the rope can hang over the edge of the table without the rope sliding off the table? whiteboard_friction.doc (173_wb_4a.doc) - froehlich